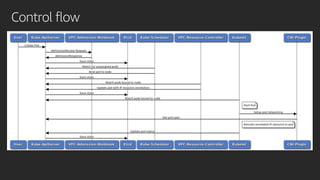
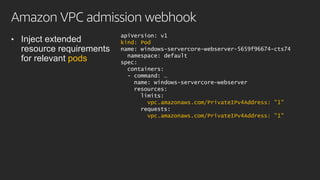
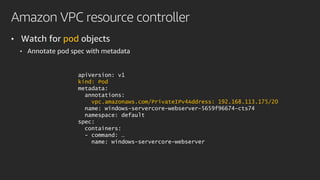
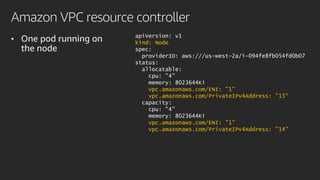
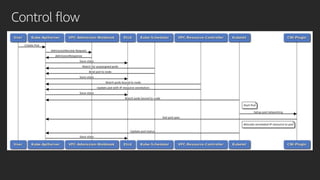
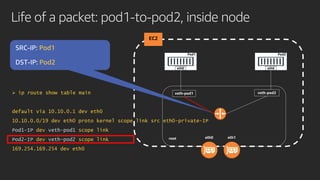
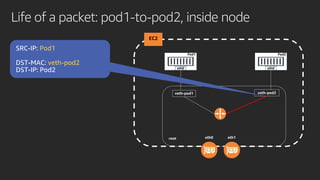
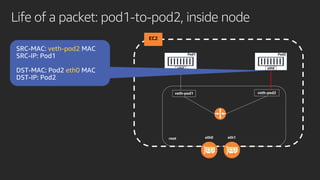
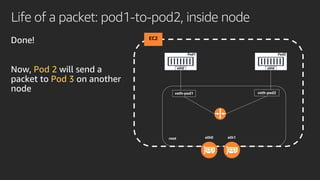
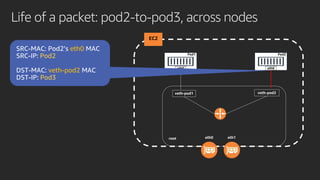
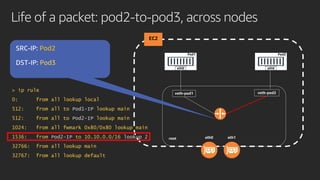
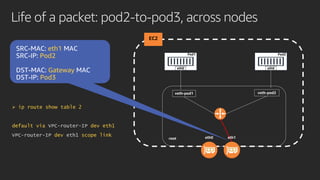
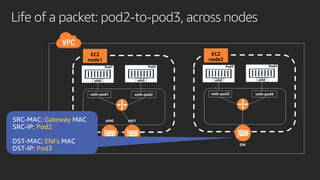
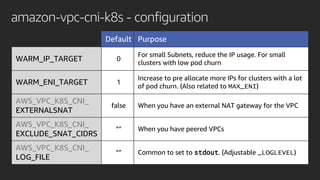
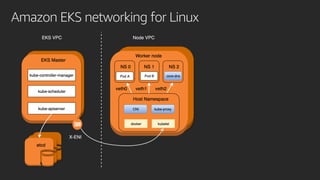
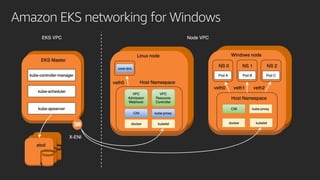
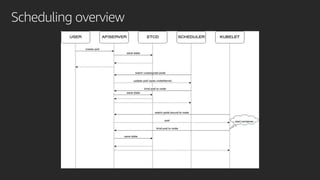
The document discusses advanced network resource management within Amazon EKS, focusing on the AWS Container Network Interface (CNI) solutions, architecture, and configuration details. It covers the benefits and challenges of the Amazon VPC CNI, recent changes, and future enhancements in networking capabilities. Additionally, it highlights the role of the Amazon VPC Resource Controller in managing network resources and optimizing scheduling processes in Kubernetes environments.





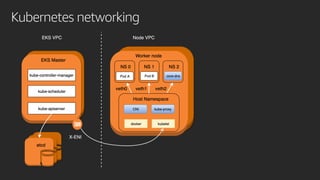




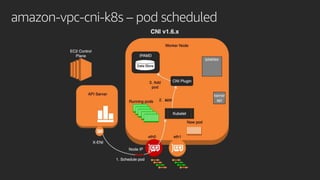
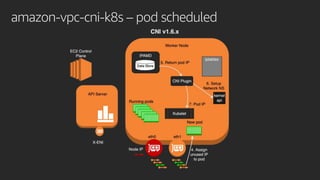
![amazon-vpc-cni-k8s
• aws-cni binary plugin
• Called by kubelet
• Communicates with ipamd using gRPC
• /opt/cni/bin/aws-cni
• IP address management daemon
• Call EC2 control plane
• Add ENIs and IPs to a cache
• Setup host networking
• Config file
• /etc/cni/net.d/10-aws.conflist
{
"cniVersion": "0.3.1",
"name": "aws-cni",
"plugins": [
{
"name": "aws-cni",
"type": "aws-cni",
"vethPrefix": ”eni"
},
{
"type": "portmap",
"capabilities":
{"portMappings": true},
"snat": true
}
]
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/con411-r-advancednetworkresourcemanagementonamazoneks-191209174958/85/CON411-R-Advanced-network-resource-management-on-Amazon-EKS-11-320.jpg)
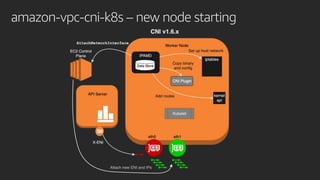











![Amazon VPC resource controller
type Provider interface {
GetResourceName() string
GetDesiredWarmPoolSize() (int, int)
InitResourcePool(node Node) (*Pool, error)
CreateResource(node Node, quantity int) (resourceIDs []string, err error)
DeleteResource(node Node, resourceID string) error
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/con411-r-advancednetworkresourcemanagementonamazoneks-191209174958/85/CON411-R-Advanced-network-resource-management-on-Amazon-EKS-40-320.jpg)