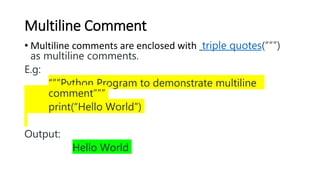
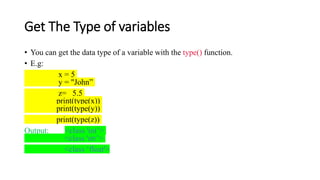
This document provides an overview of core concepts in Python including variables, keywords, data types, comments, and basic programs. It discusses how variables are used to store data values without needing declaration. The different data types in Python like integers, floats, strings, lists, tuples, and dictionaries are explained along with examples. It also demonstrates how to write single line and multiline comments and includes examples of basic Python programs to perform mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division of numbers.








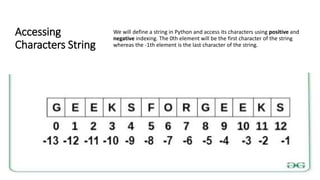
![Example
String1 = "Hello"
print("Initial String: ")
print(String1)
print("nFirst character of String is: ")
print(String1[0])
print("nLast character of String is: ")
print(String1[-1])
Output:
Initial String:
Hello
First character of String is:
H
Last character of String is:
O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coreconceptpython-240127091754-d0e091a8/85/Core-Concept_Python-pptx-13-320.jpg)
![List
• Lists are used to store multiple items in a single variable.
• Lists are created using square brackets:
E.g:
thislist = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
print(thislist)
Output: [‘apple’, ’banana’, ’cherry’] ', 'cherry']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coreconceptpython-240127091754-d0e091a8/85/Core-Concept_Python-pptx-14-320.jpg)
![Tuple
• Tuples are used to store multiple items in a single variable.
• A tuple is a collection which is ordered and unchangeable.
• Tuples are written with round brackets.
E.g:
thistup = ("apple", "banana", "cherry“)
print(thistup)
Output: (‘apple’, ’banana’, ’cherry’), 'banana', 'cherry']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coreconceptpython-240127091754-d0e091a8/85/Core-Concept_Python-pptx-15-320.jpg)
![Dictionary
• Dictionaries are used to store data values in key:value pairs. ‘
thisdict = {
"brand": "Ford",
"model": "Mustang",
"year": 1964
}
print(thisdict)
Output: ‘
{"brand": "Ford","model": "Mustang", "year": 1964}
{'brand': 'Ford', 'model': 'Mustang', 'year': 1964} c
{'brand': 'Ford', 'model': 'Mustang', 'year': 1964}herry']](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coreconceptpython-240127091754-d0e091a8/85/Core-Concept_Python-pptx-16-320.jpg)