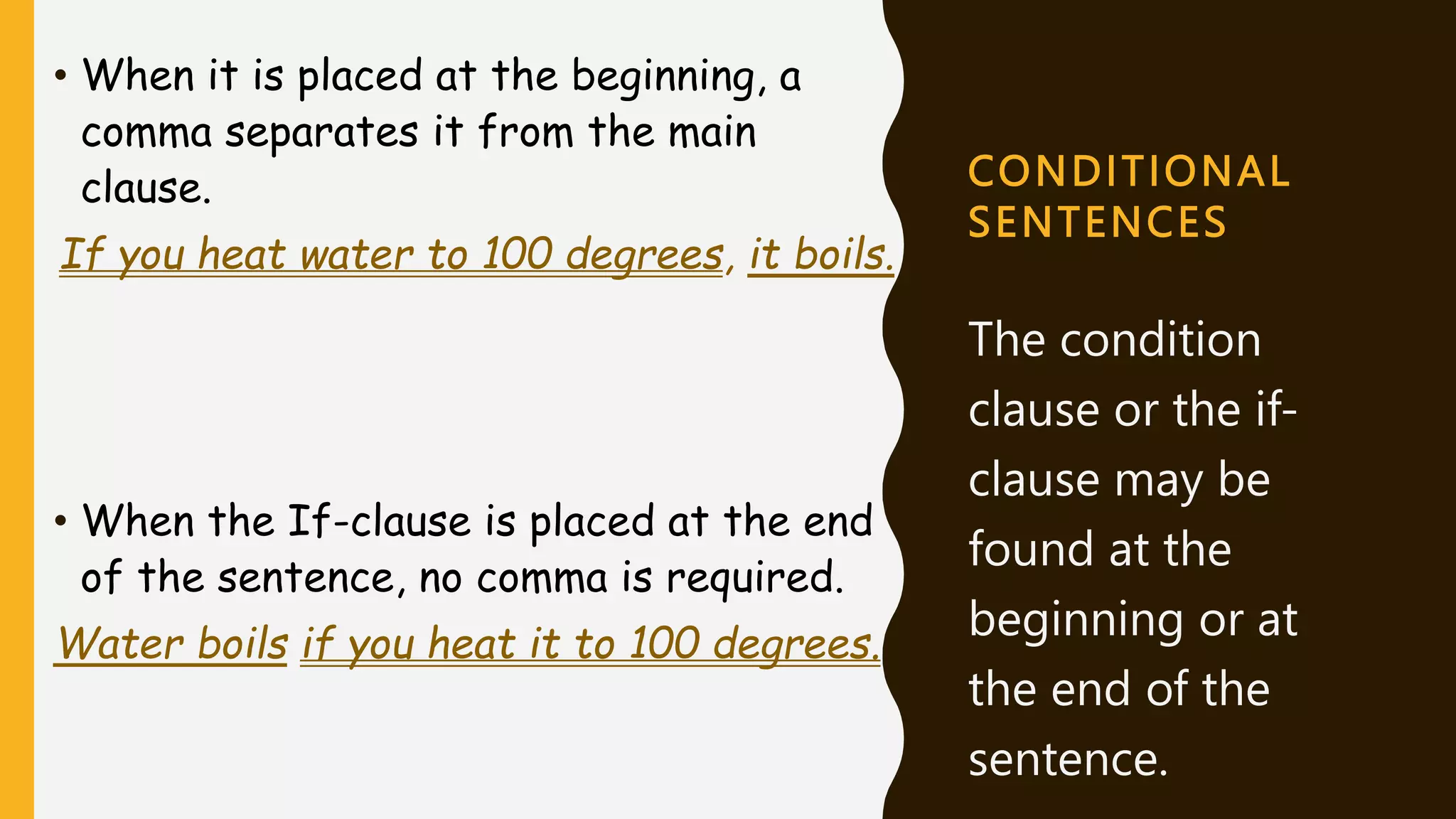
The document discusses different types of conditional sentences. It explains that conditional sentences contain two clauses: the if-clause which states a condition, and the main clause which states a result. There are four types of conditional sentences - zero, first, second and third conditionals. The zero conditional expresses facts, the first conditional possible future situations, the second conditional unlikely future situations, and the third conditional imaginary past situations. The document provides examples of the structure and uses of each type of conditional sentence.




























![0
nal
sults are
fic facts and
of a verb] +
se of a verb].
tional
ges.
hey cry.
x hydrogen
1
NAL
ons
ure.
verb] +
of the
oes not
ters
nt, it
2
AL
s in
ing
hing
nd
erb]
the
y
he
if
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conditionalsentences-230903111241-d7c73dd6/75/CONDITIONAL-SENTENCES-pptx-30-2048.jpg)

![REAL CONDITIONALS UNREAL CONDITIONALS
ZERO CONDITIONAL
-used when the results are always true,
like a scientific facts and general truths.
SECOND CONDITIONAL
-used to: (1) talk about conditions in
the future that are probably not going
to happen; and (2) talk about
something in the present, which is
impossible and imaginary.
[If + simple past tense of a verb,] +
[would + base form of a verb]
FIRST CONDITIONAL
-used to talk about conditions that
might happen in the future.
[If + present tense of a verb,] + [will +
base form of a verb]
THIRD CONDITIONAL
-often used when we regret something
or imagine a past unreal situation; a
past condition
that did not happen.
[If + past perfect tense of a verb,] +
[would + have + past participle
form of a verb]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conditionalsentences-230903111241-d7c73dd6/75/CONDITIONAL-SENTENCES-pptx-32-2048.jpg)
