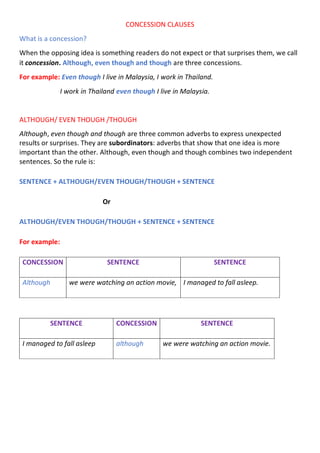
This document discusses concession clauses, which are used to express unexpected or surprising information. It defines concession as an opposing idea that readers do not expect. Common concession words include although, even though, and though. These words combine two independent clauses, with the concession clause being less important. The document also discusses despite the fact that/in spite of the fact that as concessions, and contrasts their grammar with despite/in spite of. Several examples are provided and exercises ask the reader to rephrase sentences using concession words and identify concession words in sentences.