This document outlines the forms and uses of four types of conditional sentences in English:
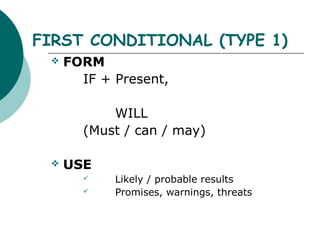
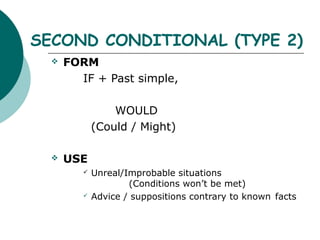
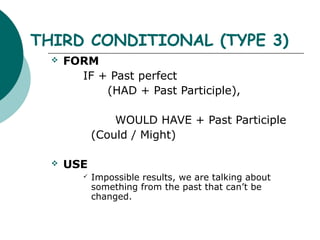
Type 0/universal conditionals use the present tense and are used for true facts or instructions. Type 1 conditionals use "if + present" and "will" to describe likely or probable results. Type 2 conditionals use "if + past" and "would" for unreal or improbable situations. Type 3 conditionals use "if + past perfect" and "would have" to describe impossible past results that cannot be changed. The order of clauses can be reversed and "unless" can be substituted for "if not".