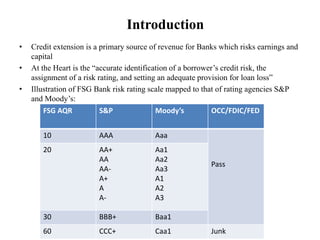
This document discusses credit concentrations and the importance of identifying, monitoring, measuring, and controlling related risks. It provides examples of how loans can be grouped into pools based on similar risk characteristics and aggregated if certain conditions are met. The document also outlines house and portfolio limits established by the bank's board to control concentration risk and discusses the value of stress testing and robust management information systems in mitigating risk.