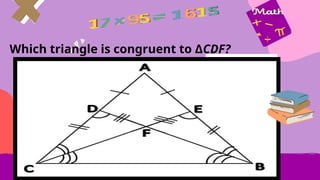
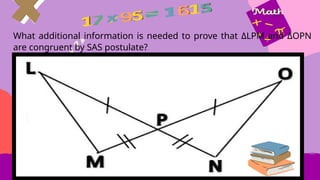
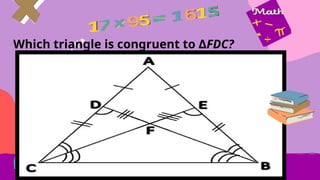
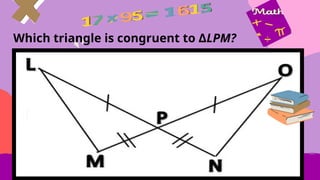
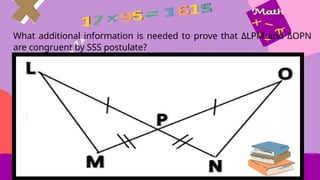
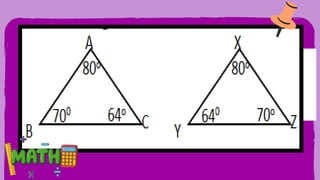
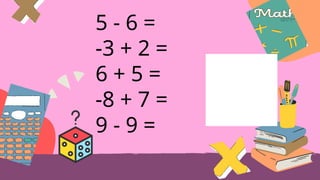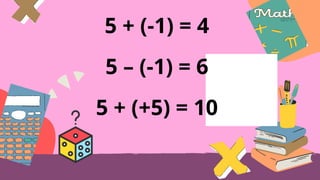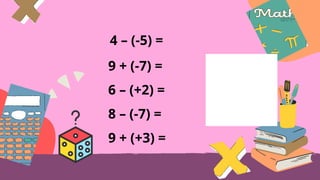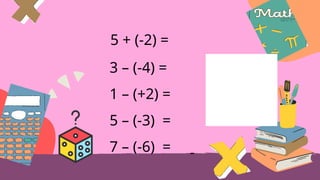This document provides an overview of integers, including their definition, operations such as addition and subtraction, and the concept of factoring polynomials. It explains how to find the greatest common factor (GCF) of integers and polynomials using prime factorization and illustrates its application with examples. Additionally, it touches on properties of triangles, congruence, and various mathematical properties related to equality.