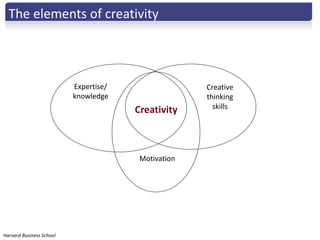
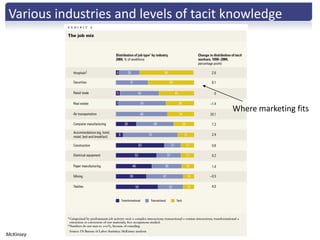
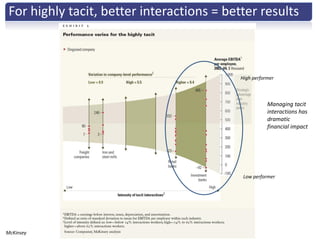
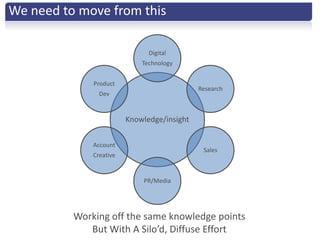
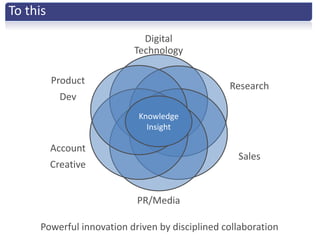
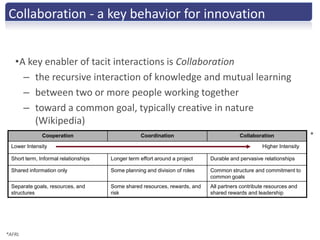
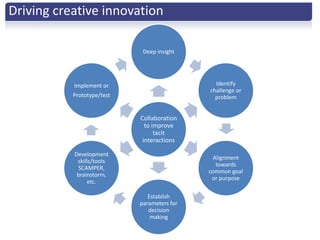
The document discusses the importance of creative innovation in today's challenging brand environment, emphasizing the need for deep customer insights and collaboration to drive business impact. It defines innovation as a change that increases economic value and identifies key elements such as tacit knowledge and effective collaboration. The implications for brands include fostering an environment that prioritizes collaboration and insight gathering to enhance innovation and achieve better economic outcomes.