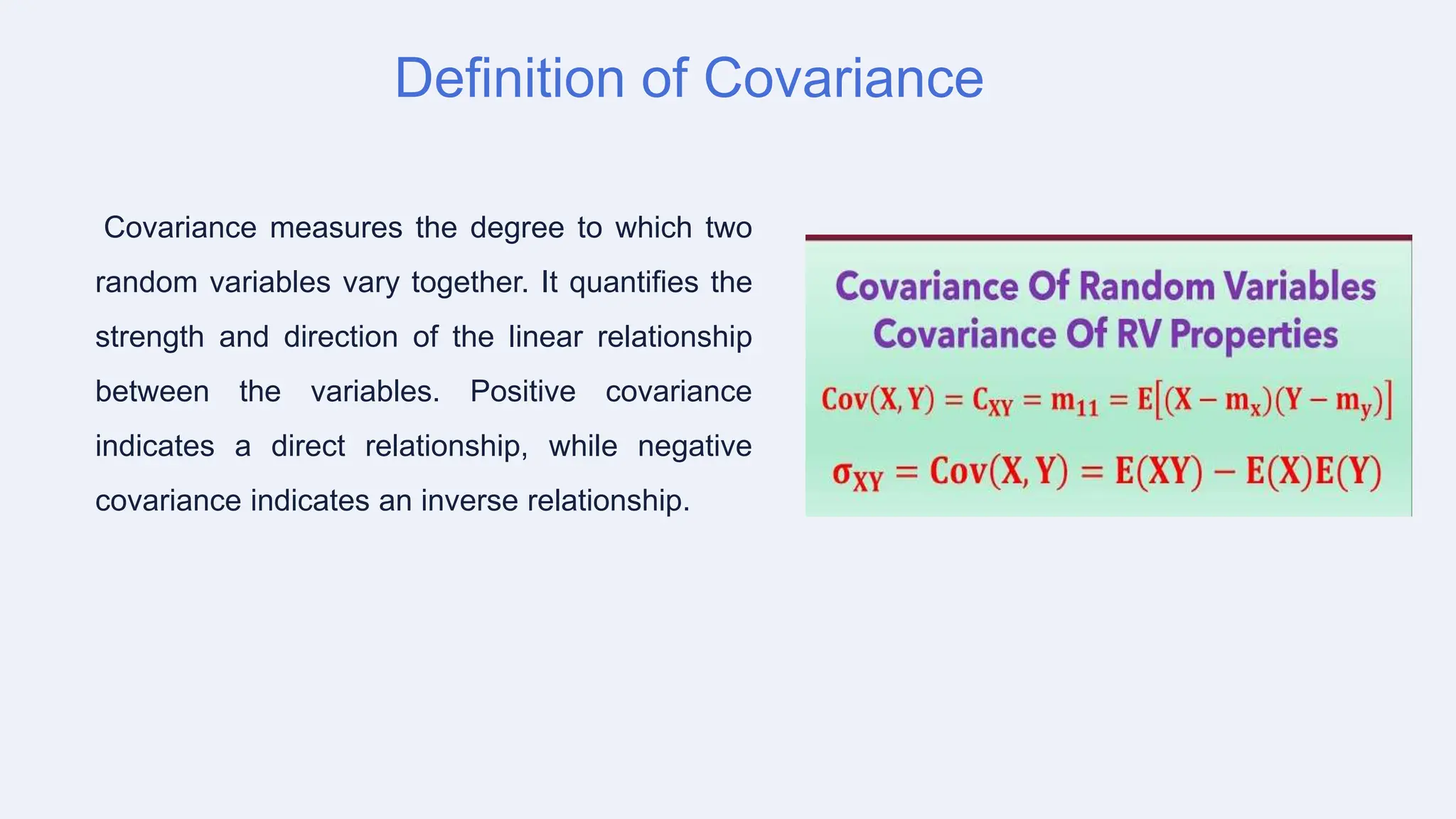
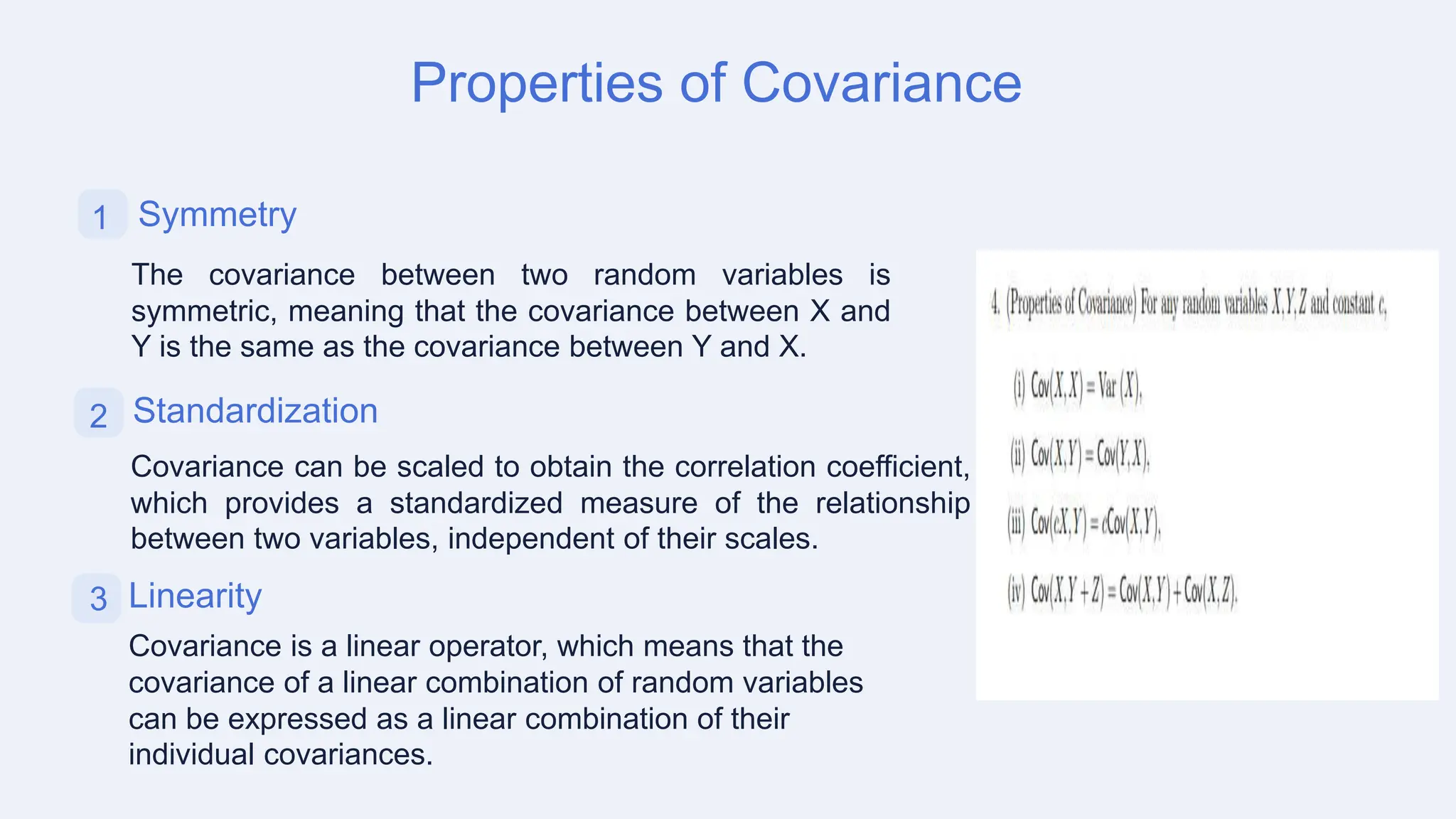
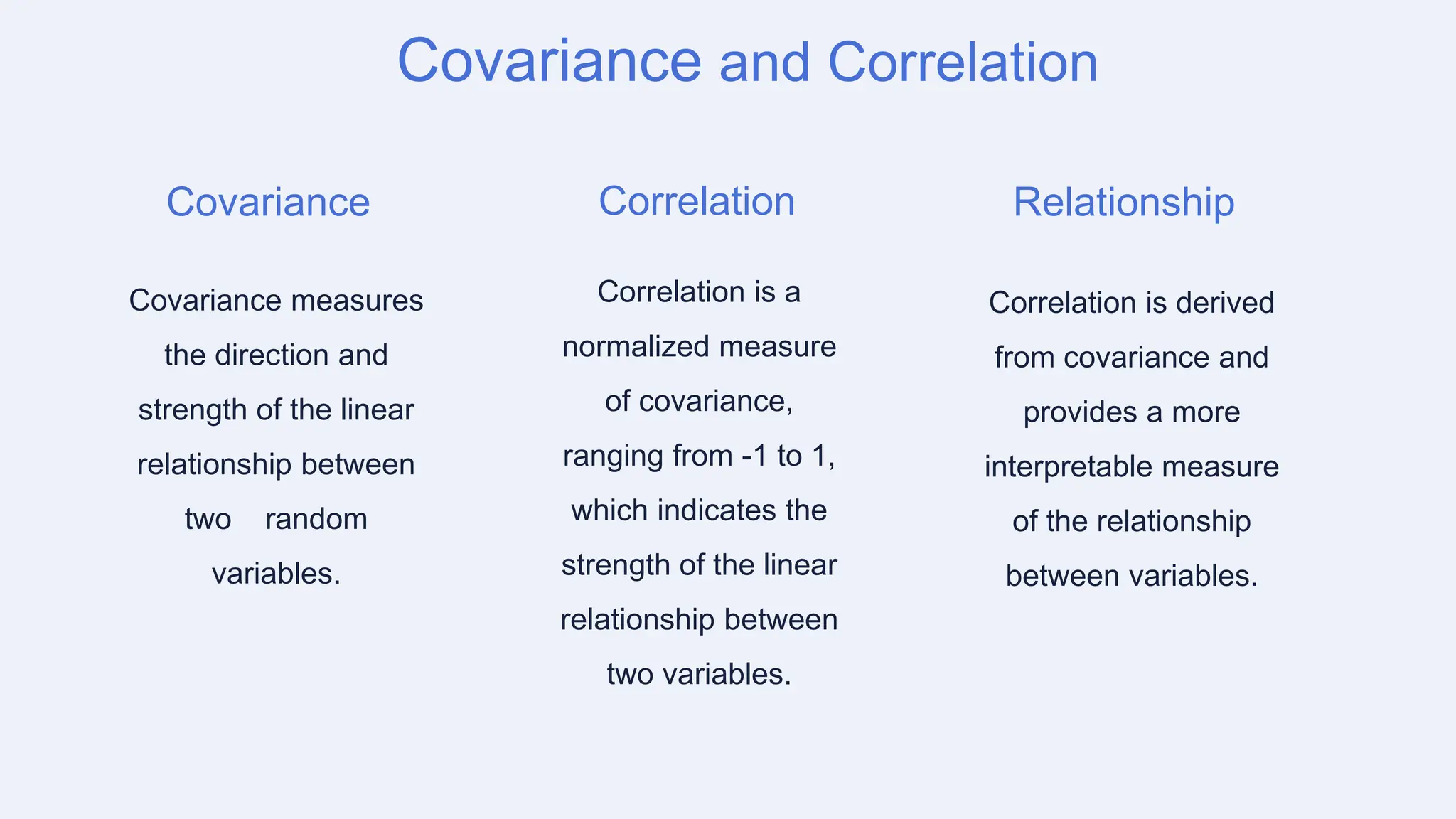
The document discusses covariance and its applications in probability and random processes, highlighting its importance in measuring relationships between random variables. It also covers the role of system transfer functions in engineering design and optimization, with practical examples related to various fields such as automotive and biomedical engineering. Key takeaways emphasize the significance of covariance and transfer functions in analyzing complex systems and presenting opportunities for advanced modeling techniques.





![Covariance-in-Probability-and-Random-Processes_(1)[1] - Read-Only.pptx](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/covariance-in-probability-and-random-processes11-read-only-240525034859-1ab60675/75/Covariance-in-Probability-and-Random-Processes_-1-1-Read-Only-pptx-14-2048.jpg)