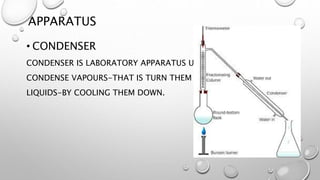
Condensation is the change of water from vapor to liquid. It occurs when water vapor condenses, such as from visible breath on a cold day or morning dews on grass. Condensation can be observed using a condenser, which cools vapors until they condense into liquids. An experiment demonstrates condensation by placing a glass over a tub of boiling water covered with a plastic wrap and ice. Vapors from the tub hit the cold ice and condense into liquid droplets inside the plastic wrap, which collect in the glass to produce purified water. Factors like temperature, humidity, and density affect condensation rates.