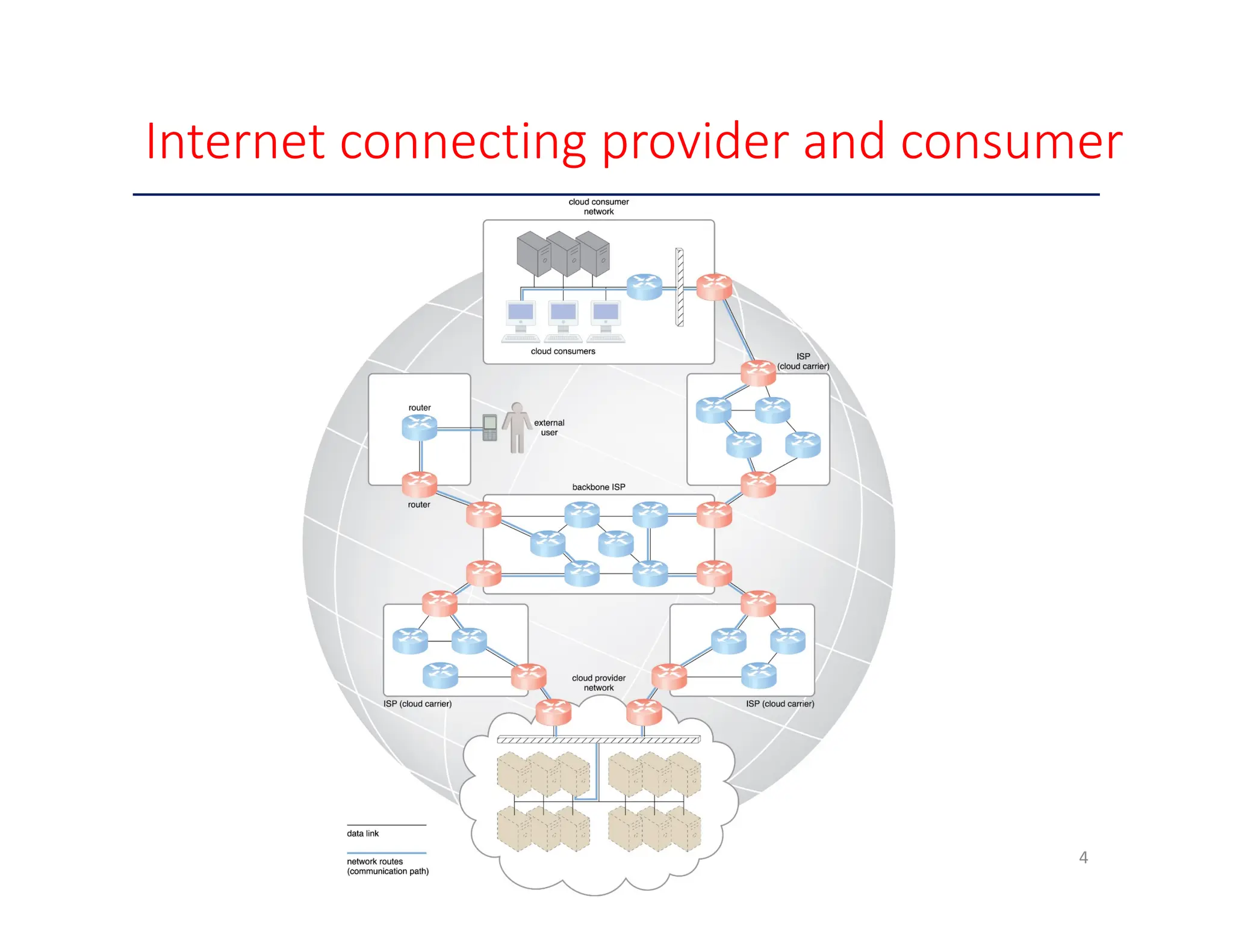
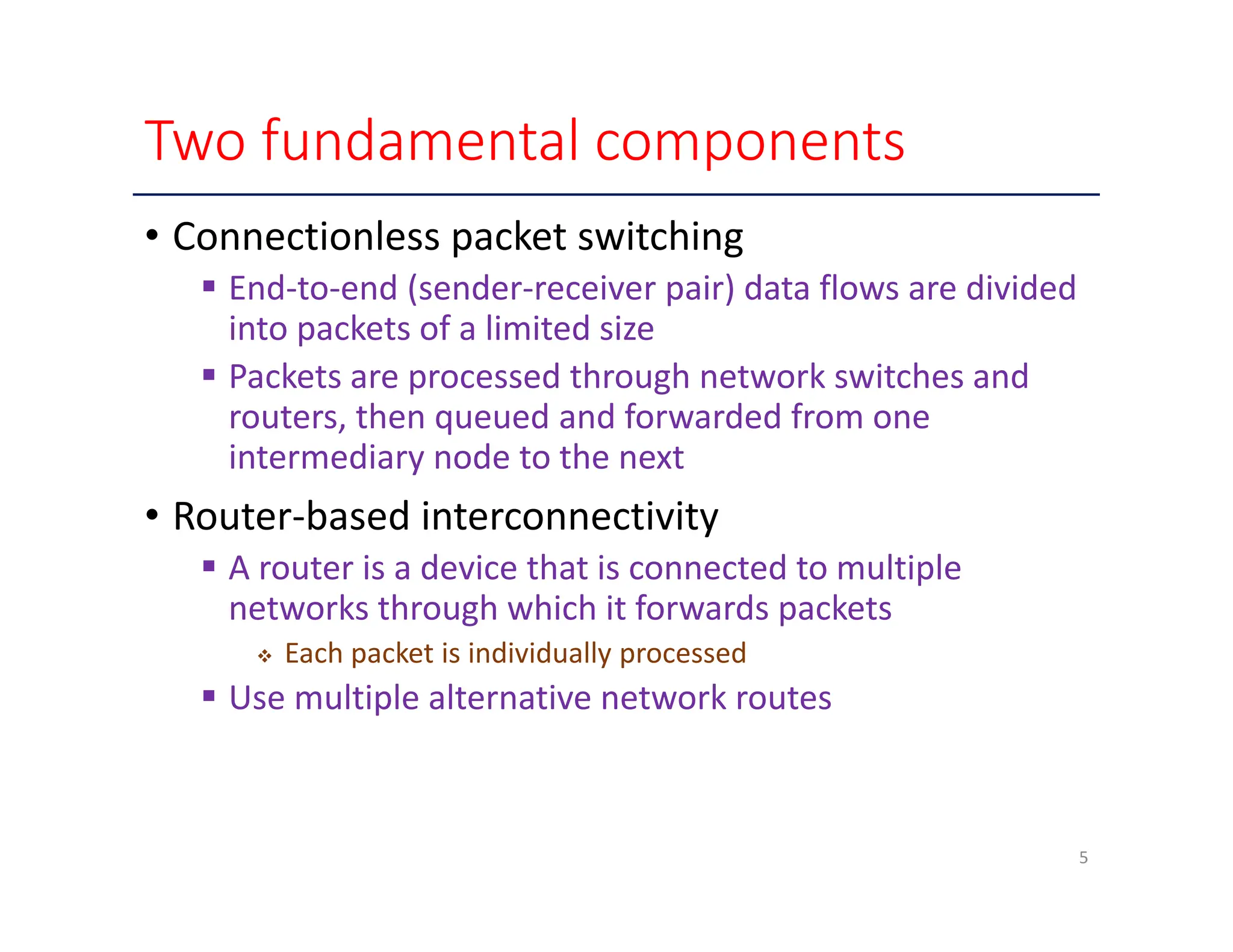
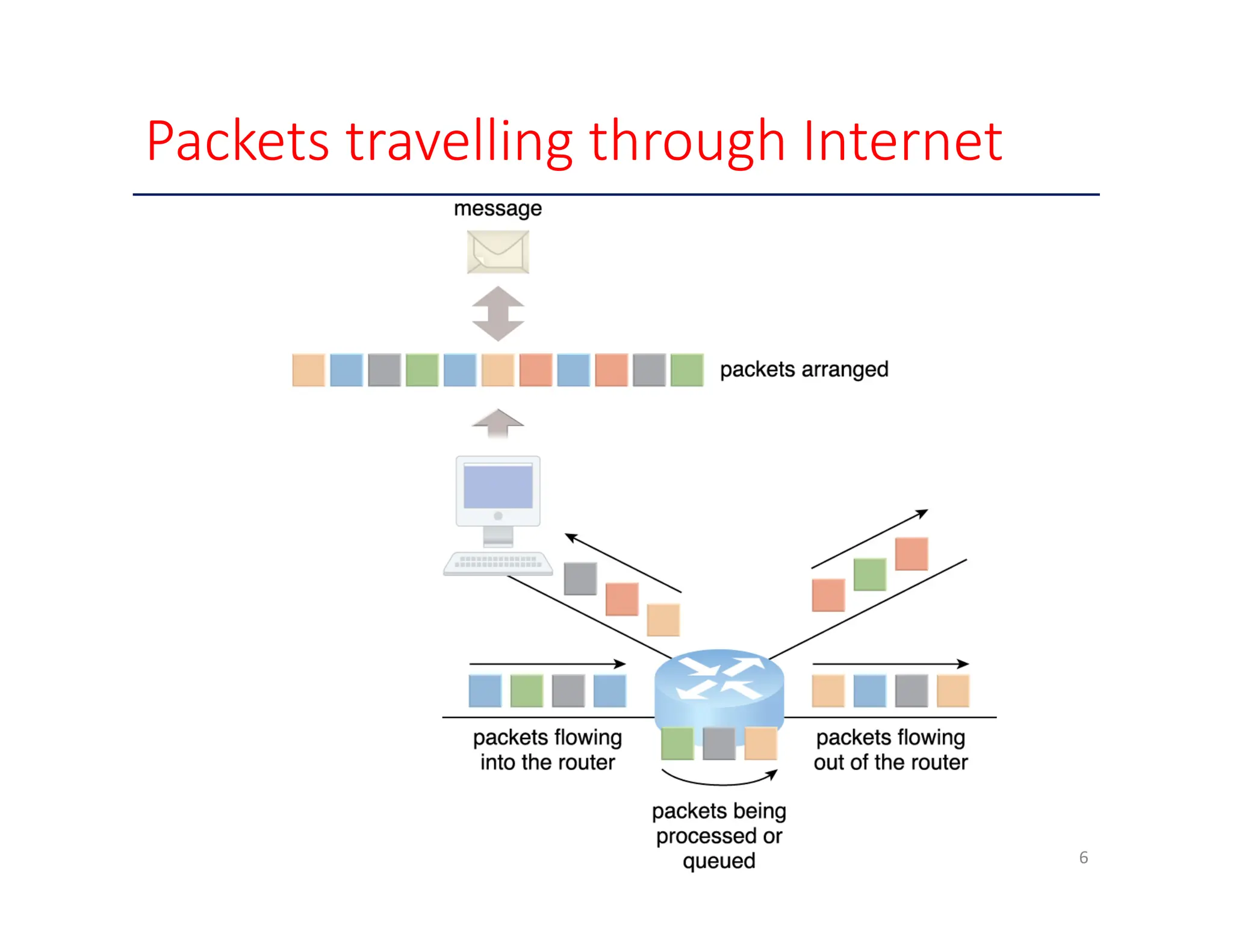
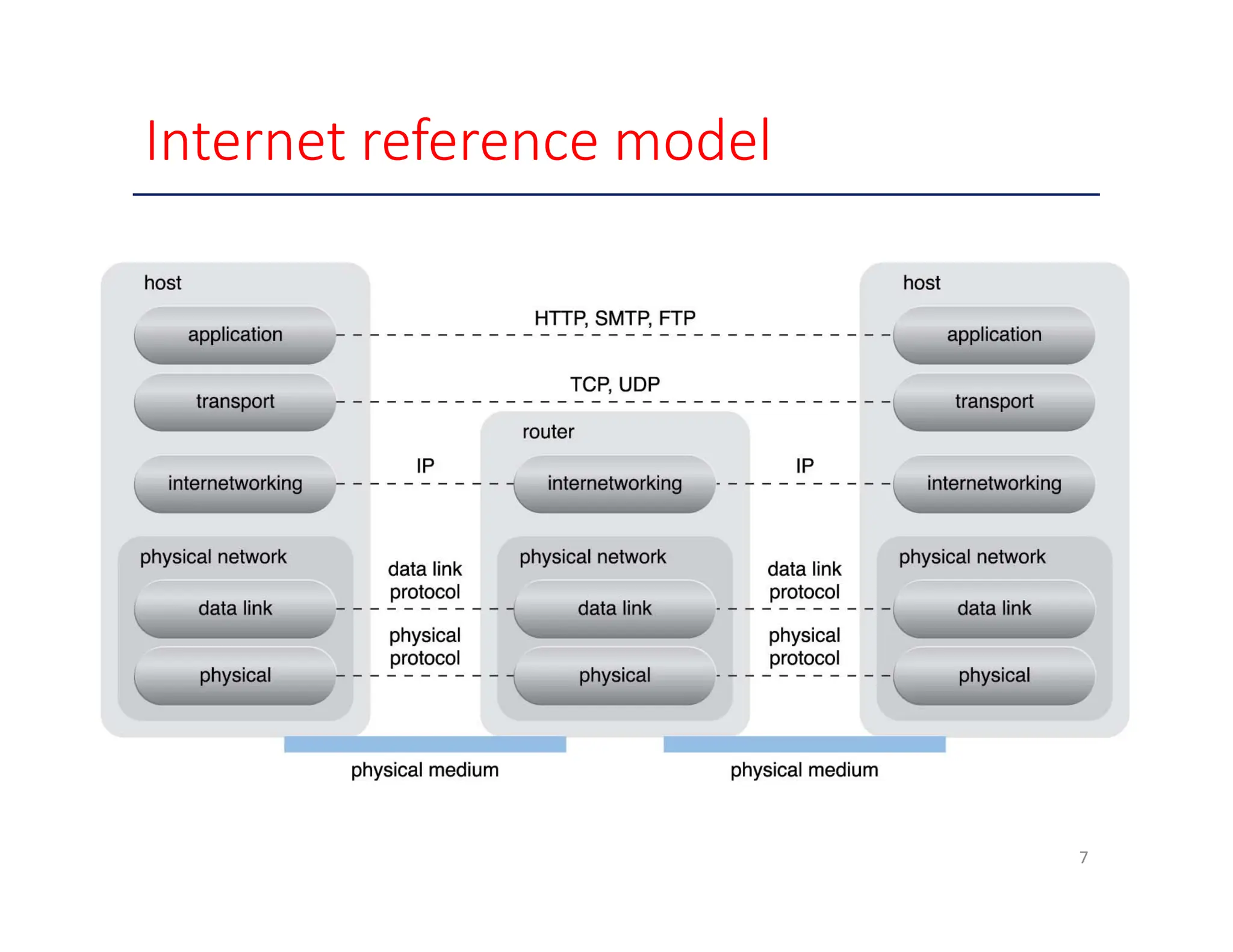
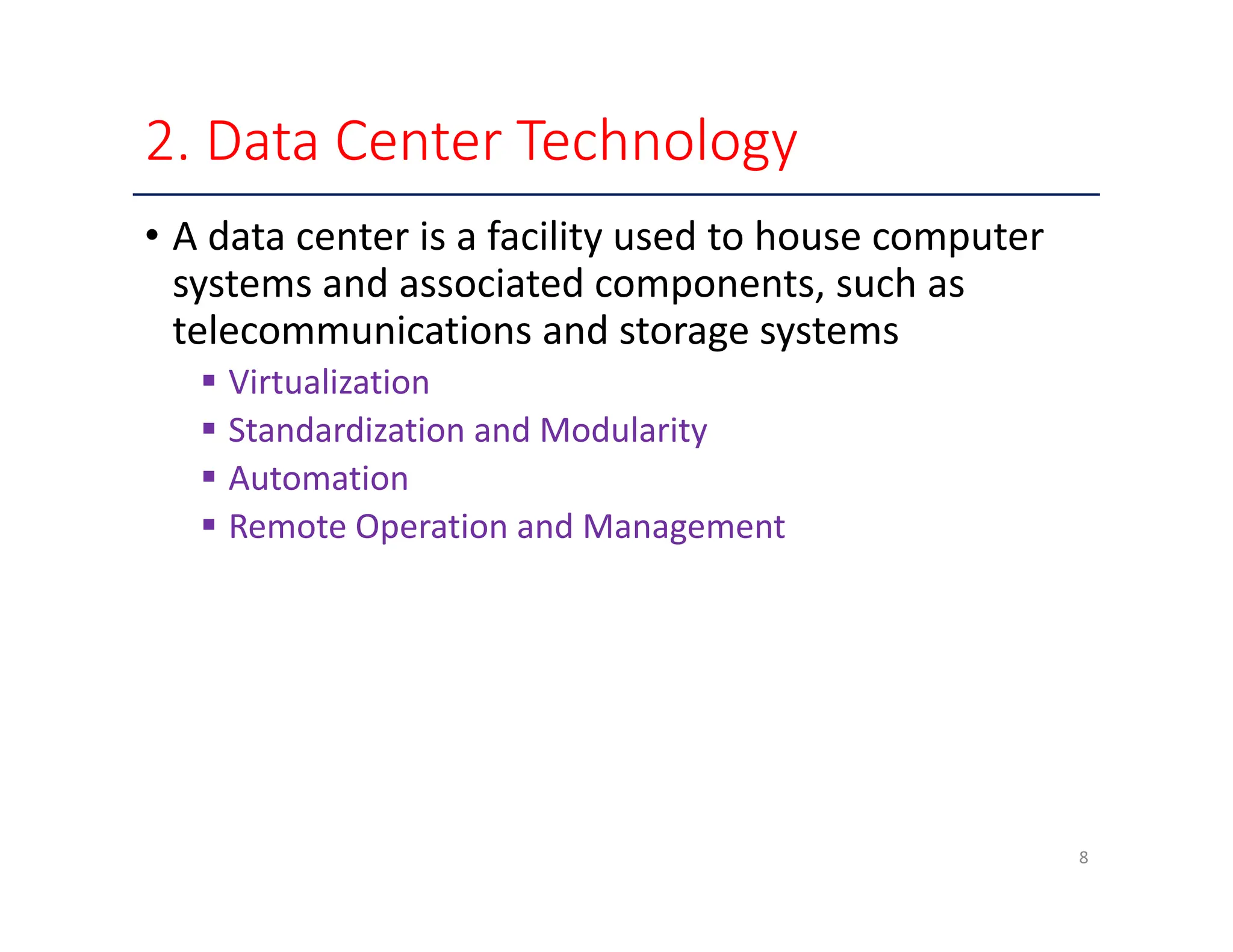
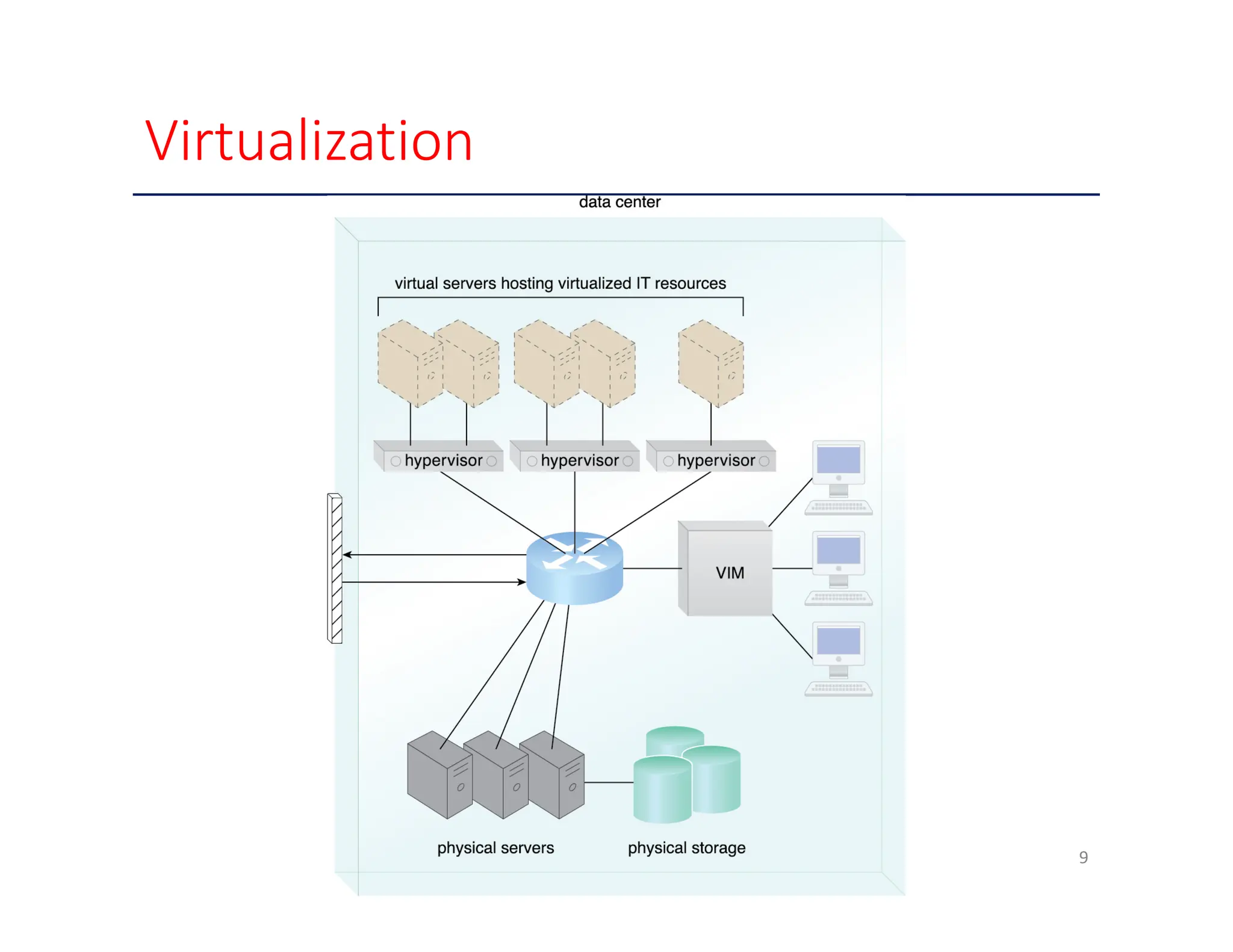
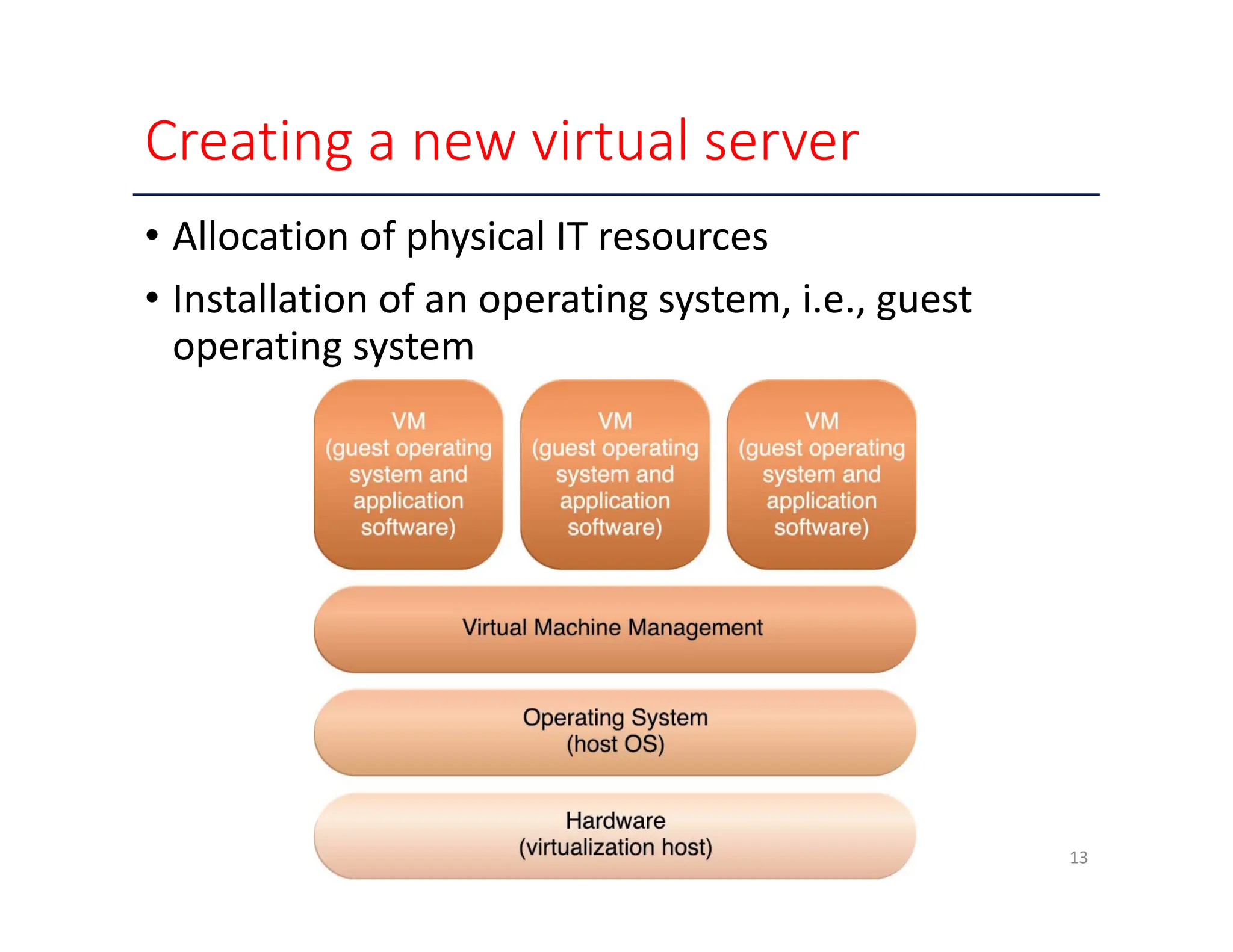
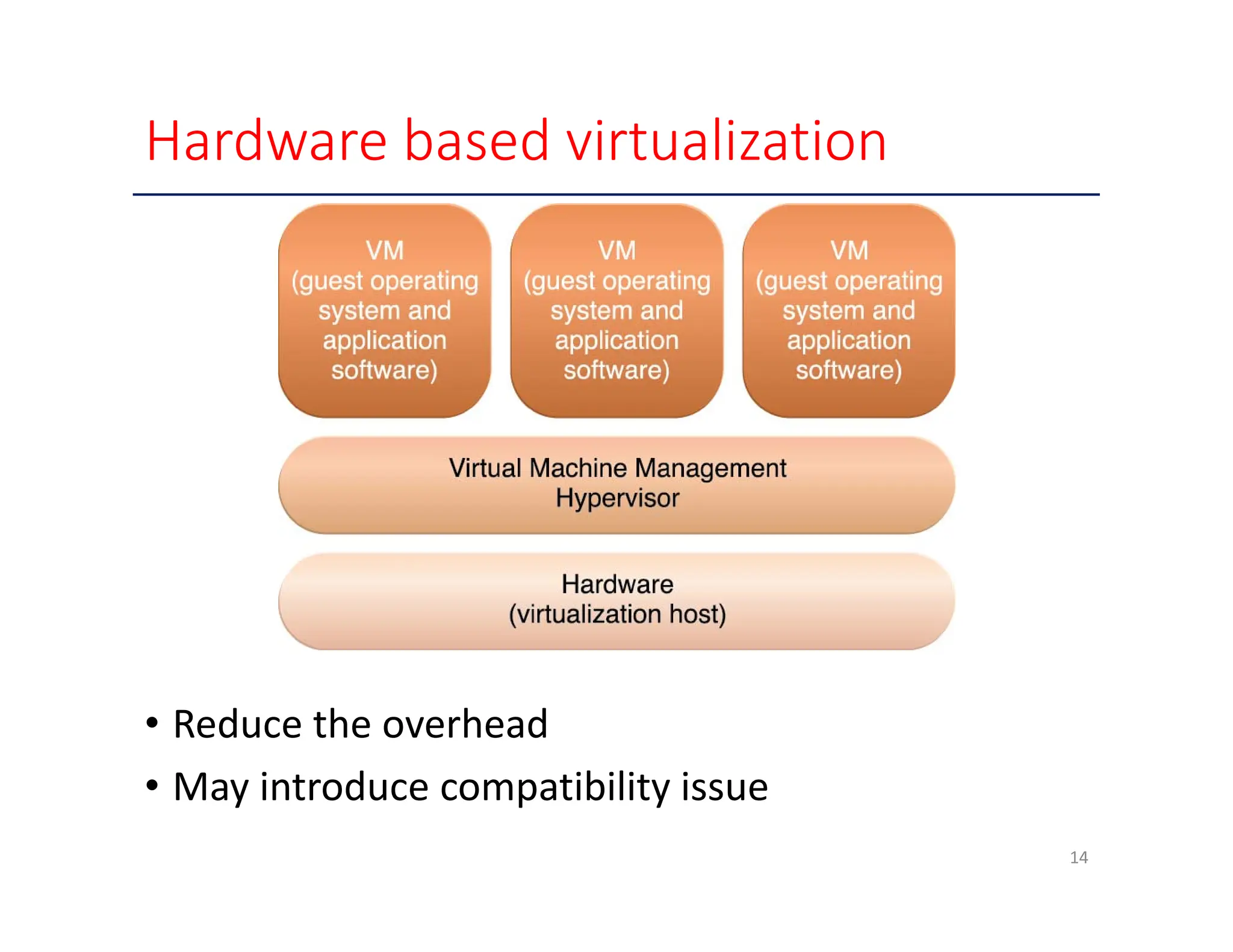
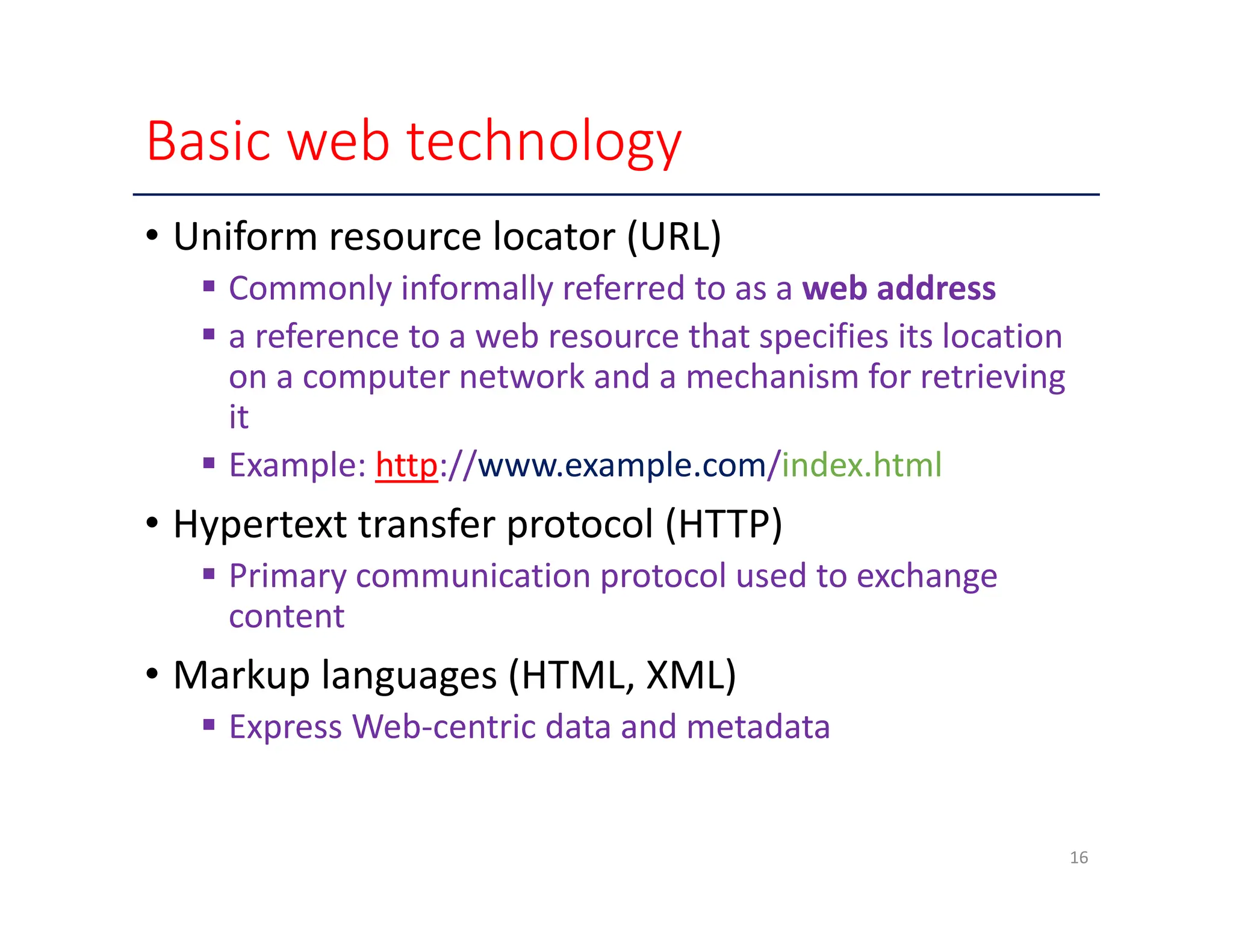
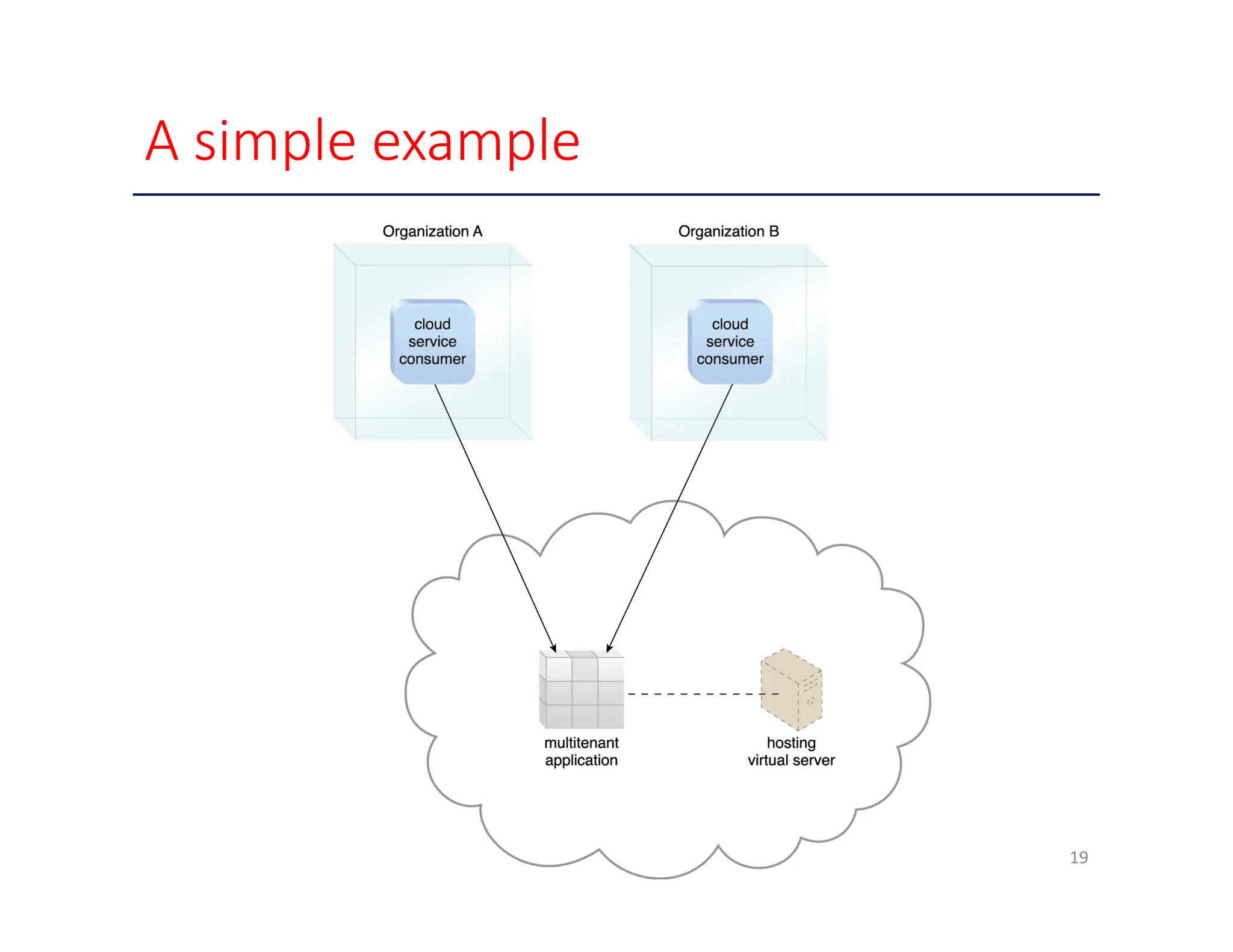
The document outlines key enabling technologies for cloud computing, including broadband networks, data center technology, virtualization, web technology, and multitenant technology. It describes broadband networks as essential for connecting users and data centers, emphasizing virtualization as a method for optimizing IT resources. Additionally, it highlights web technology as the interface for cloud services and multitenant technology for simultaneous user access while ensuring data security.