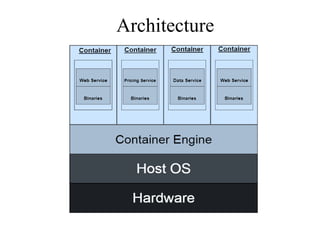
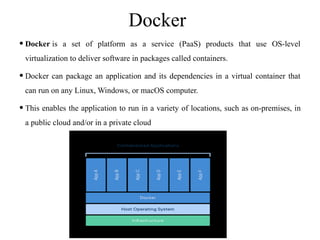
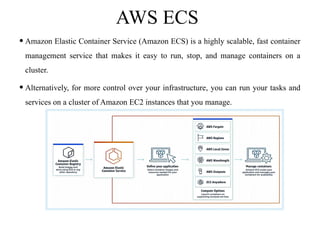
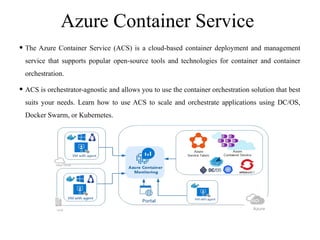
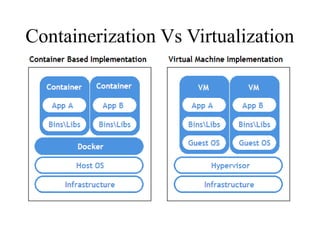
Containerization is a method of operating system virtualization that allows applications to run in isolated environments known as containers, which package all necessary dependencies. Key tools in containerization include Docker, Kubernetes, AWS ECS, and Azure Container Service, each facilitating the management and orchestration of containers. While containerization offers advantages such as portability, speed, and cost-efficiency, it also poses challenges like security concerns and monitoring complexities.