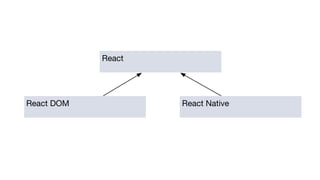
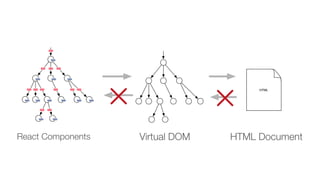
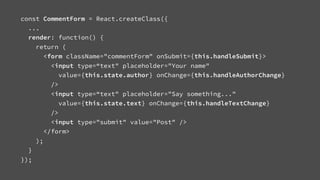
The document discusses the architecture and development of content-driven mobile applications using React, highlighting the transition from a hybrid app based on Cordova and Angular to a more performant React-based solution. It outlines the key concepts of React, Redux, and immutable data, emphasizing how these technologies enhance user experience and app efficiency while allowing for code reusability and customization. Additionally, it introduces 'Girders Elements,' a framework derived from their experiences, which is still under development and aims to facilitate further app customization.




























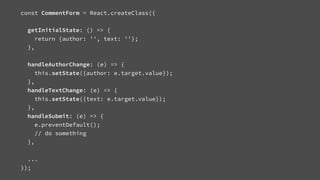






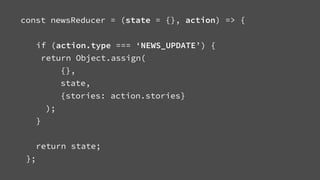


![Content API
{
"kind": ["image", "diagram"],
"imageUrl": “http://example.com/diagram.png"
"caption": “Super Cool Diagram"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/content-driven-apps-with-react-20161017-161018075032/85/Content-Driven-Apps-with-React-49-320.jpg)

![Content API
{
"kind": [“image”, “diagram”, “interactive”],
“dataUrl”: “https://example.com/data/diagram.json”,
"imageUrl": “https://example.com/diagram.png"
"caption": “Super Cool Diagram"
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/content-driven-apps-with-react-20161017-161018075032/85/Content-Driven-Apps-with-React-51-320.jpg)
![Notes
Content API
New sub-type ‘interactive’
Data URL for loading the data for the diagram
But the component is also an [‘image’, ‘diagram’] with
‘imageUrl’ and ‘caption’
If a client does not support ‘interactive’ yet, the component
can also just be rendered as an image/diagram](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/content-driven-apps-with-react-20161017-161018075032/85/Content-Driven-Apps-with-React-52-320.jpg)