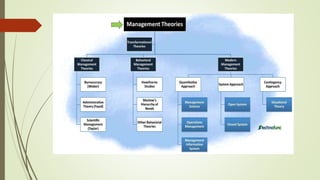
The document discusses the concept of management and management theories. It provides definitions of management from various theorists that describe management as a process of achieving goals effectively and efficiently. It also outlines some key characteristics of management such as it being goal-oriented, all-pervasive, and multidimensional. Popular management theories are described, including scientific management theory, systems management theory, and contingency management theory. The document also discusses forces like social, economic, and political forces that have influenced the evolution of management theories.