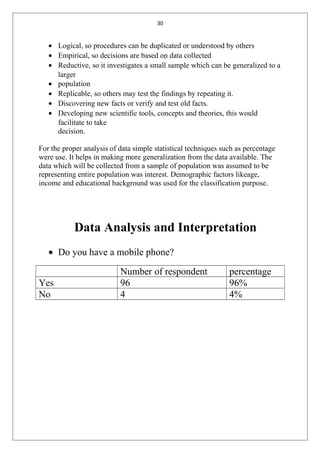
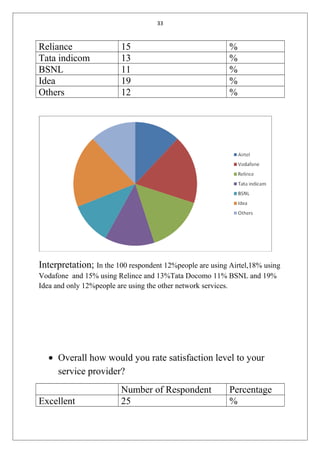
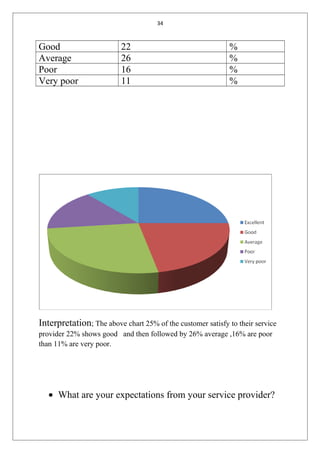
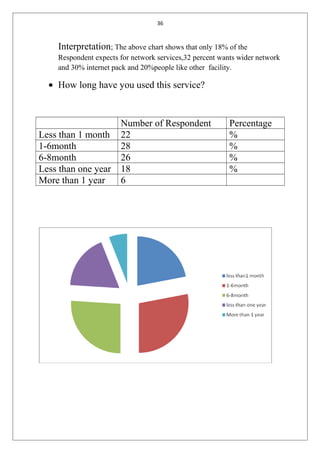
The document is a student's summer training report on customer satisfaction with mobile service providers in India. It includes an introduction describing customer satisfaction and factors that influence it. It also discusses the telecom industry in India, including key milestones in its evolution, current market shares of public and private operators, and the global cellular industry. The report will analyze customer satisfaction data collected through surveys to draw conclusions and suggestions.
































![45
REFERANCES
1. Jallet, Frederic, “Yield management, Dynamic pricing and CRM in
telecommunications”,
(http://www.emeraldinsight.com/Insight/viewContentItem.do;jsessionid=
236E2B6B45CF101465D540FD4401AEB9?
contentType=Article&hdAction=lnkhtml&contentId=1747102&history=t
rue>) [Viewed 13/3/09]
2. Debnath, Roma Mitra, “Benchmarking telecommunication service in
India”, 2008
(http://www.emeraldinsight.com/Insight/viewContentItem.do;jsessionid=
236E2B6B45CF101465D540FD4401AEB9?
contentType=Article&hdAction=lnkhtml&contentId=1742535&history=t
rue>) [Viewed 2/3/09]
3. Robins, Fread, “The marketing of 3G”, vol 21, no 6, 2008
(http://www.emeraldinsight.com/Insight/viewContentItem.do;jsessionid=
236E2B6B45CF101465D540FD4401AEB9?
contentType=Article&hdAction=lnkhtml&contentId=854647&history=tr
ue>) [Viewed 2/4/09]
4. Kalwani, Banumathy, “Consumer’s Attitude towards Cell phone
Services”, 2006
5. Fernandez, Fronnie, “Understanding Dynamics in an Evolving Industry:
Case of Mobile VAS in India”, 2007
(http://www.emeraldinsight.com/Insight/viewContentItem.do;jsessionid=
2086527F0757A565F9A6CBAC8800F658?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalproject-150809231152-lva1-app6891/85/consumer-Satisfaction-45-320.jpg)
![46
contentType=Article&hdAction=lnkhtml&contentId=881588&history=tr
ue>) [Viewed 4/4/09]
6. Kumar, Kaliyamoorthy, “Influence of Demographic Variables on
Marketing Strategies in the Competitive Scenario”, 2007
(http://www.emeraldinsight.com/Insight/viewContentItem.do;jsessionid=
2086527F0757A565F9A6CBAC8800F658?
contentType=Article&hdAction=lnkhtml&contentId=881588&history=tr
ue>) [Viewed 4/4/09]
7. Seth et, Etal, “Managing the Customer Perceived Service Quality for
Cellular Mobile Telephone: an Empirical Investigation”, 2008
(http://www.emeraldinsight.com/Insight/viewContentItem.do;jsessionid=
2086527F0757A565F9A6CBAC8800F658?
contentType=Book&hdAction=lnkhtml&contentId=1758667&history=tr
ue>) [Viewed 6/4/09]
8. Tecor, Jha, “Understanding Mobile Phone Usage Pattern among College-
Goers”, 2008
(http://www.emeraldinsight.com/Insight/viewContentItem.do;jsessionid=
2086527F0757A565F9A6CBAC8800F658?
contentType=Book&hdAction=lnkhtml&contentId=1760544&history=tr
ue>) [Viewed 7/4/09]
9. Bhatt, Andre, “A Study of Mobile Phone Usage Among the Post
Graduate Students”, 2008
10.Chris, Kambitsis, “Telecom advertising in print media”, 2003
Journal
• The Indian Telecom Industry, IIM Calutta, Vatsal Goyal, 2007](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/finalproject-150809231152-lva1-app6891/85/consumer-Satisfaction-46-320.jpg)



