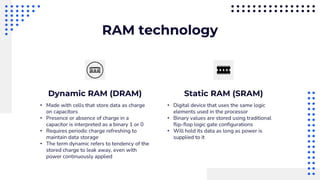
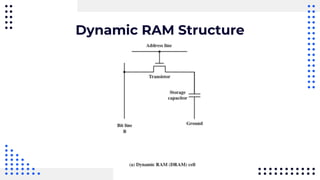
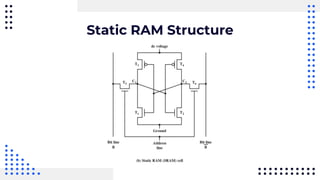
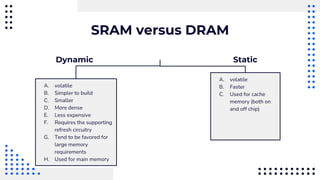
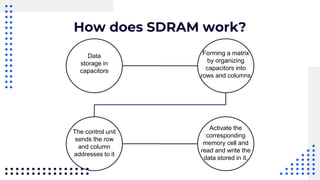
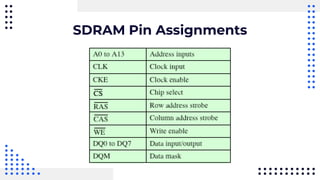
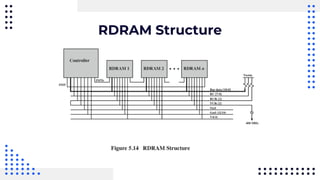
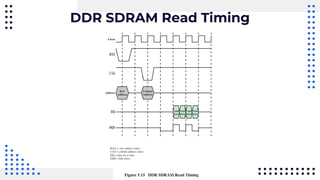
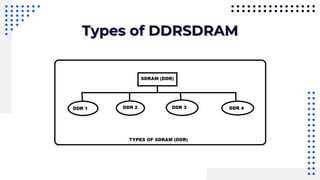
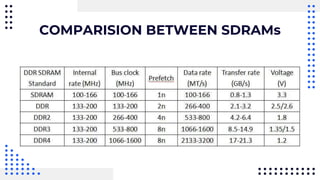
This document summarizes different types of internal memory technologies. It discusses static RAM (SRAM) which retains data as long as power is supplied but is more expensive and less dense than dynamic RAM (DRAM) which requires periodic refreshing. SDRAM was developed to synchronize with the CPU clock and transfer data without wait states. Later, RDRAM and DDR SDRAM were created to provide faster transfer rates by sending data over multiple wires or on both clock cycle edges. Newer DDR standards like DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4 provide lower voltages and faster speeds to interface with modern processors.