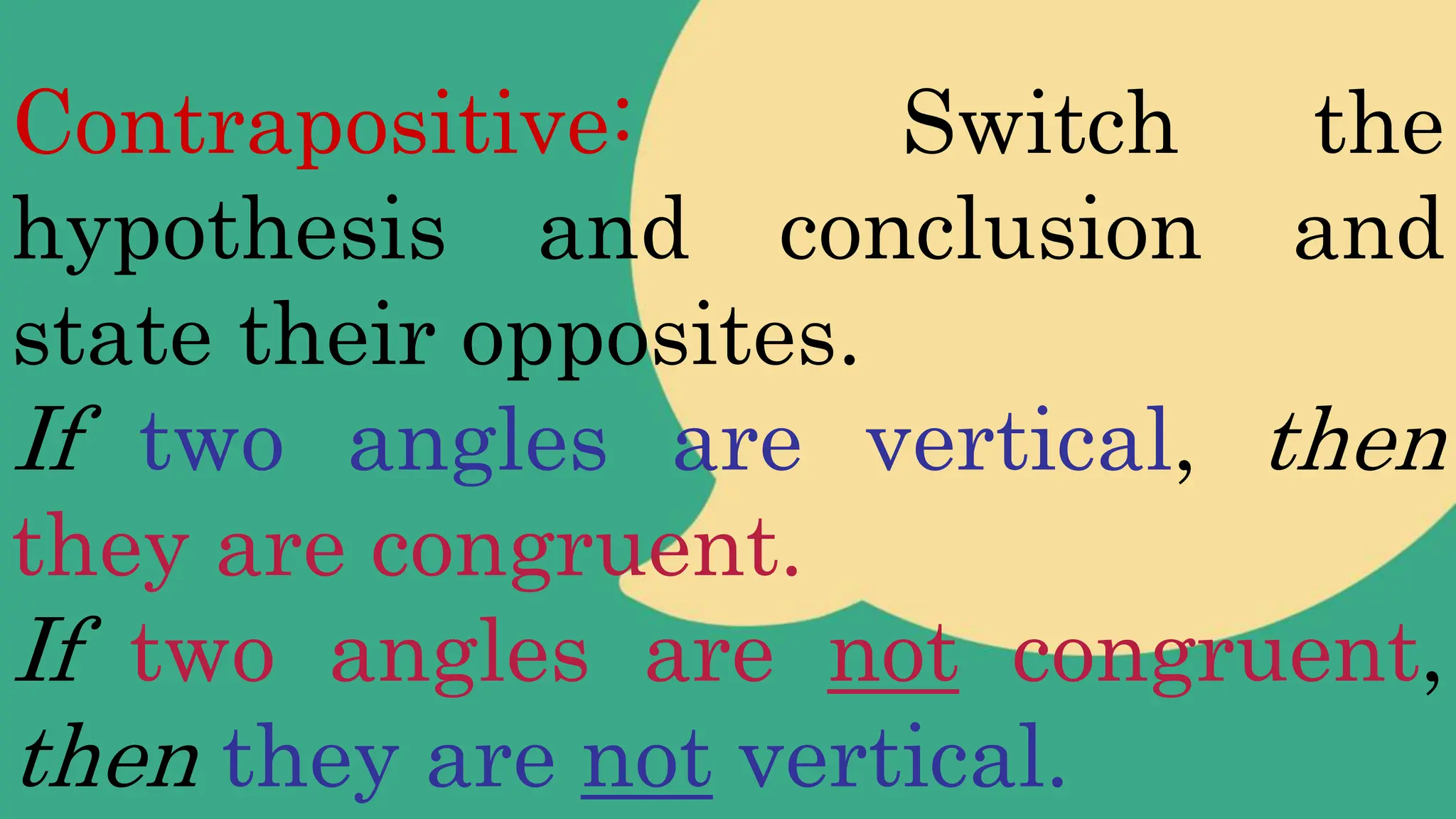
The document defines and provides examples of the converse, inverse, and contrapositive of conditional statements. The converse is formed by interchanging the hypothesis and conclusion of a conditional statement. The inverse is formed by negating both the hypothesis and conclusion. The contrapositive is logically equivalent to the original statement and is formed by switching the hypothesis and conclusion and stating their opposites. Examples are provided to illustrate each type of statement transformation.