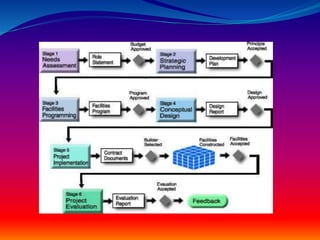
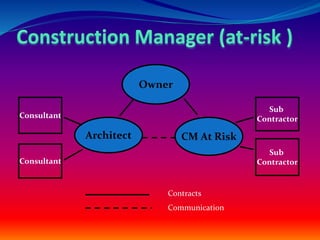
The document discusses construction management (CM) project delivery systems. It defines CM as planning, organizing, and overseeing construction project tasks. There are three main types of CM: agency CM, corporate CM, and CM at risk. CM at risk contracts in two stages - for conceptual design services and then to agree on a fixed price and schedule to complete construction. Benefits of CM at risk include innovation recommendations during design while the agency retains control, and the CM holds construction contracts to transfer performance risk. Potential downsides are excluding smaller contractors and difficulty for contractors managing resources without knowing task order details in advance.