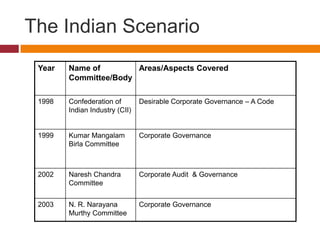
This document provides an overview of corporate governance practices and regulations in India. It discusses several committees formed over time to address different aspects of corporate governance. It outlines the process for incorporating a new company. For public companies, an additional step of obtaining a commencement of business certificate is required. The document also details requirements for audit committees as per the Companies Act and Clause 49 of the listing agreement. This includes composition, roles, powers, and review responsibilities. Finally, it summarizes the WorldCom accounting fraud case and identifies failure of management, shareholders, and oversight committees as contributing factors.