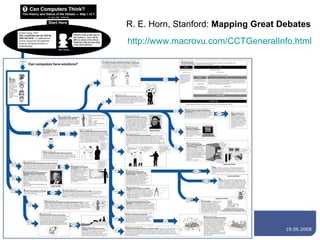
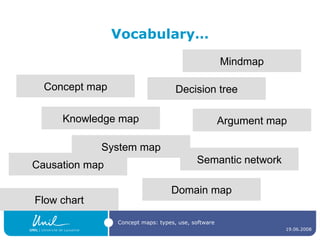
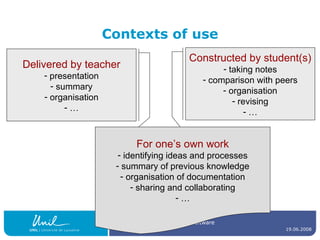
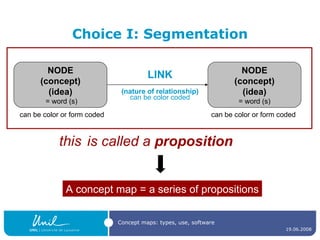
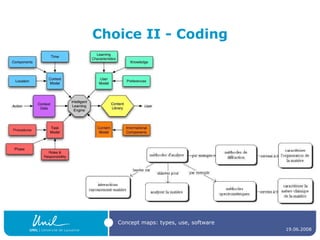
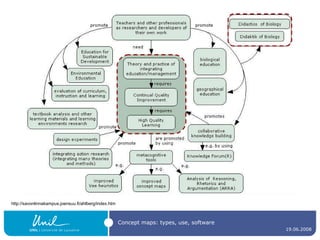
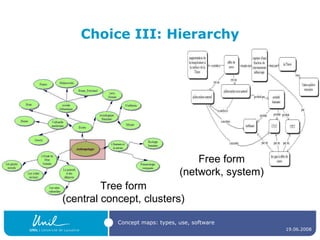
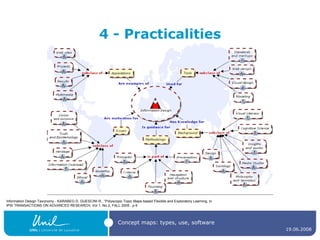
The document discusses concept maps, their types, uses, and the software available for creating them. It emphasizes the importance of representing knowledge for improved understanding, learning, and cognitive processing, outlining practical steps for building effective concept maps. Various software options for concept mapping and mind mapping are also reviewed, highlighting tools suited for individual and collaborative use.








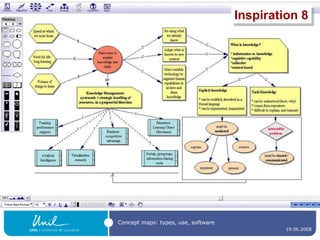
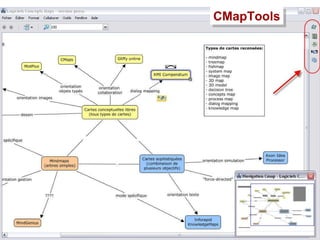
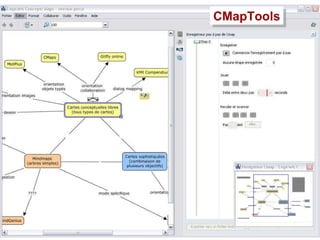
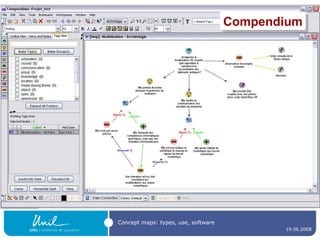
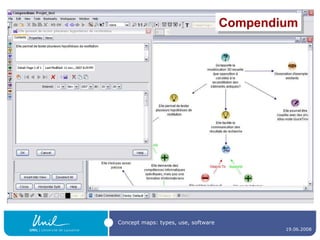
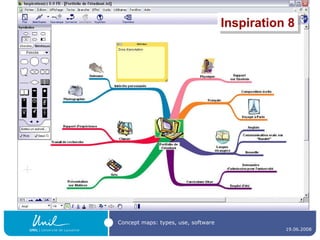
![Concept map editors A concept map editor , like [Commercial] Inspiration ( http://www.inspiration.com/ ) [multiplatform freeware] CmapTools ( http:// cmap.ihmc.us / ) Compendium ( http:// www.compendiuminstitute.org / ) Vue ( http:// vue.uit.tufts.edu / ) [GNU GPL-licenced] Conzilla ( http:// www.conzilla.org / ) in Java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipconceptmaps-090904120658-phpapp01/85/Concept-Maps-Types-uses-software-20-320.jpg)
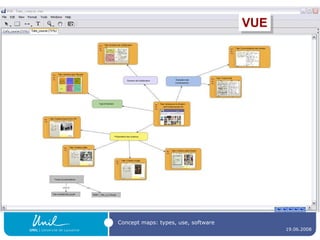
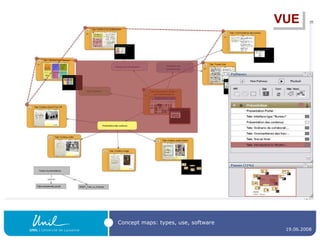

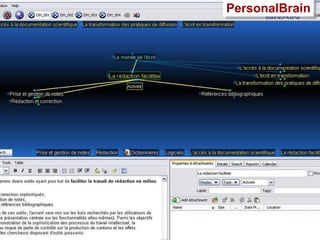
![Mind mapping software Freeware , like FreeMind ( http:// freemind.sourceforge.net/wiki/index.php/Main_Page ) Thinkgraph ( http:// www.thinkgraph.com ) VYM - View Your Mind ( http://www.insilmaril.de/vym ) or Kdissert ( http://freehackers.org/~tnagy/kdissert/ ) [Linux only] Commercial software , like Inspiration ( http:// www.inspiration.com / ) MindManager ( http:// www.mindjet.com / ) MindGenius ( http:// www.mindgenius.com / ) Visual Mind ( http://www.visual-mind.com / ) MindMapper ( http:// www.mindmapperusa.com / )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipconceptmaps-090904120658-phpapp01/85/Concept-Maps-Types-uses-software-30-320.jpg)

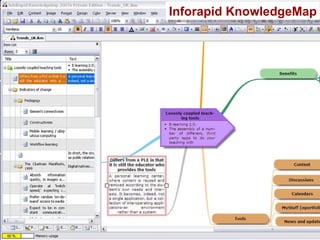
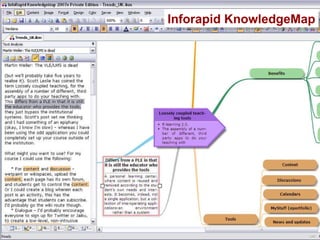

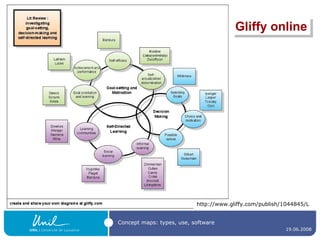
![Presentation software Microsoft PowerPoint OpenOffice Impress … and others, depending on your objective ! [On the next slide, an example that could not easily be achieved with the software mentioned today]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipconceptmaps-090904120658-phpapp01/85/Concept-Maps-Types-uses-software-37-320.jpg)