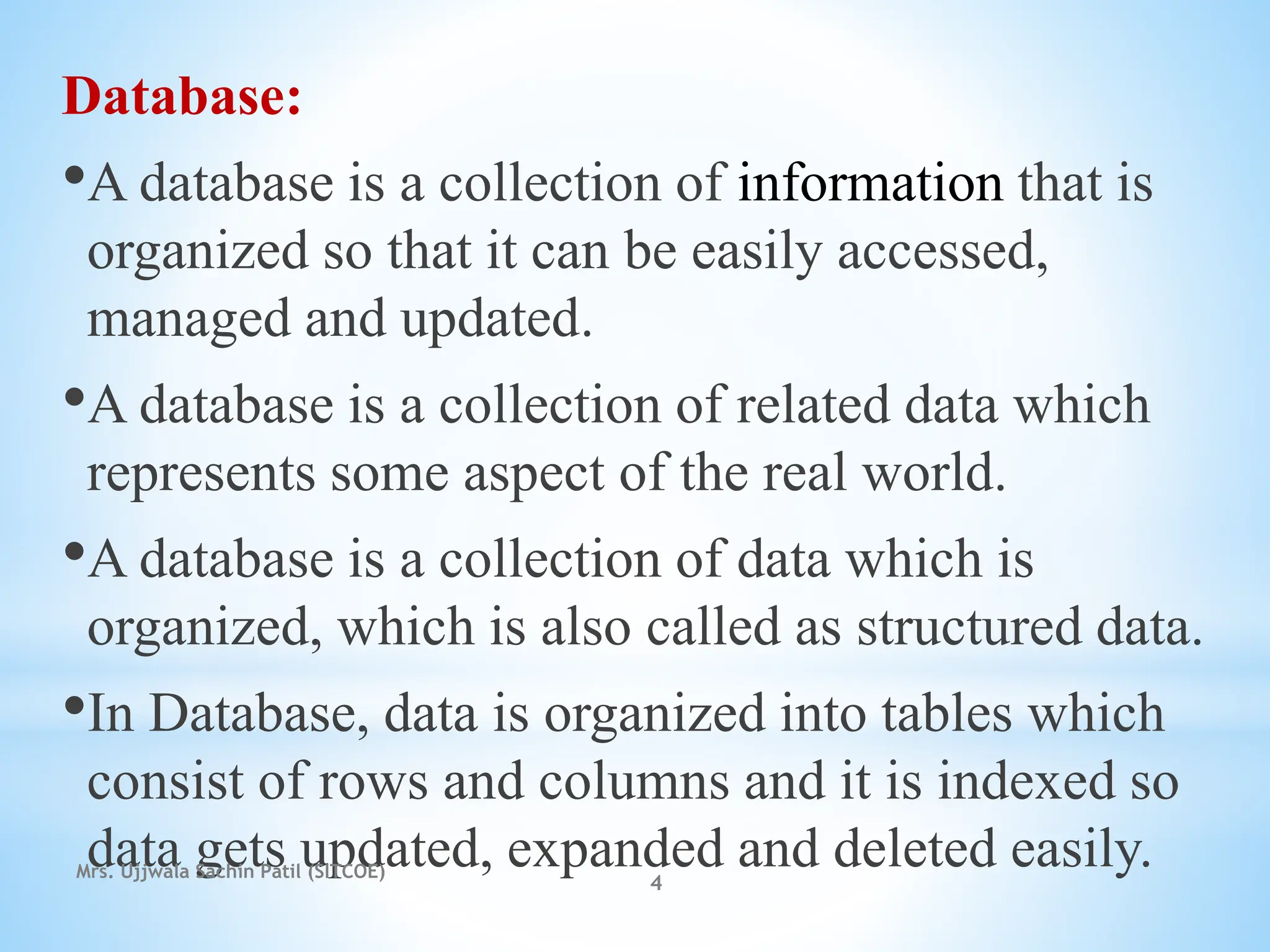
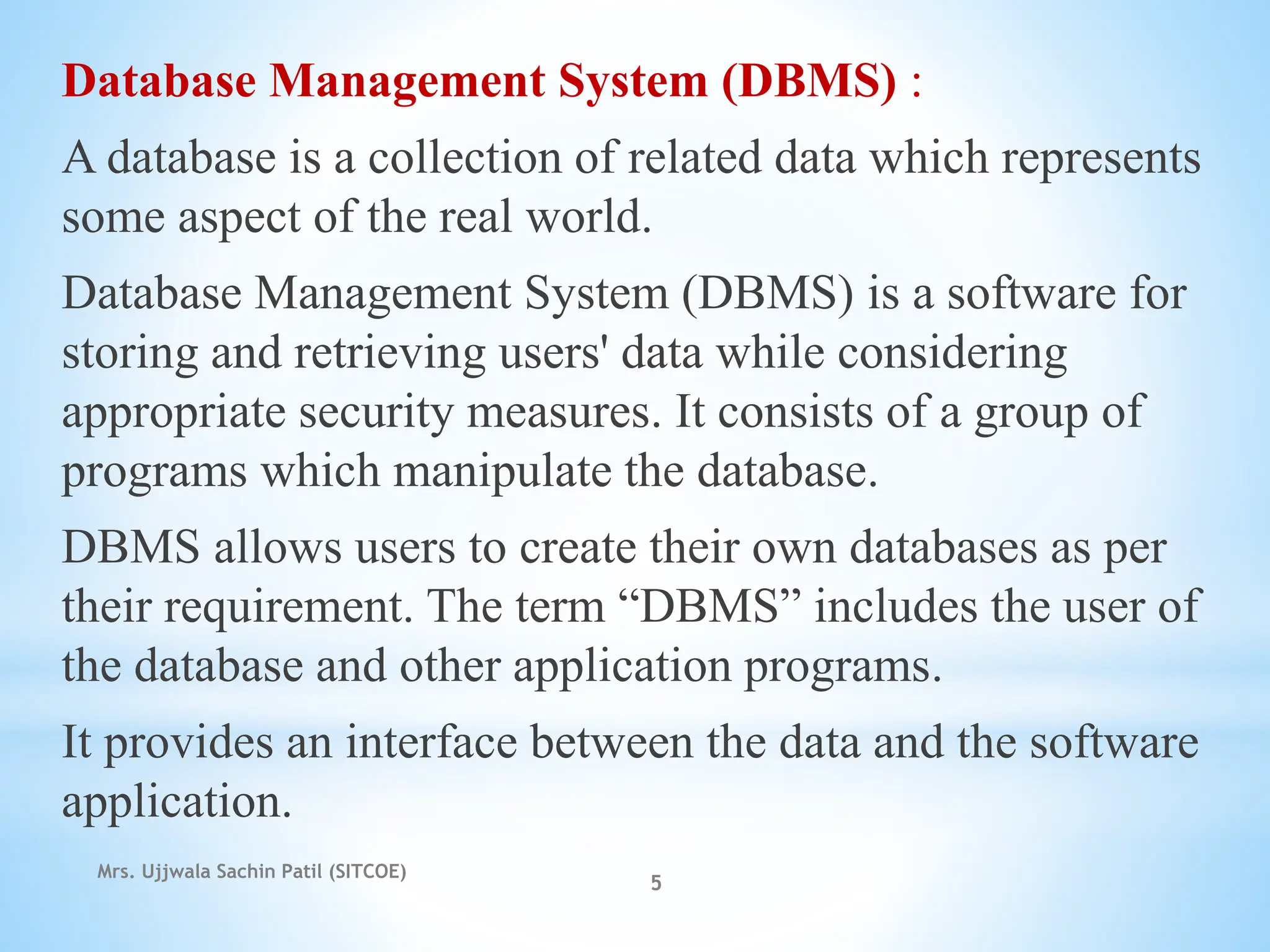
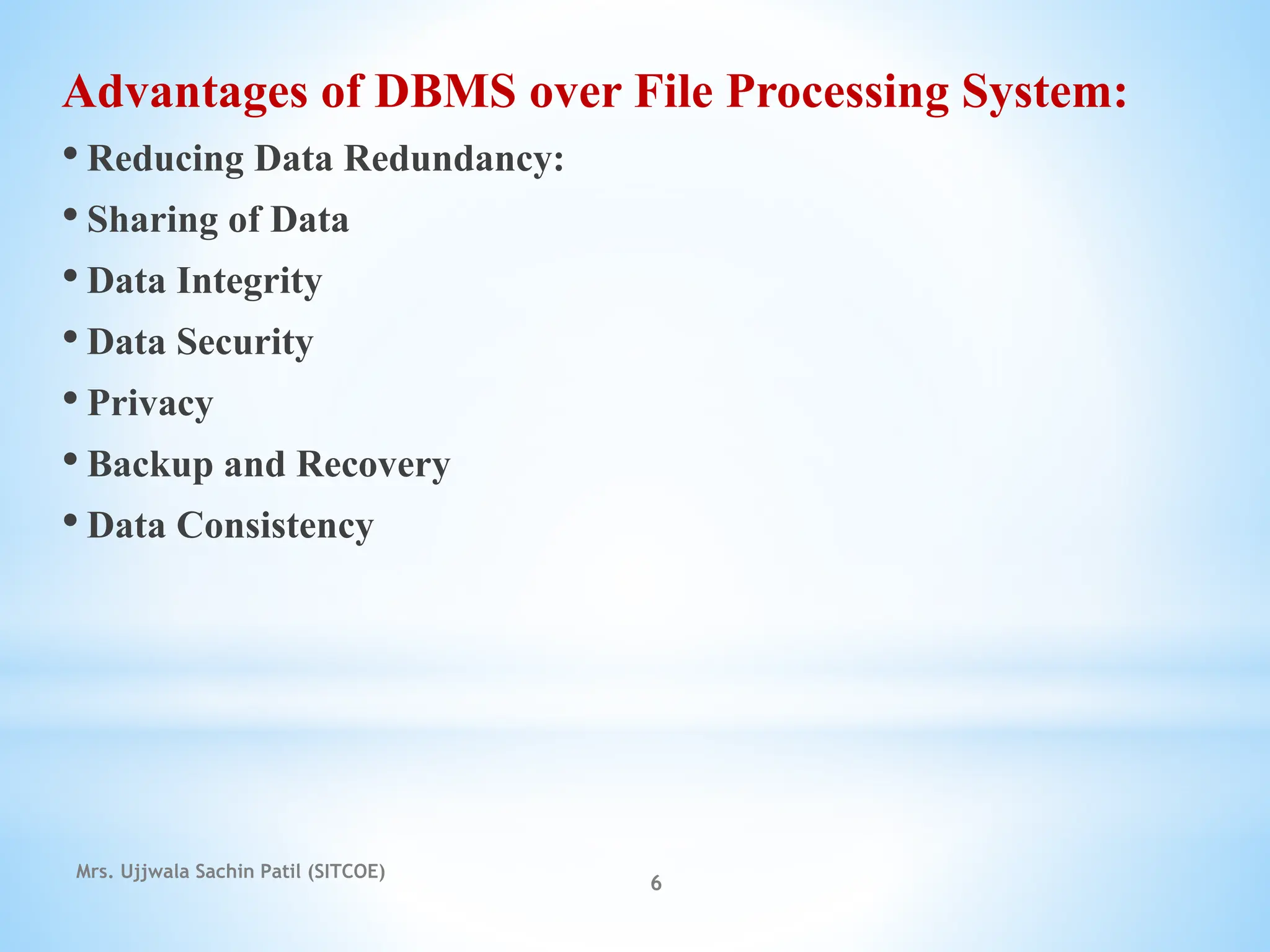
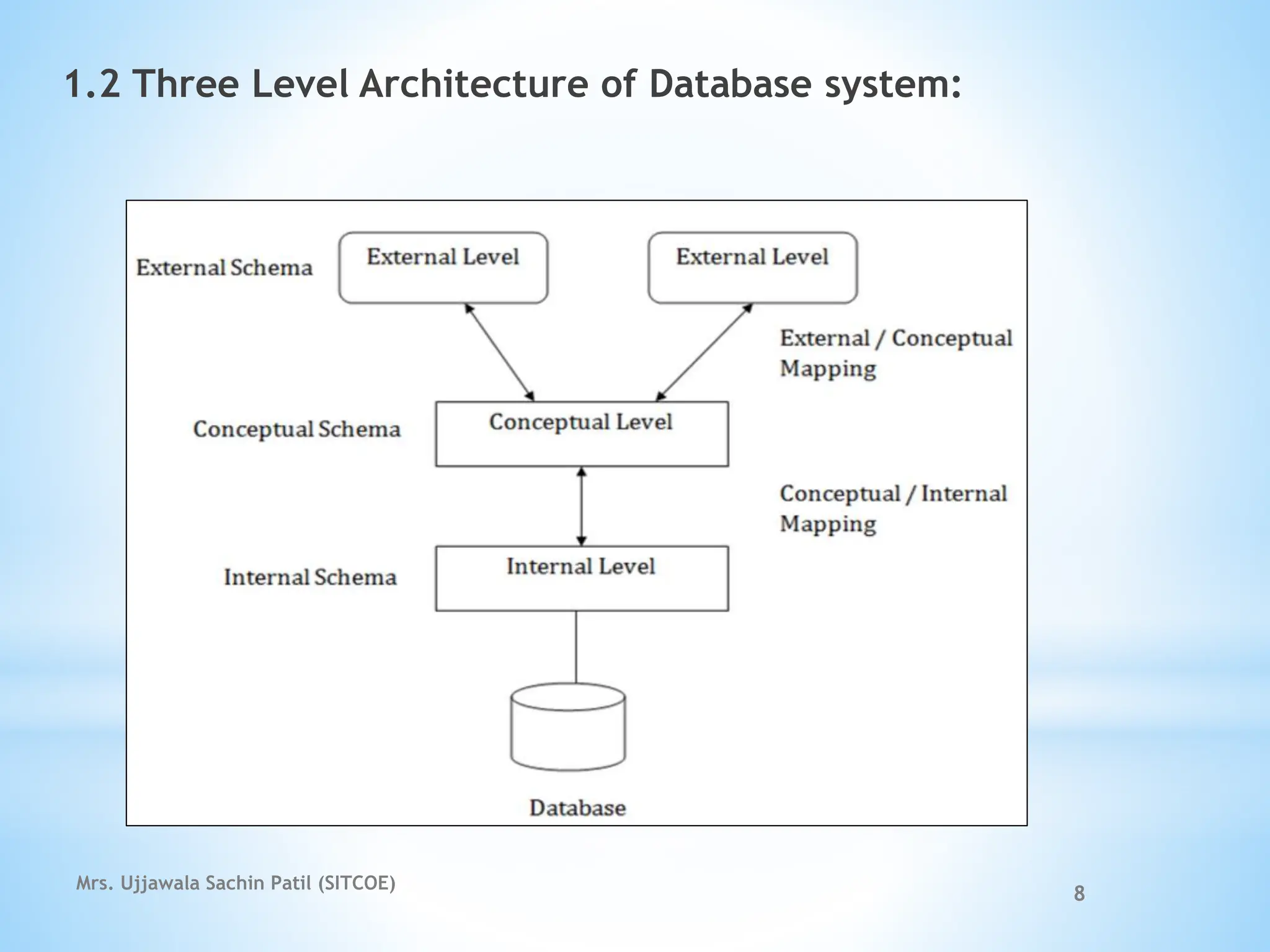
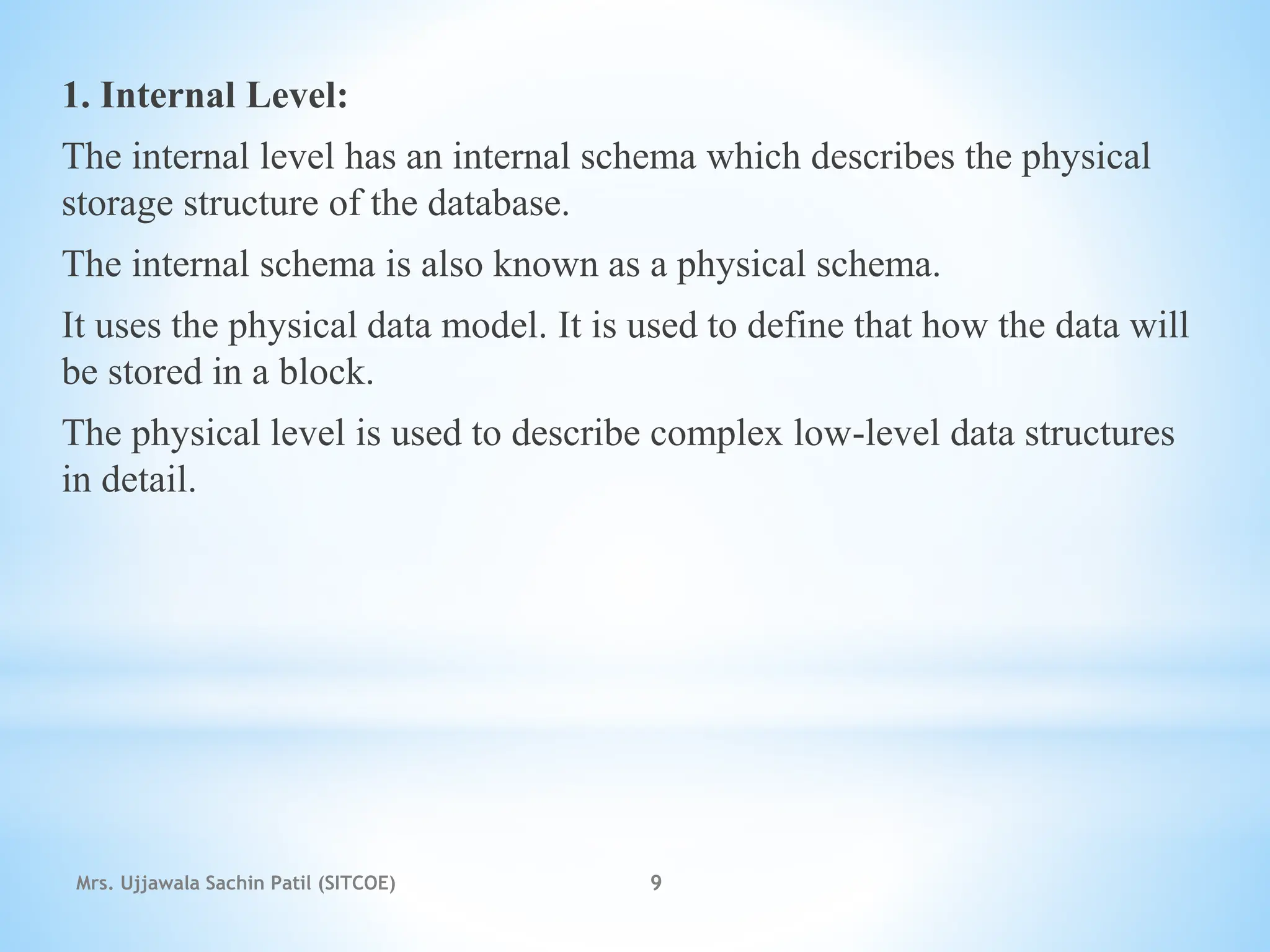
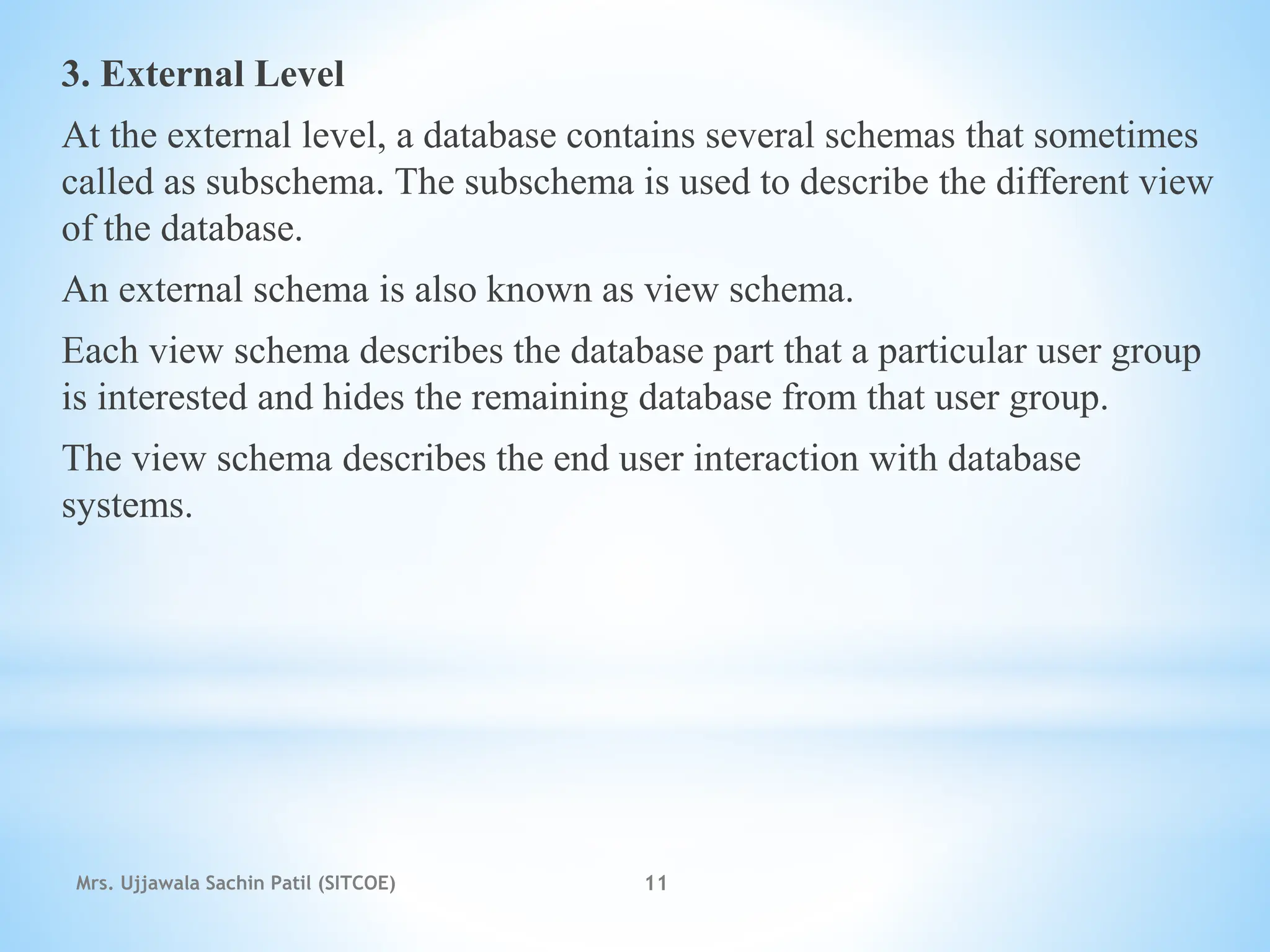
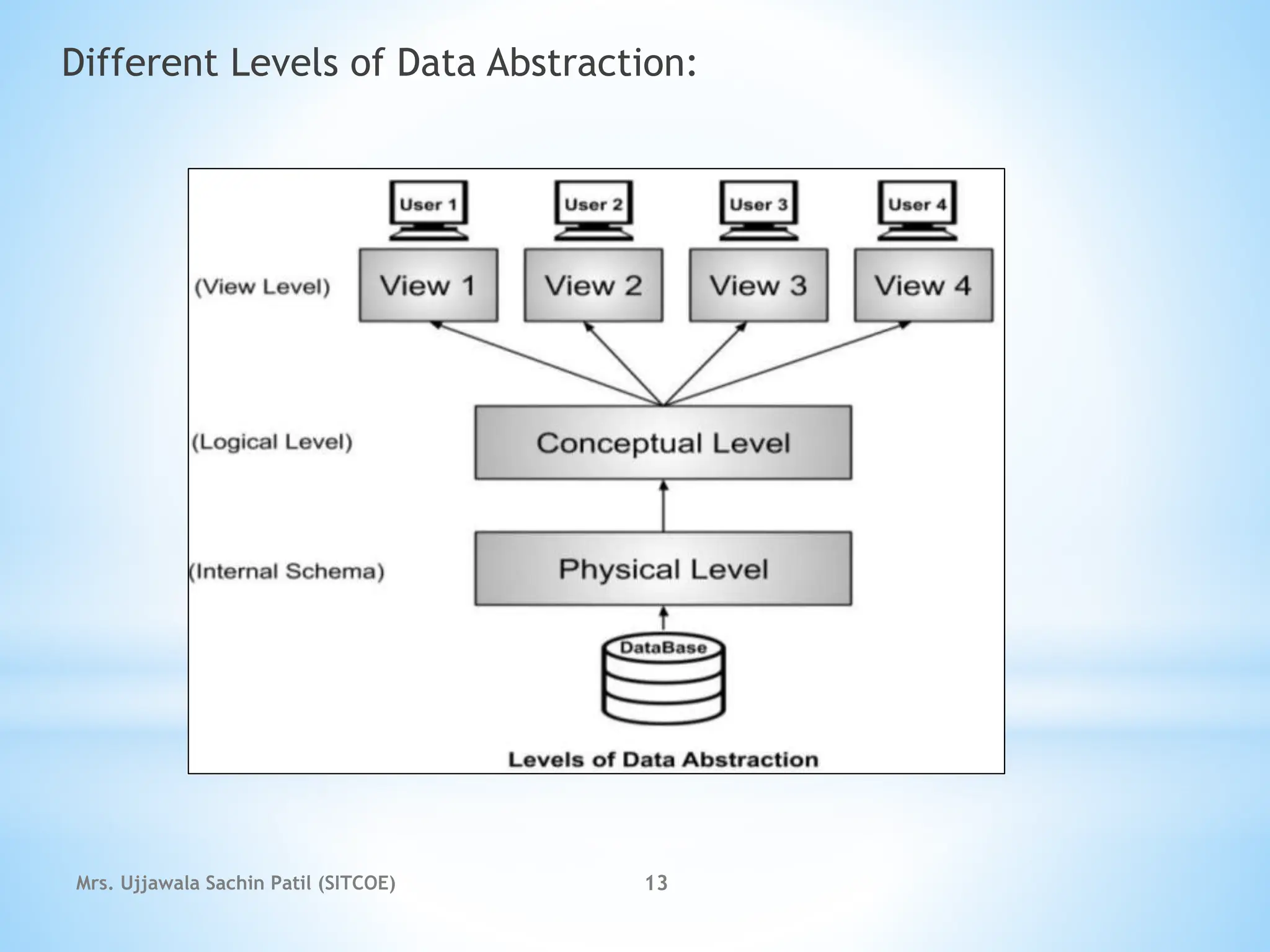
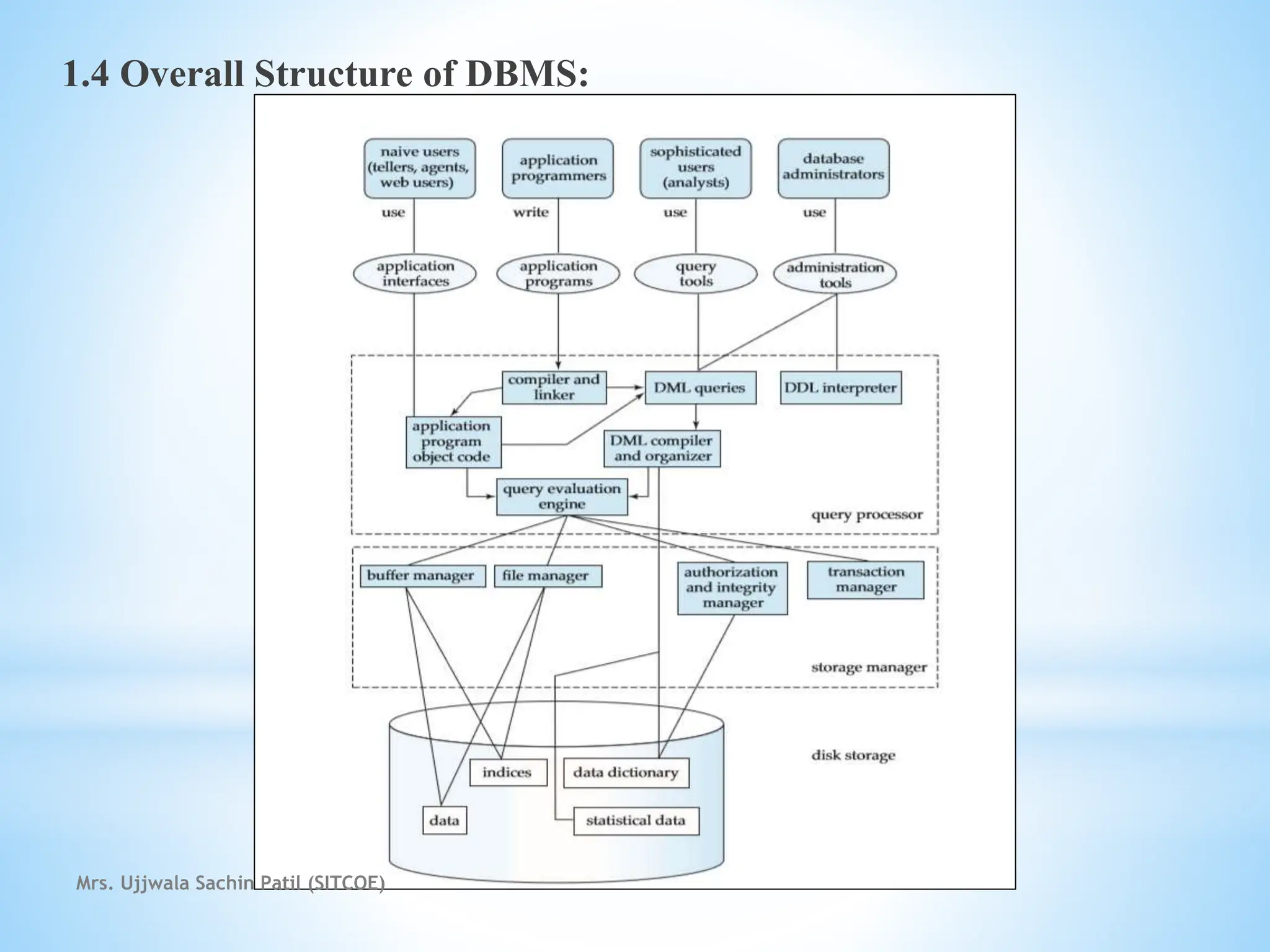
The document outlines fundamental concepts of database systems, including data definitions, organizational structures, and the advantages of database management systems (DBMS) over traditional file processing. It describes the three-level architecture of databases: internal, conceptual, and external, along with data abstraction levels and data independence. Additionally, it highlights applications of database systems in various sectors such as banking, telecommunications, and e-commerce.