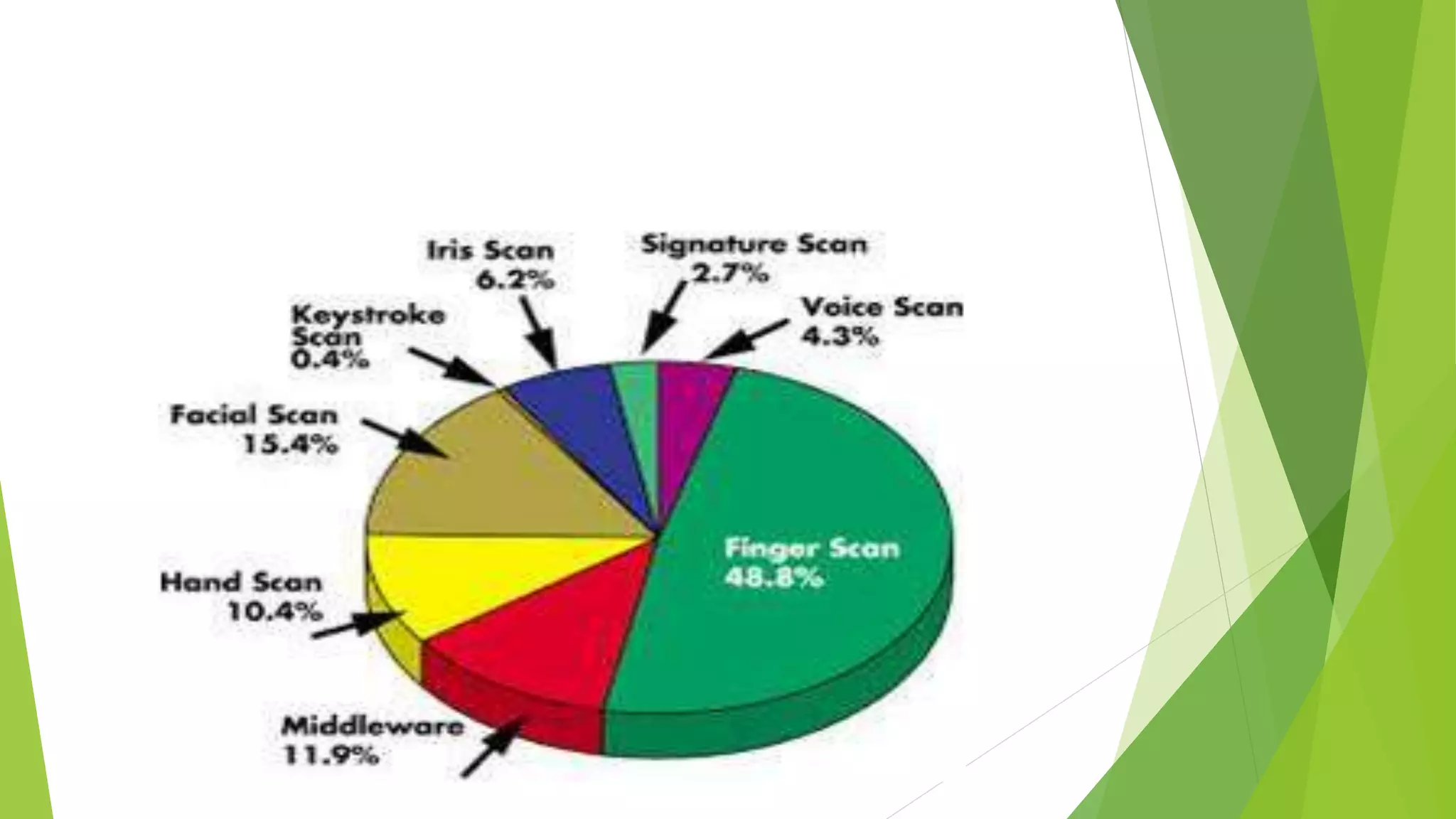
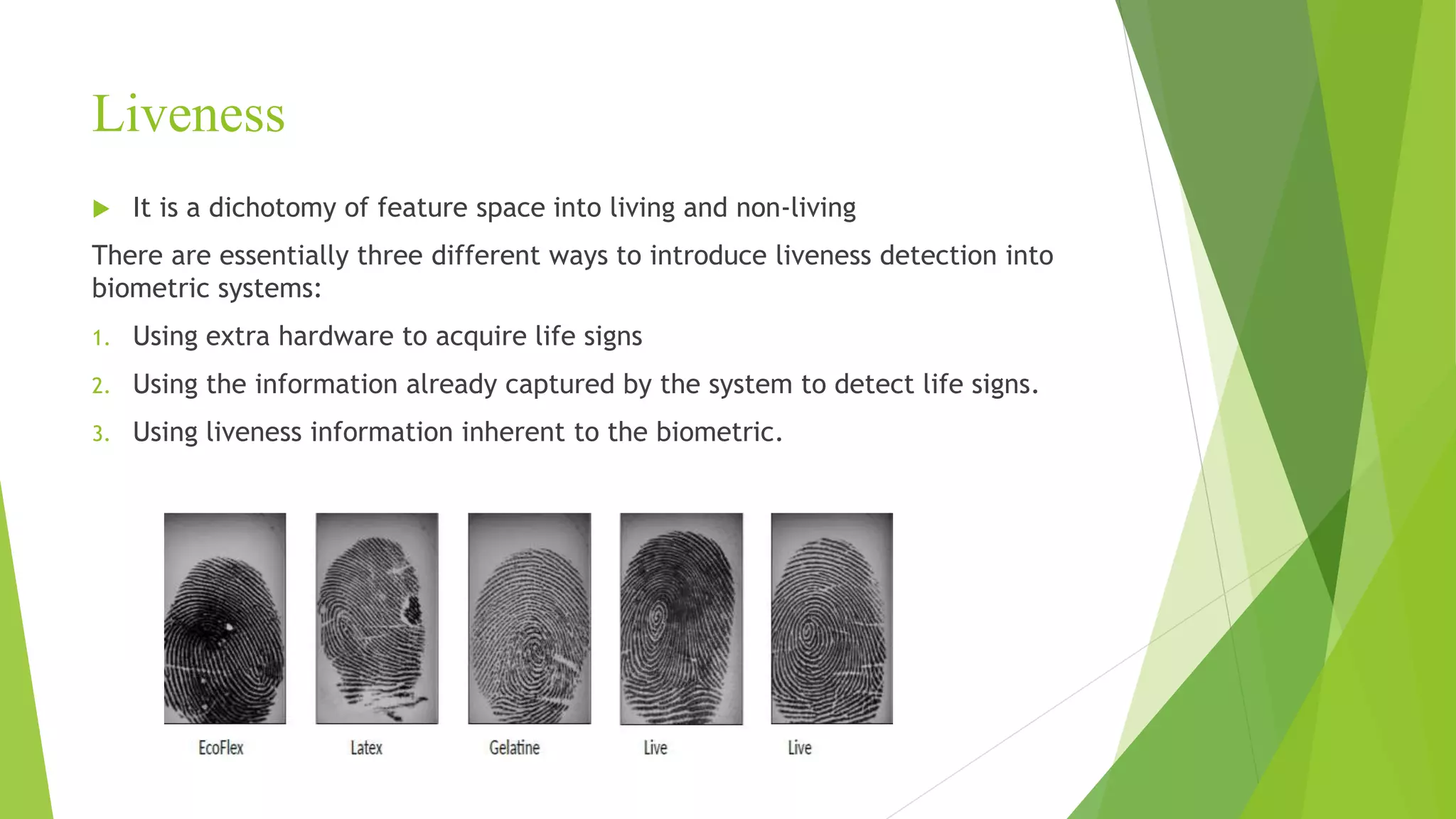
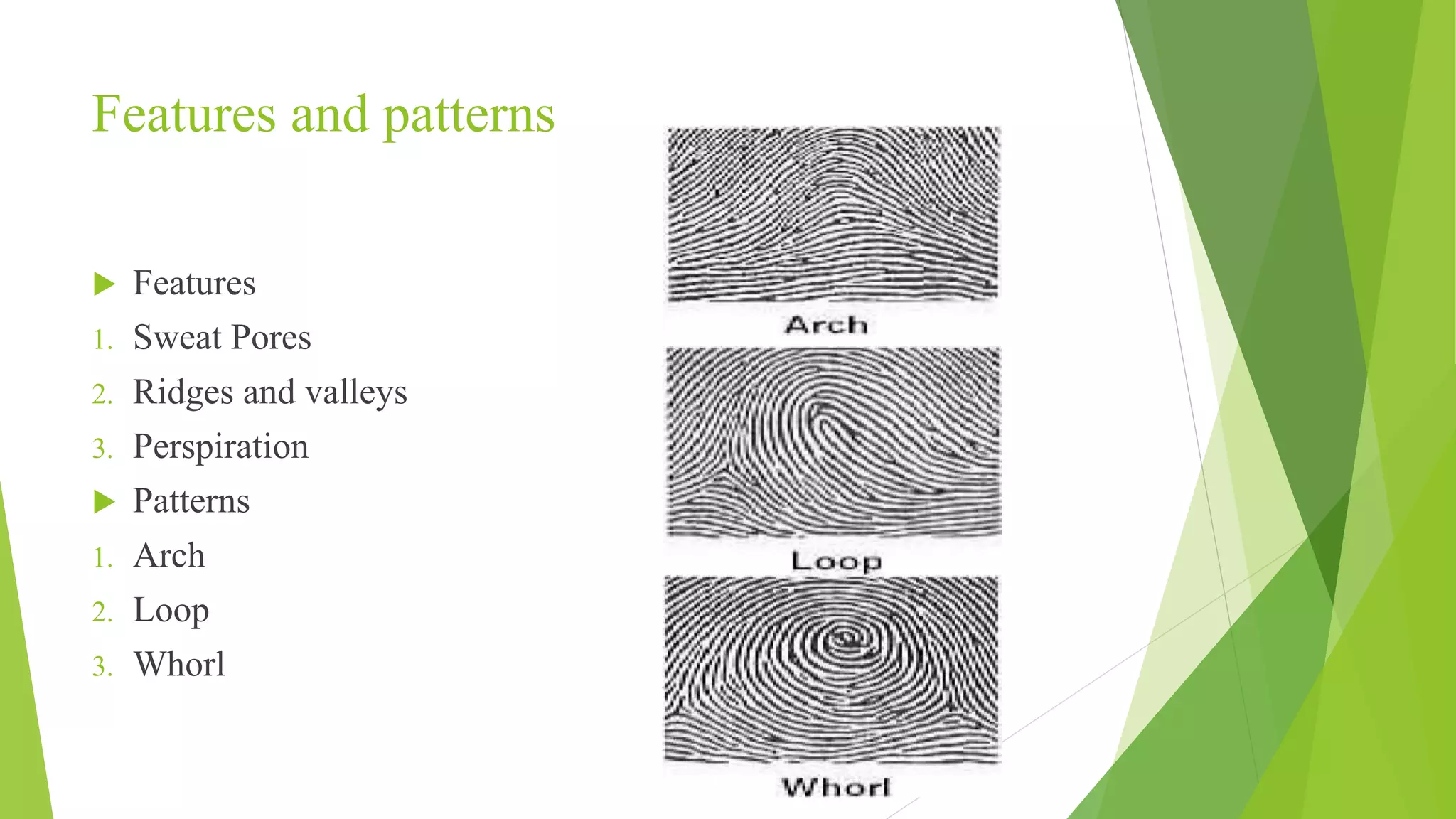
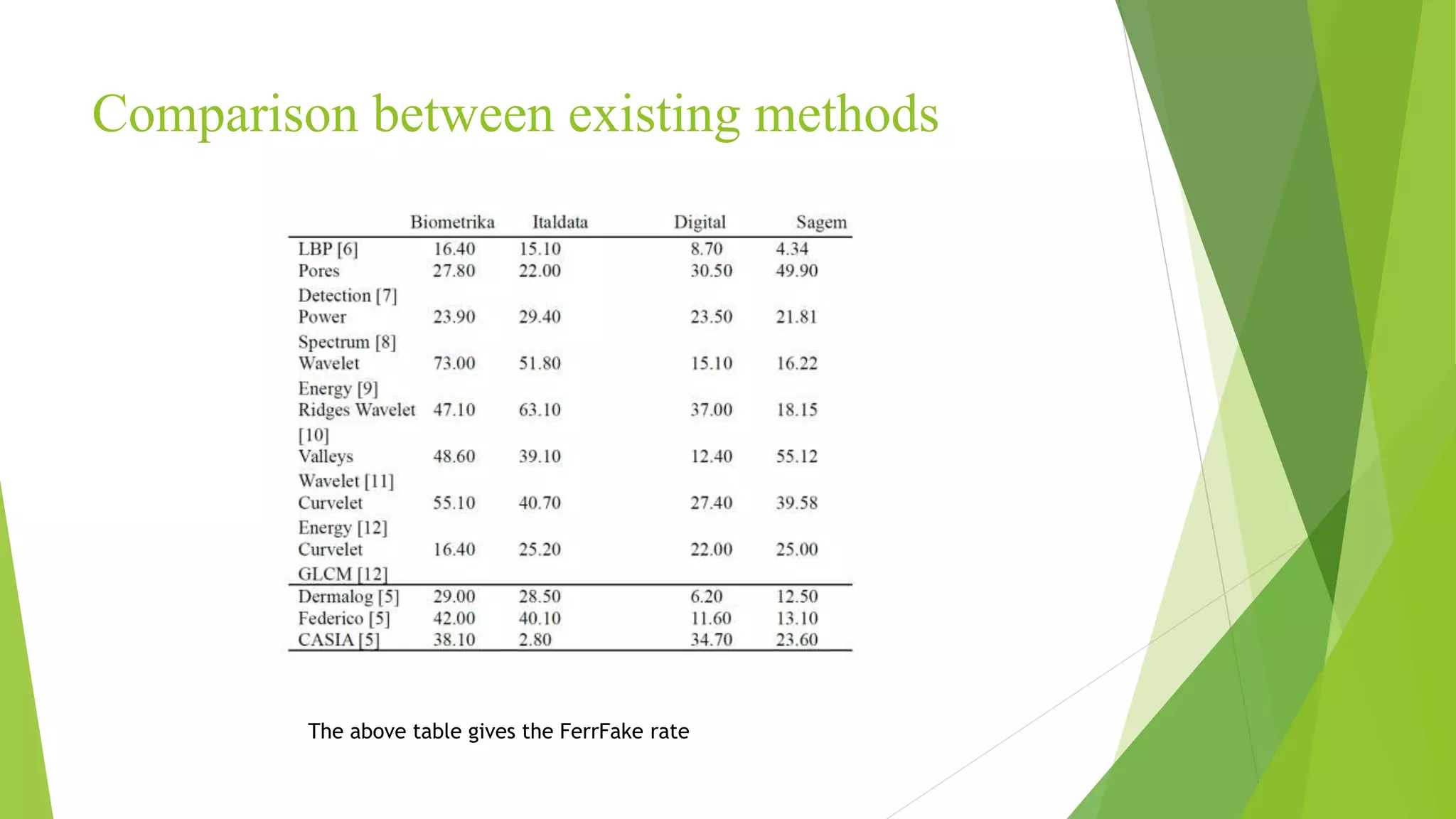
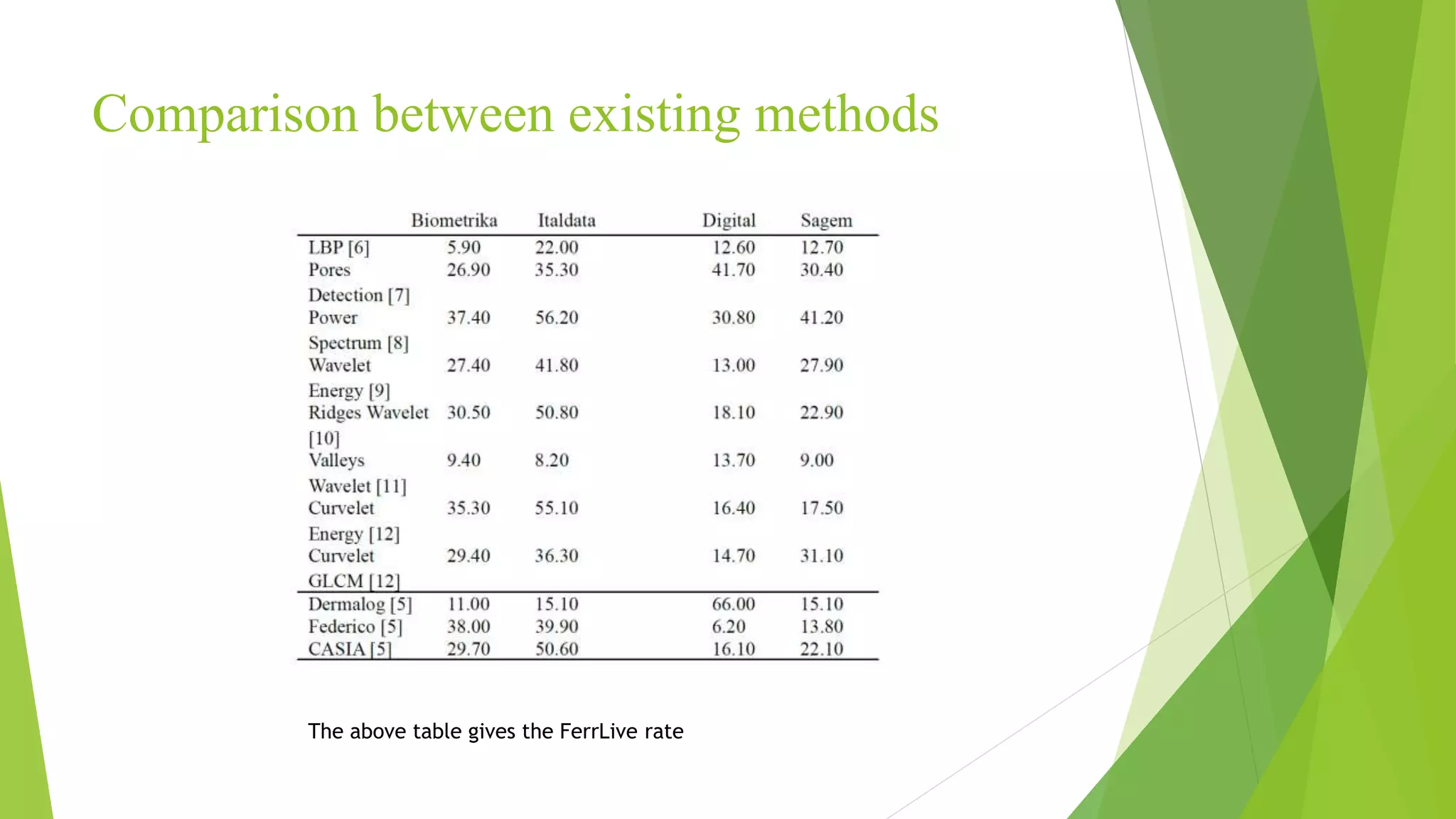
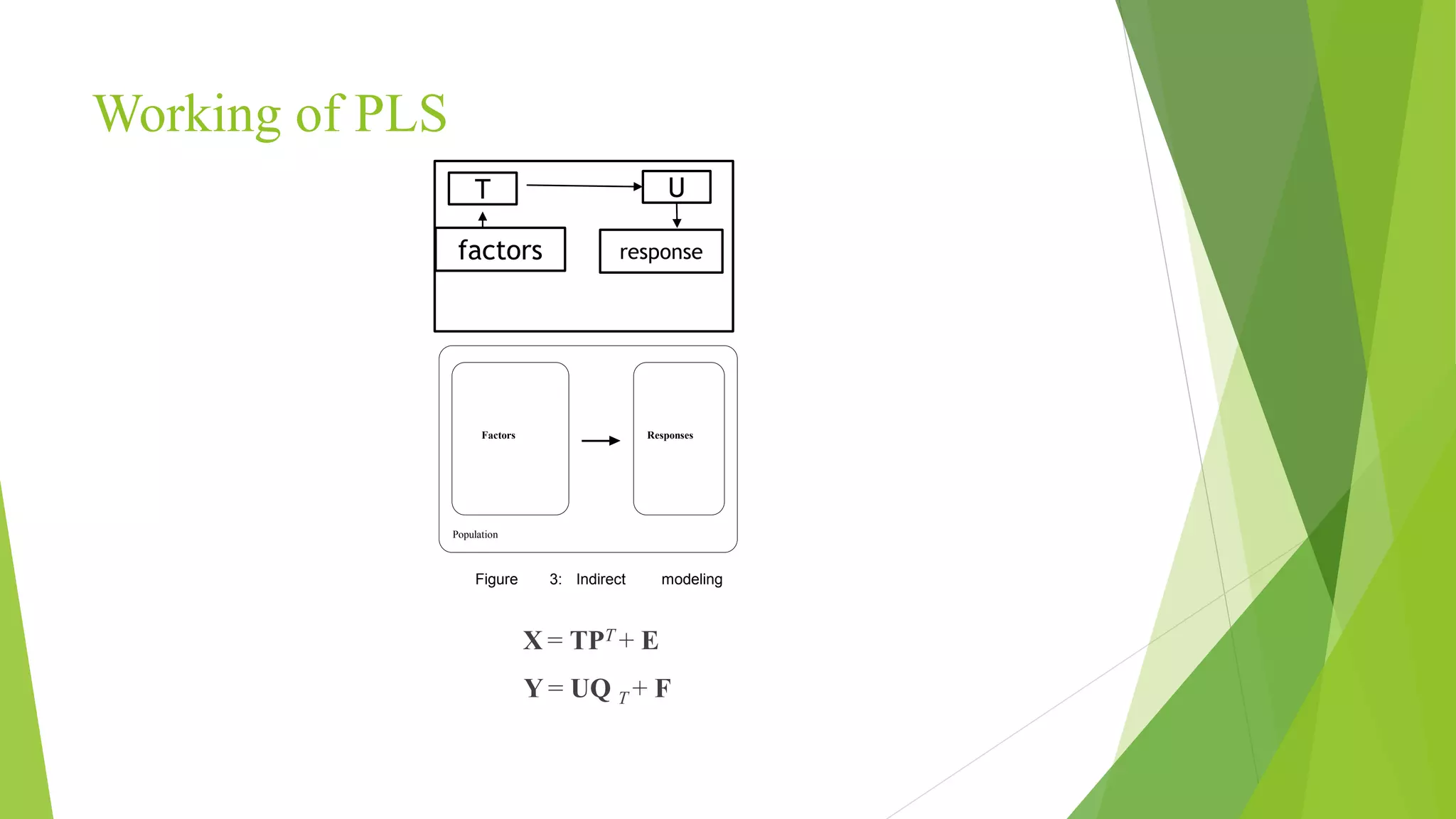
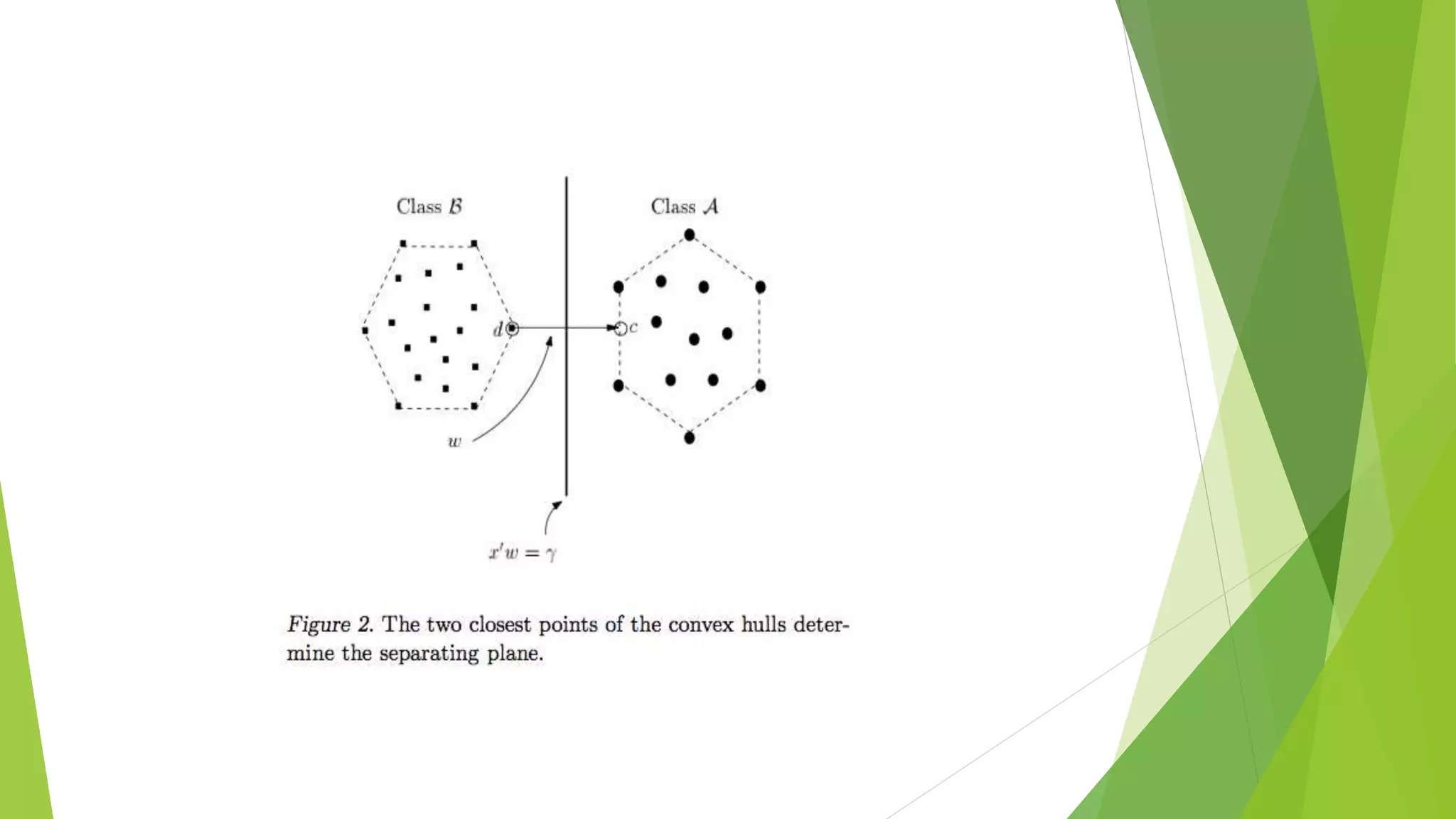
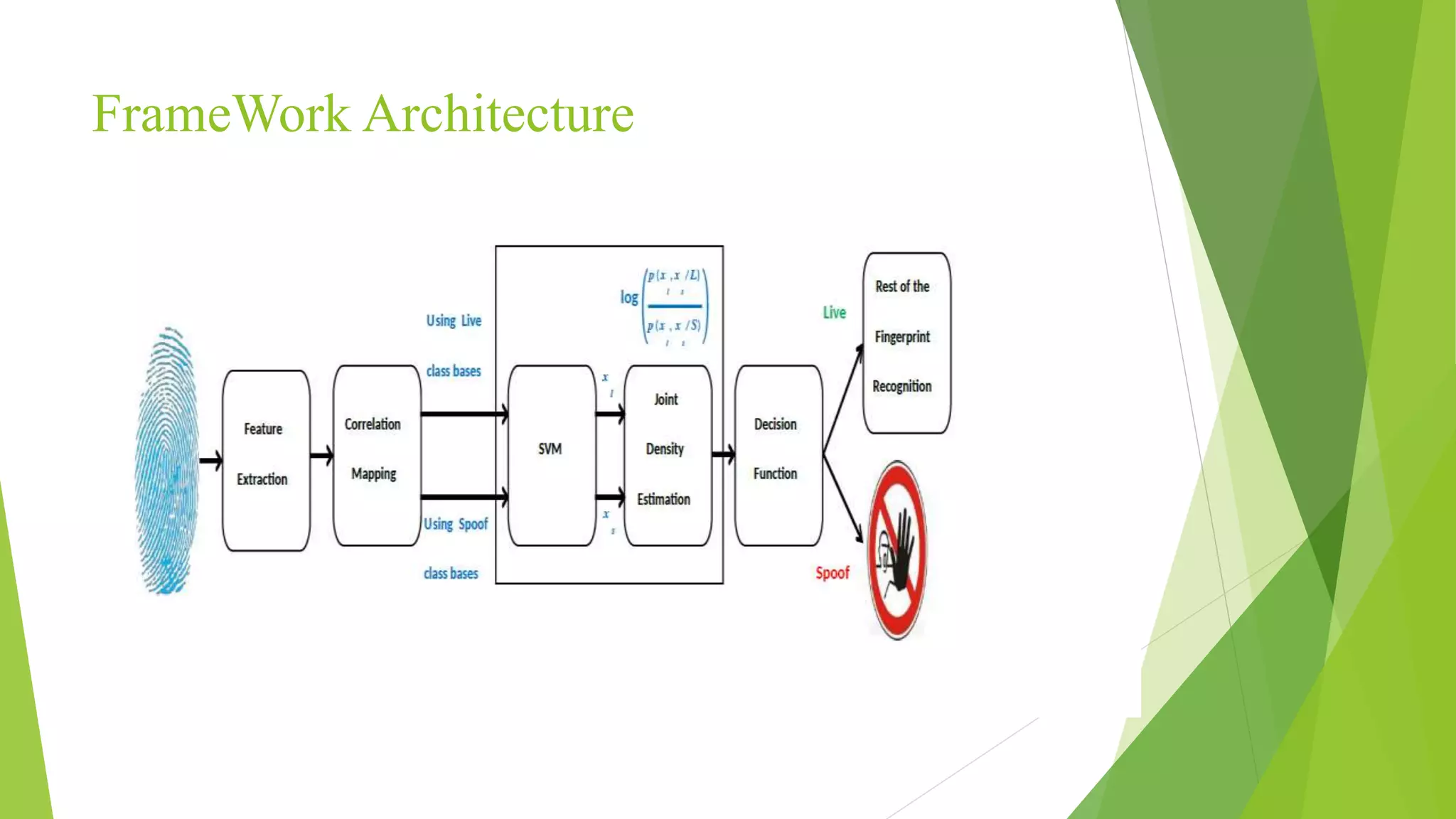
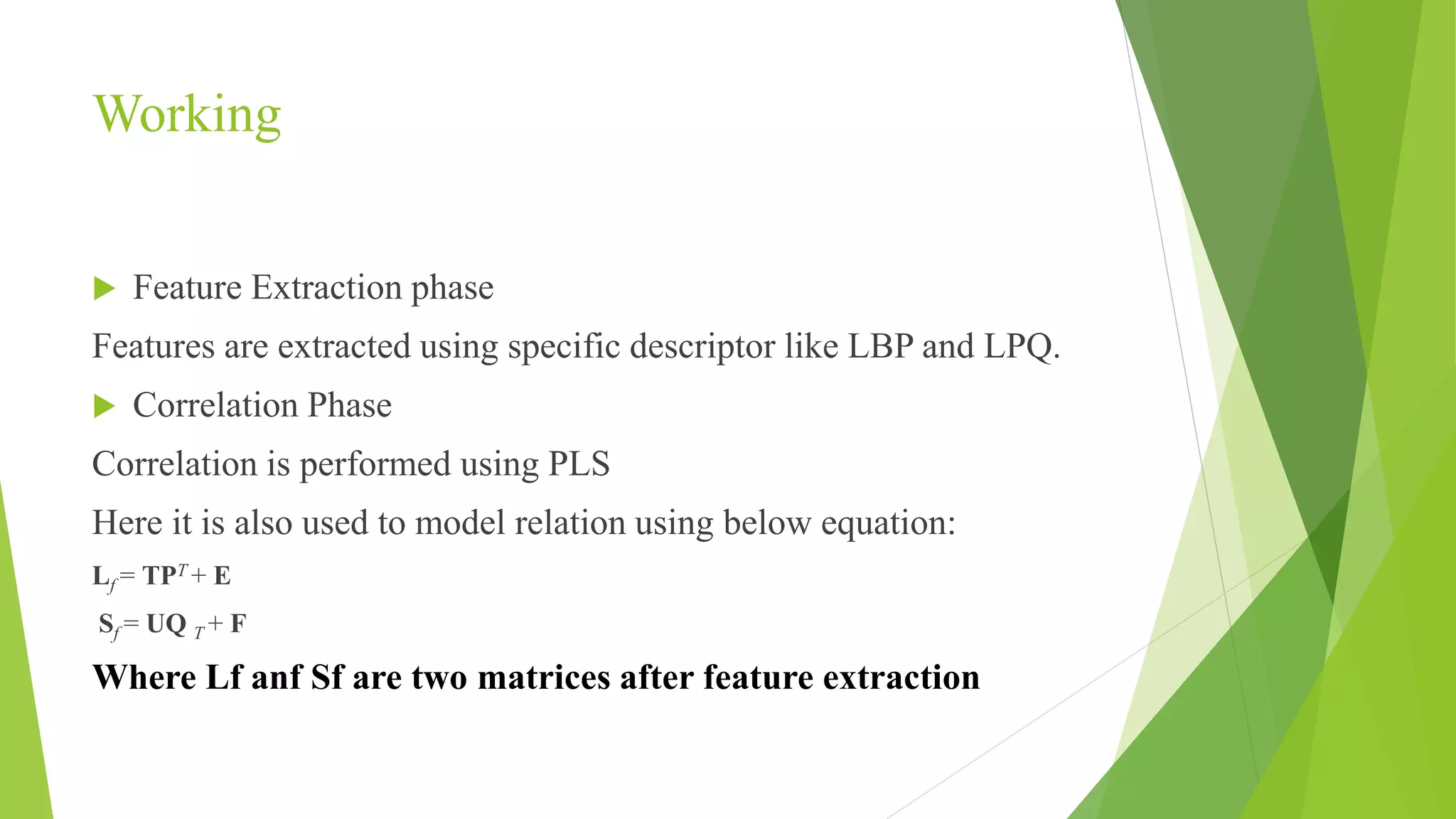
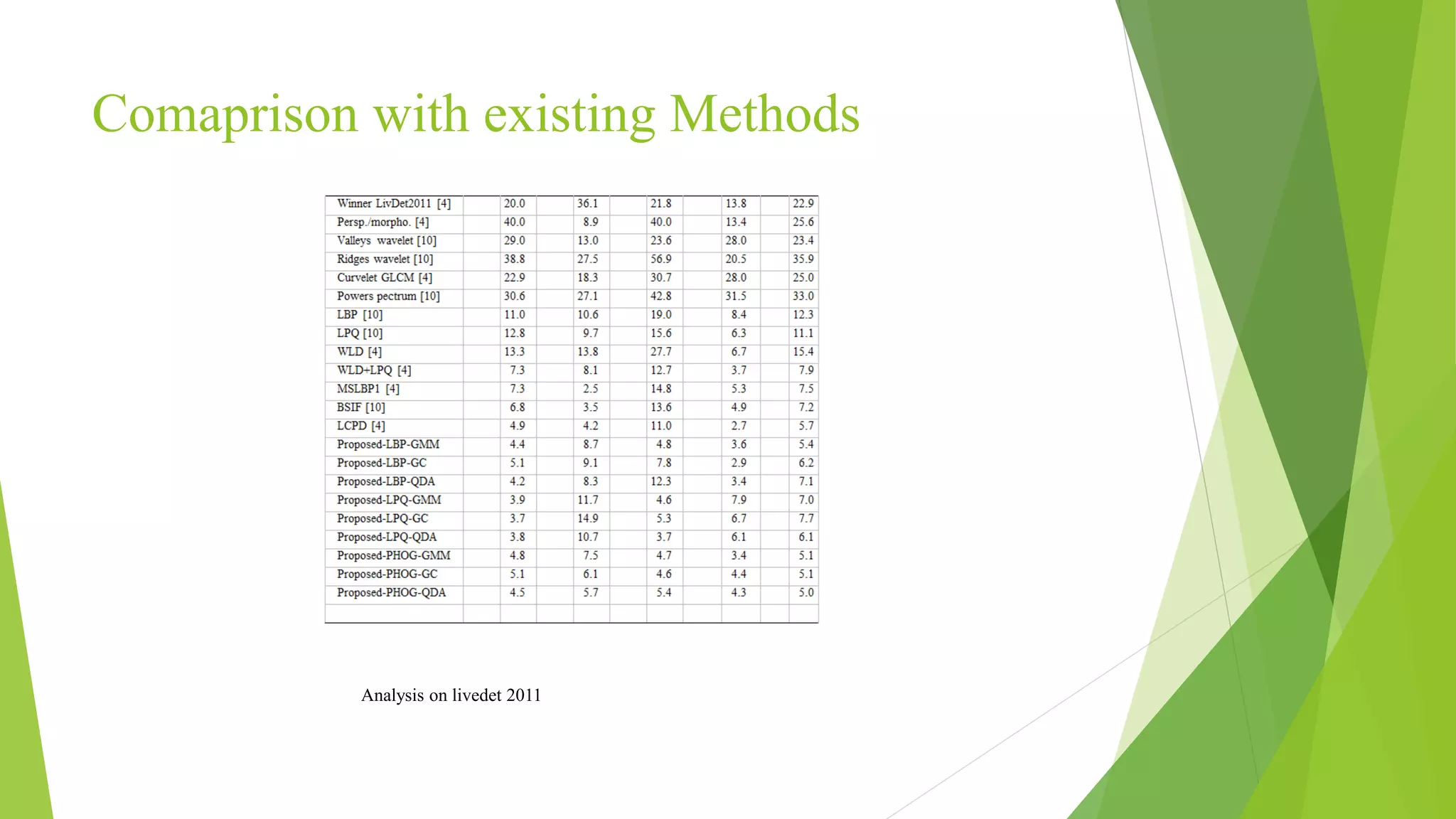
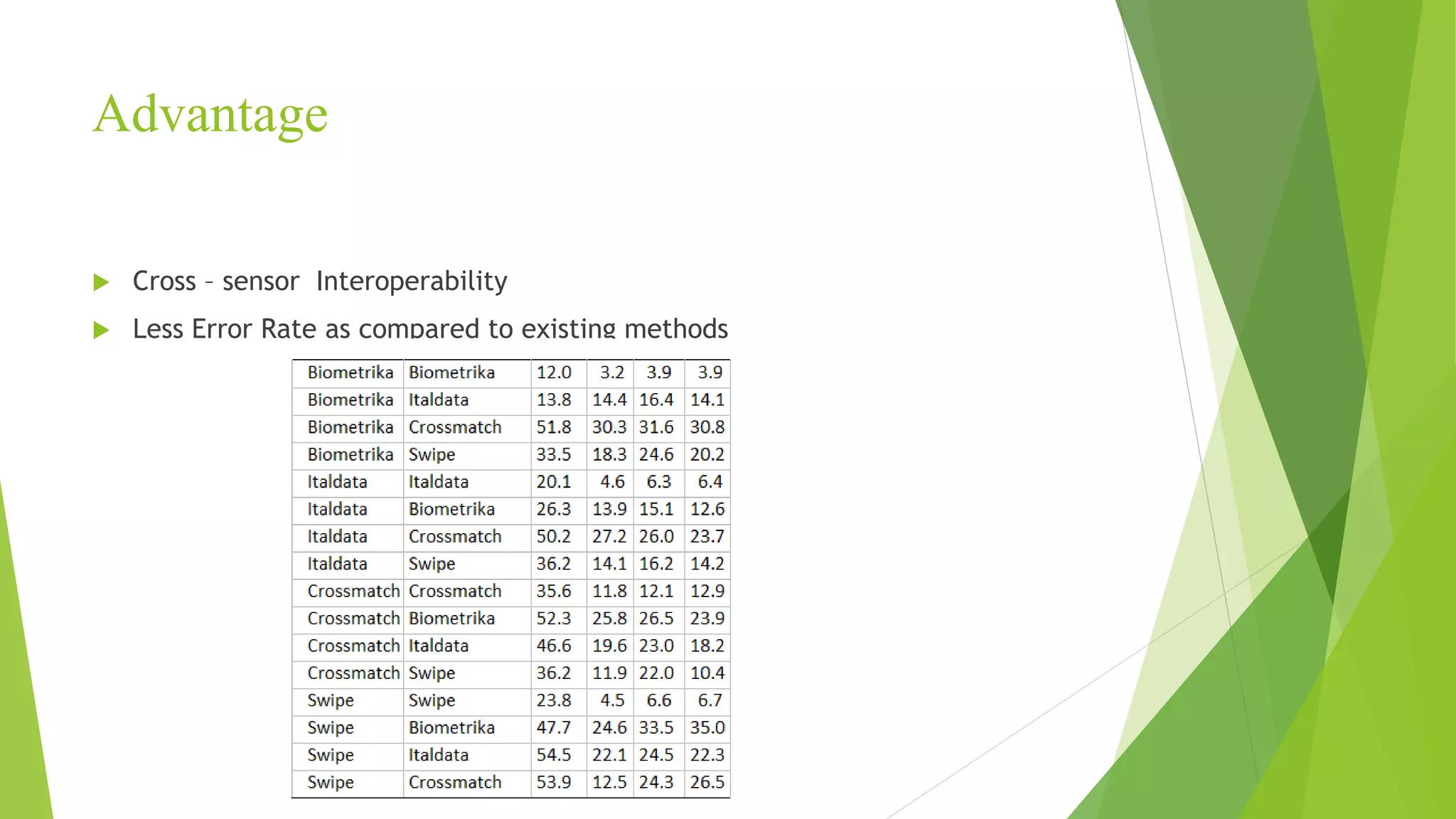
This document proposes a correlation based fingerprint liveness detection method using partial least squares and support vector machines. It discusses existing liveness detection techniques like local binary pattern and pore detection, as well as the need for liveness detection in fingerprint authentication systems. The proposed method works by extracting features from fingerprints, performing correlation analysis using partial least squares, calculating live and spoof probabilities using support vector machines, and classifying the fingerprints using generative classifiers. It is shown to achieve better cross-sensor performance and lower error rates than existing liveness detection methods.