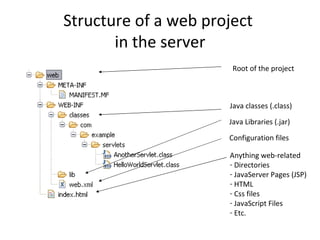
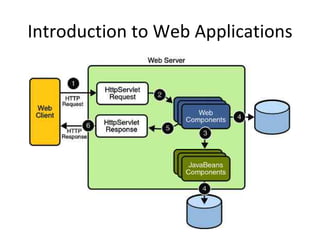
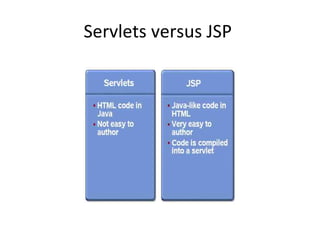
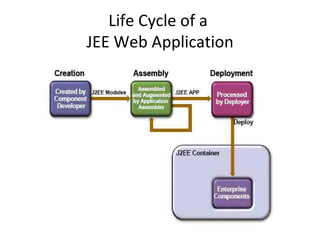
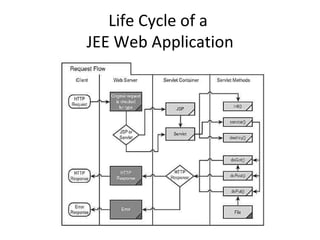
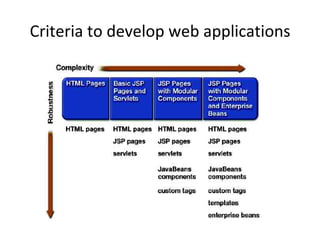
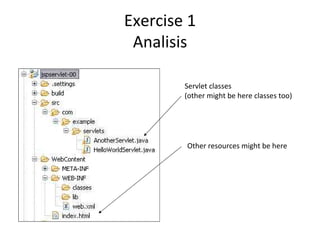
The document outlines topics covered in a Servlet and JSP course, including introductions to servlets and JavaServer Pages, how to use MVC pattern, share information and access databases in web applications, and how to secure applications using features like filters and listeners.