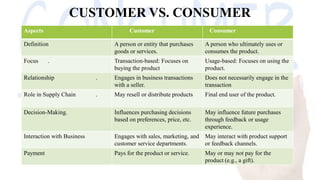
The document discusses consumer behavior, which involves how individuals or groups select and use goods and services to meet their needs, influenced by various factors including psychological and social elements. It highlights the importance of understanding consumer behavior for effective marketing strategies, product development, and enhancing customer satisfaction, while also exploring the consumer decision-making process and the concept of divestment. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of customer involvement in a company's business for better alignment with consumer needs and improving overall satisfaction.