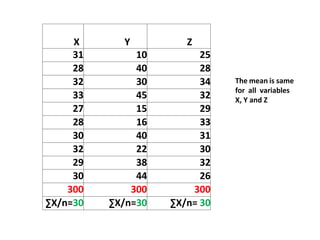
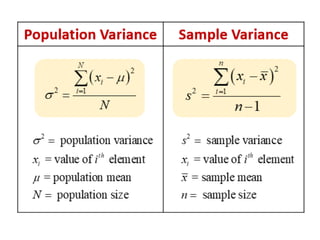
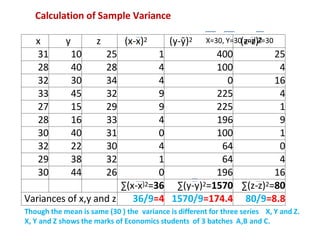
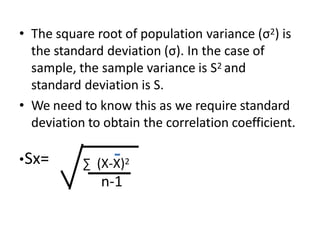
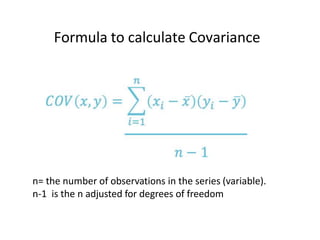
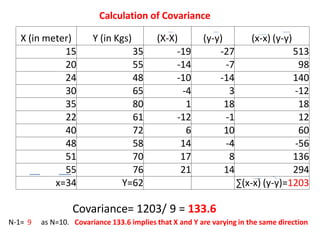
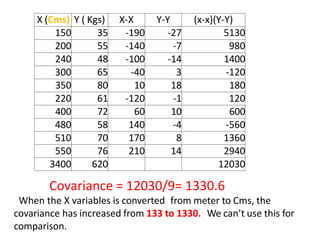
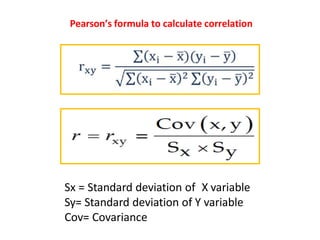
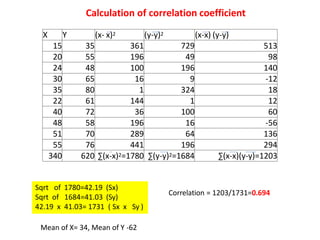
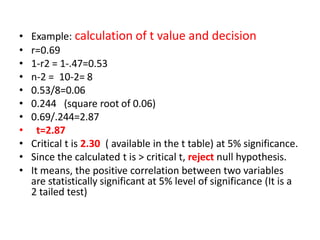
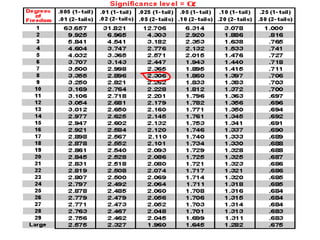
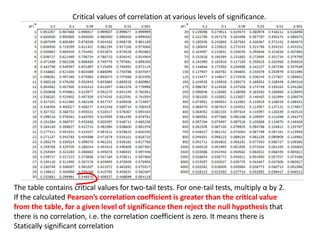
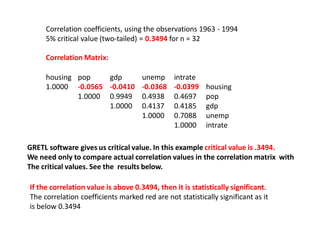
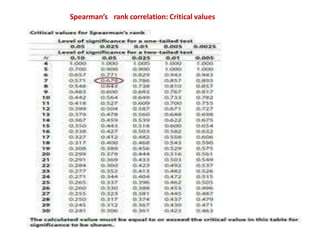
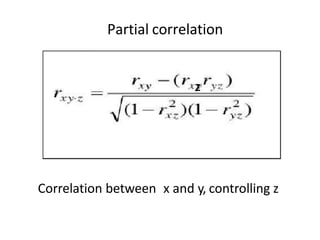
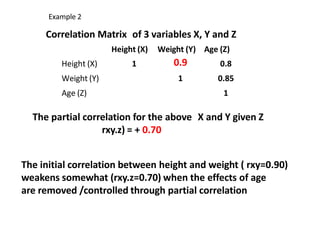
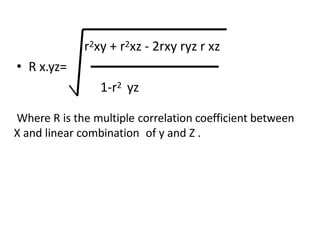
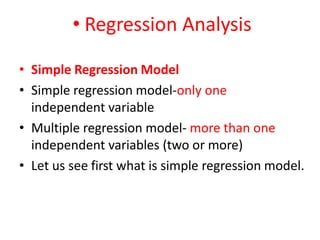
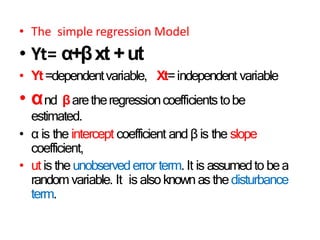
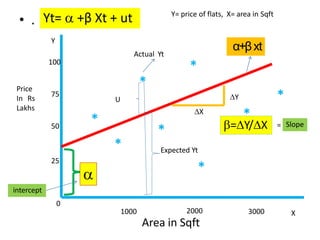
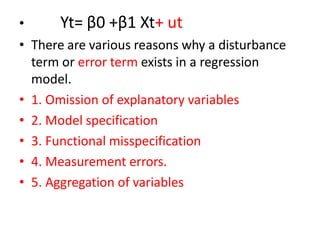
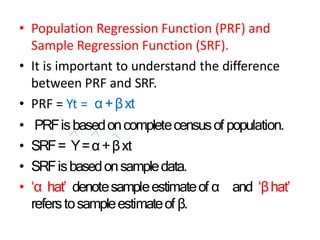
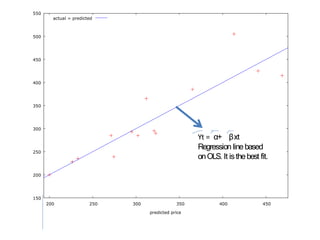
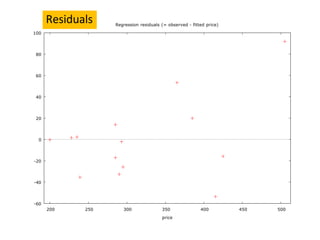
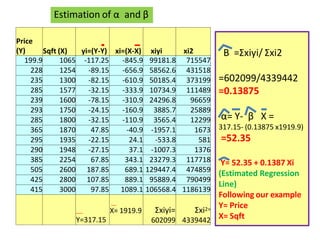
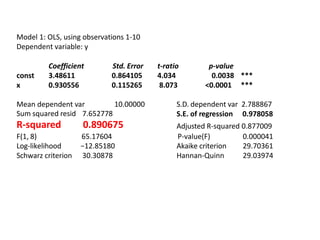
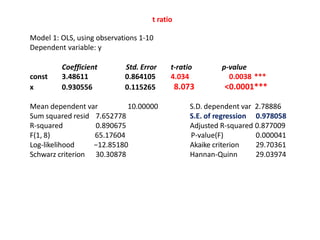
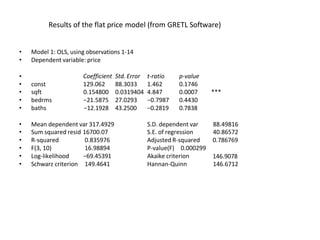
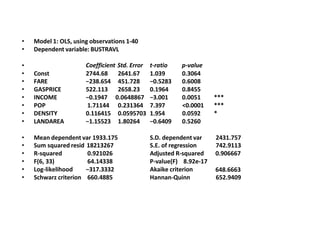
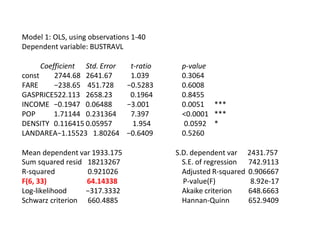
This document discusses correlation and related statistical concepts. Correlation measures the strength and direction of association between two quantitative variables. A correlation of 0 means no association, 1 means perfect positive association, and -1 means perfect negative association. Correlation is independent of measurement units and scaling of variables. Hypothesis testing is used to make inferences about the population correlation based on a sample correlation. The null hypothesis is that the population correlation is 0, and alternative hypotheses specify a non-zero correlation. The test statistic used is Student's t distribution. The null is rejected if the calculated t exceeds the critical value or if the p-value is less than the significance level.