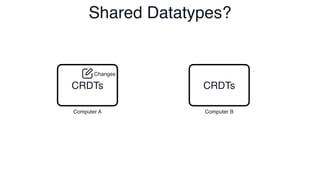
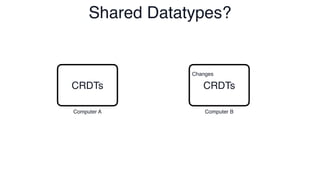
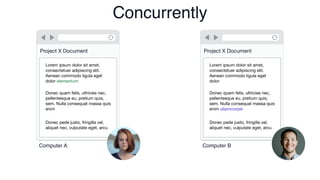
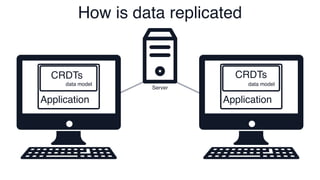
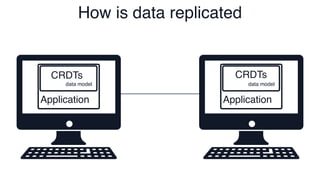
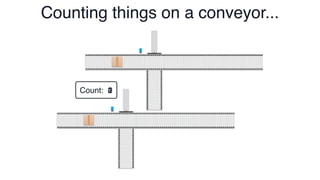
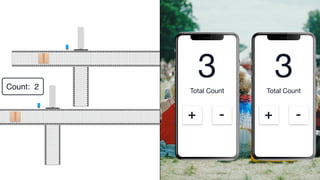
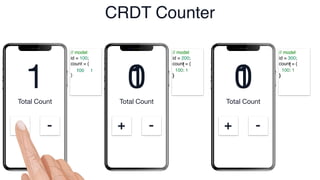
The document discusses Conflict-Free Replicated Data Types (CRDTs), which allow for shared mutable data across multiple users without conflicts. It explains that CRDTs define the shape of shared data models and use metadata to merge concurrent changes without conflicts. A key example shown is a CRDT counter that can be incremented independently by multiple users and still eventually converge to the same count. The document argues that CRDTs enable better collaborative software by making it easier to build applications where data can be edited concurrently and asynchronously without a central server.