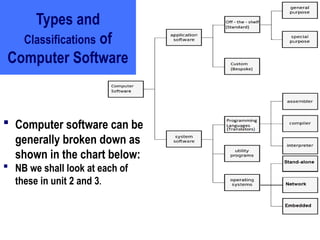
The document outlines the principles of computer software, focusing on the distinction between system software and application software. It details the characteristics of effective software, factors to consider before obtaining software, and the needs of both consumers and producers. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of usability, reliability, and adaptability in software design.