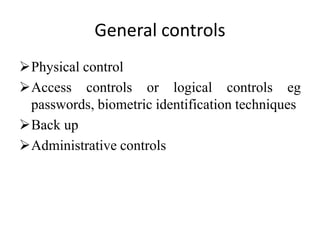
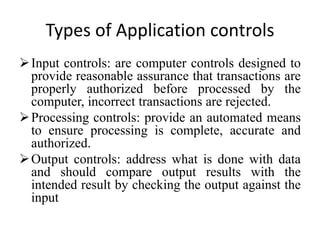
This document discusses computer system security and control. It outlines the objectives of information security as confidentiality, data integrity, and availability. It also describes various types of information security such as application security, cloud security, cryptography, and infrastructure security. Reasons why computer systems are vulnerable include increased access, disgruntled employees, complexity, cyber crimes, complacent management, and natural disasters. Controls to enhance security involve physical controls, access controls, backups, and administrative procedures.