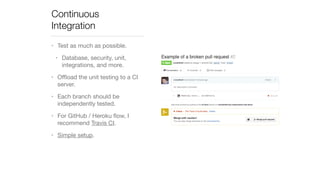
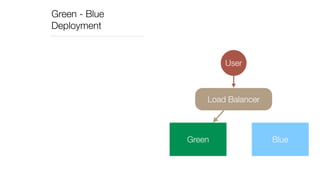
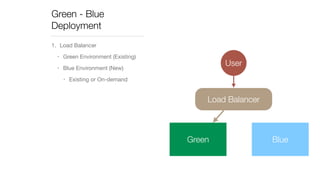
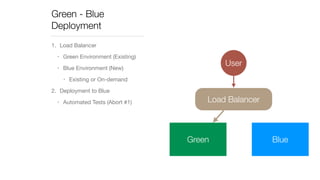
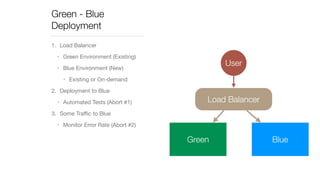
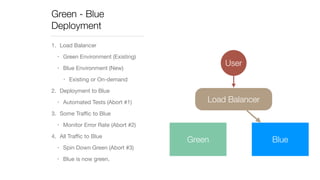
The document discusses continuous deployment strategies and best practices for software development, emphasizing the importance of version control, continuous integration, and automation. It outlines the concept of 'green-blue deployment' as a method for achieving zero downtime during updates, while also noting challenges specific to platforms like Salesforce. The author, Ron Heft, offers insights based on his experience in full stack web development and the operations of his social media marketing startup, Social Station.