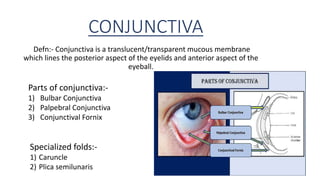
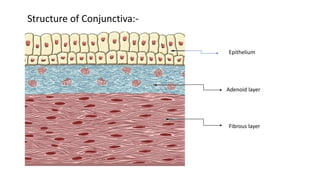
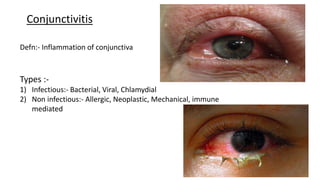
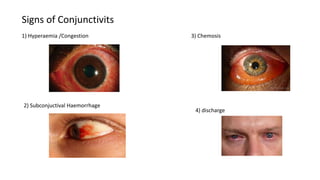
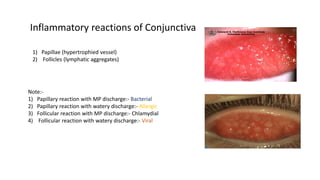
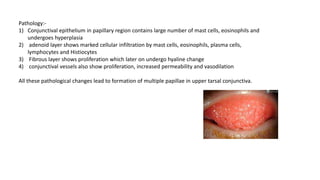
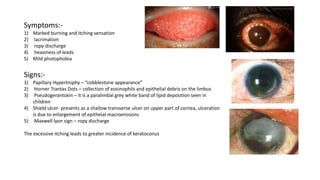
The conjunctiva is a mucous membrane that lines the eyelids and eyeball. It has three parts and specialized folds. Conjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva that can be infectious, caused by bacteria, viruses, or chlamydia, or non-infectious, such as allergic, neoplastic, or immune-mediated. Signs of conjunctivitis include redness, discharge, and swelling. Different types of conjunctivitis produce different inflammatory reactions involving papillae or follicles. Vernal keratoconjunctivitis is a recurrent, seasonal allergic inflammation seen mainly in boys, characterized by papillae on the conjunctiva and other signs like