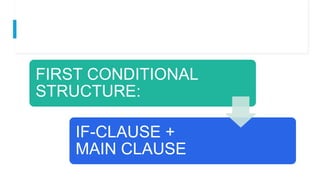
The document discusses the first conditional, which refers to possible future events that are likely or probable to happen. It has two parts: the if-clause uses a present tense verb, and the main clause uses a future tense verb or modal to indicate the result or consequence. Examples are provided like "If you don't disturb me, I will have finished in an hour" and it can also be used with words like "unless, as long as, as soon as, or in case" instead of just "if". The first conditional expresses a likely connection between a present situation and a probable future result.