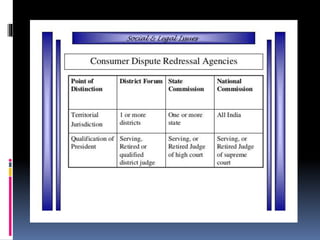
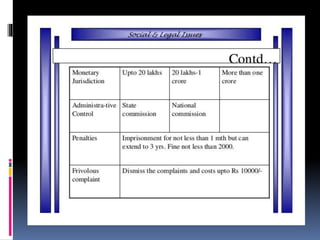
The Consumer Protection Act of 1986 was passed to protect consumer rights and welfare in India. It aims to establish consumer councils at the district, state, and national levels to address complaints related to defective goods, unfair trade practices, and deficient services. The Act defines a consumer as an individual who purchases goods or services for personal use rather than for manufacturing or resale. It gives consumers various rights such as the rights to safety, to be informed, to choose, to consumer education, and to redressal. Complaints can be filed by individual consumers, recognized consumer associations, groups of consumers with common interests, or government bodies.