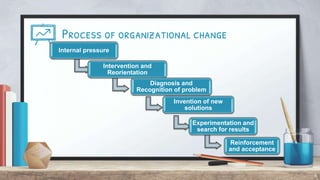
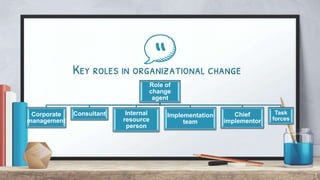
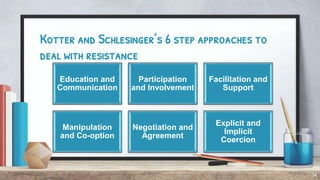
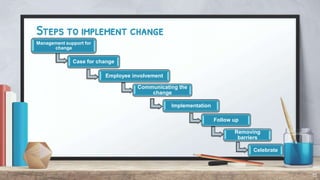
Organizational change can be caused by internal or external forces. It affects structures, procedures, and social structures, causing resistance from people accustomed to the status quo. Change management is defined as continuously aligning an organization with the marketplace more responsively than competitors. There are three types of change - adaptive, innovative, and radically innovative. The change process involves recognition of problems, invention of solutions, experimentation, and reinforcement. Key roles in change include change agents, corporate management, consultants, implementation teams, and task forces. Culture and internal/external factors also influence change management practices.