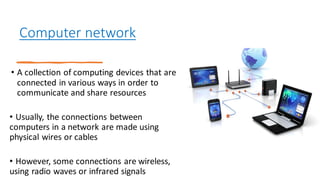
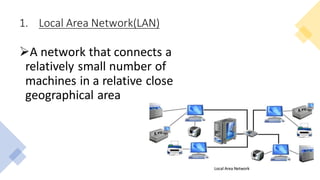
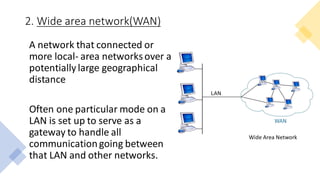
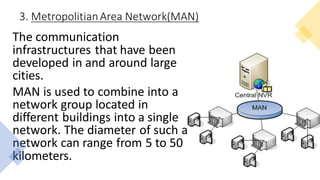
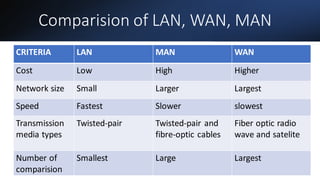
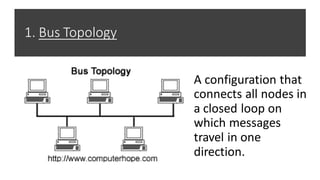
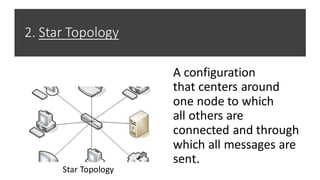
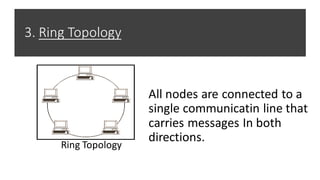
This document provides an overview of computer networks, including definitions of key terms and comparisons of different network types. It begins by defining a computer network as a collection of connected computing devices that communicate and share resources. It then describes local area networks (LANs) as connecting machines in a small geographical area, wide area networks (WANs) as connecting LANs over large distances, and metropolitan area networks (MANs) as connecting groups in different buildings within a city. The document compares LANs, WANs and MANs based on cost, size, speed and transmission media. It also outlines three common network topologies: bus, star and ring. In conclusion, it states that computer networks are used for sharing