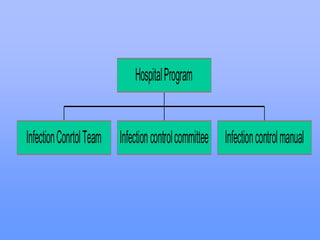
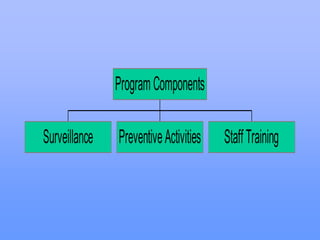
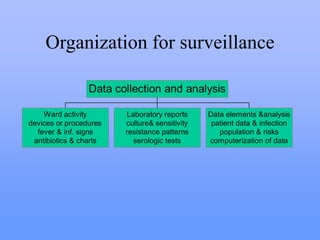
This document discusses key concepts of infection control including definitions of community-acquired infections and nosocomial (hospital-acquired) infections. It notes that nosocomial infections occur in 5-8% of hospitalized patients and are a major cause of increased costs, length of stay, and mortality. The major sites of nosocomial infections are urinary tract, surgical wounds, and lower respiratory infections. Prevention requires a multidisciplinary approach including surveillance, standard precautions like hand hygiene and barrier use, environmental controls, and staff education. The goal is to reduce infection rates and improve patient safety and outcomes.