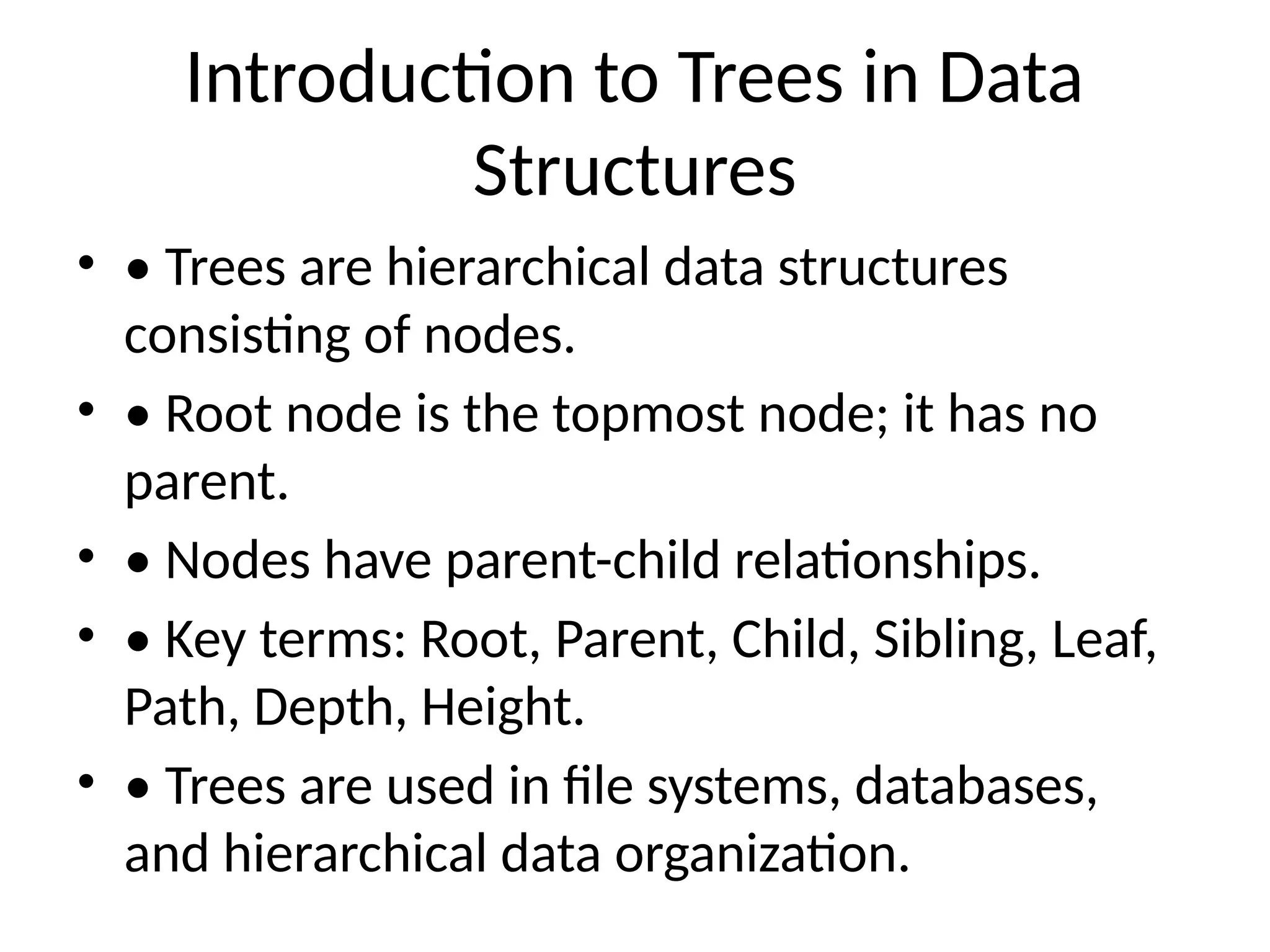
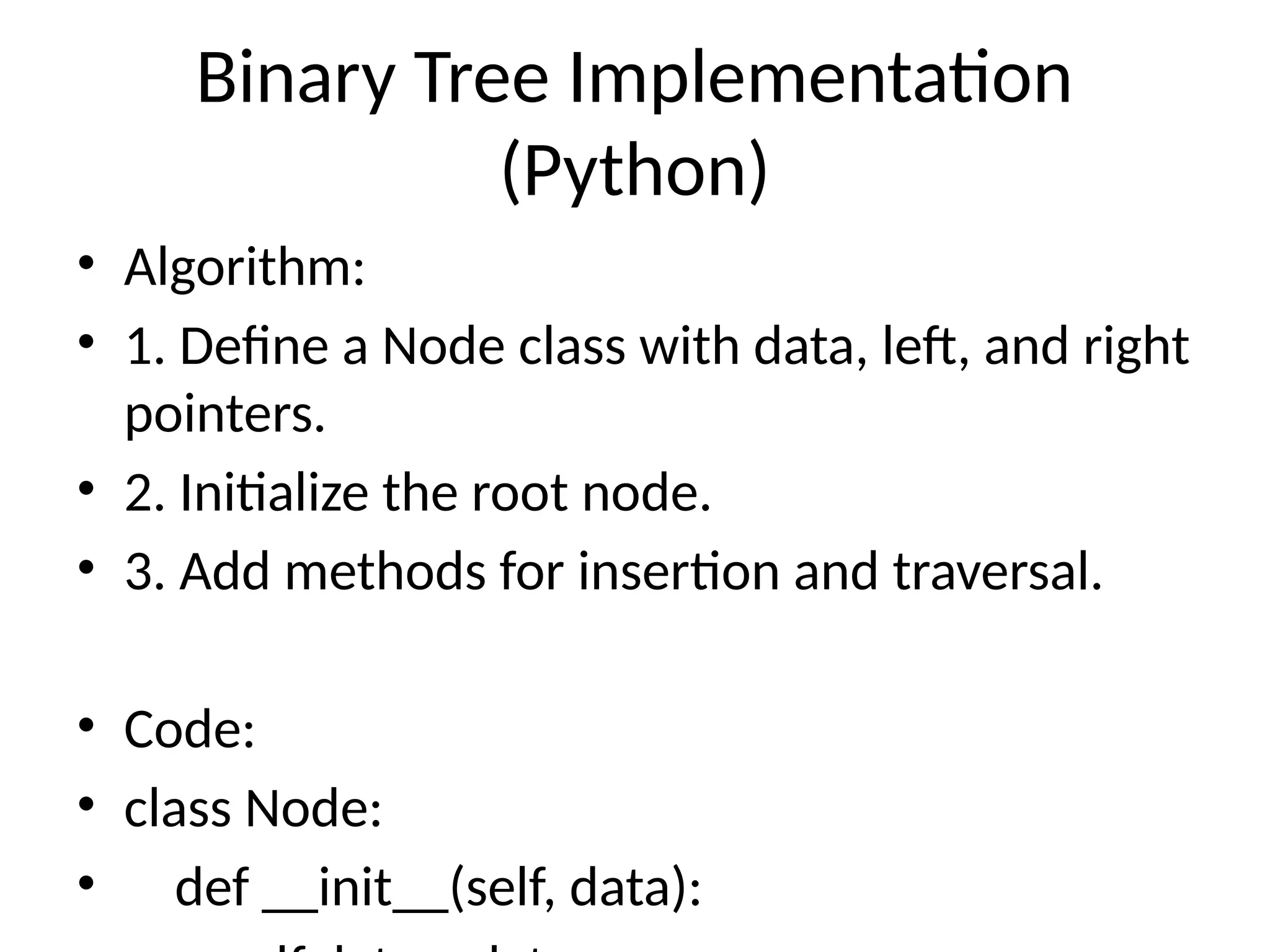
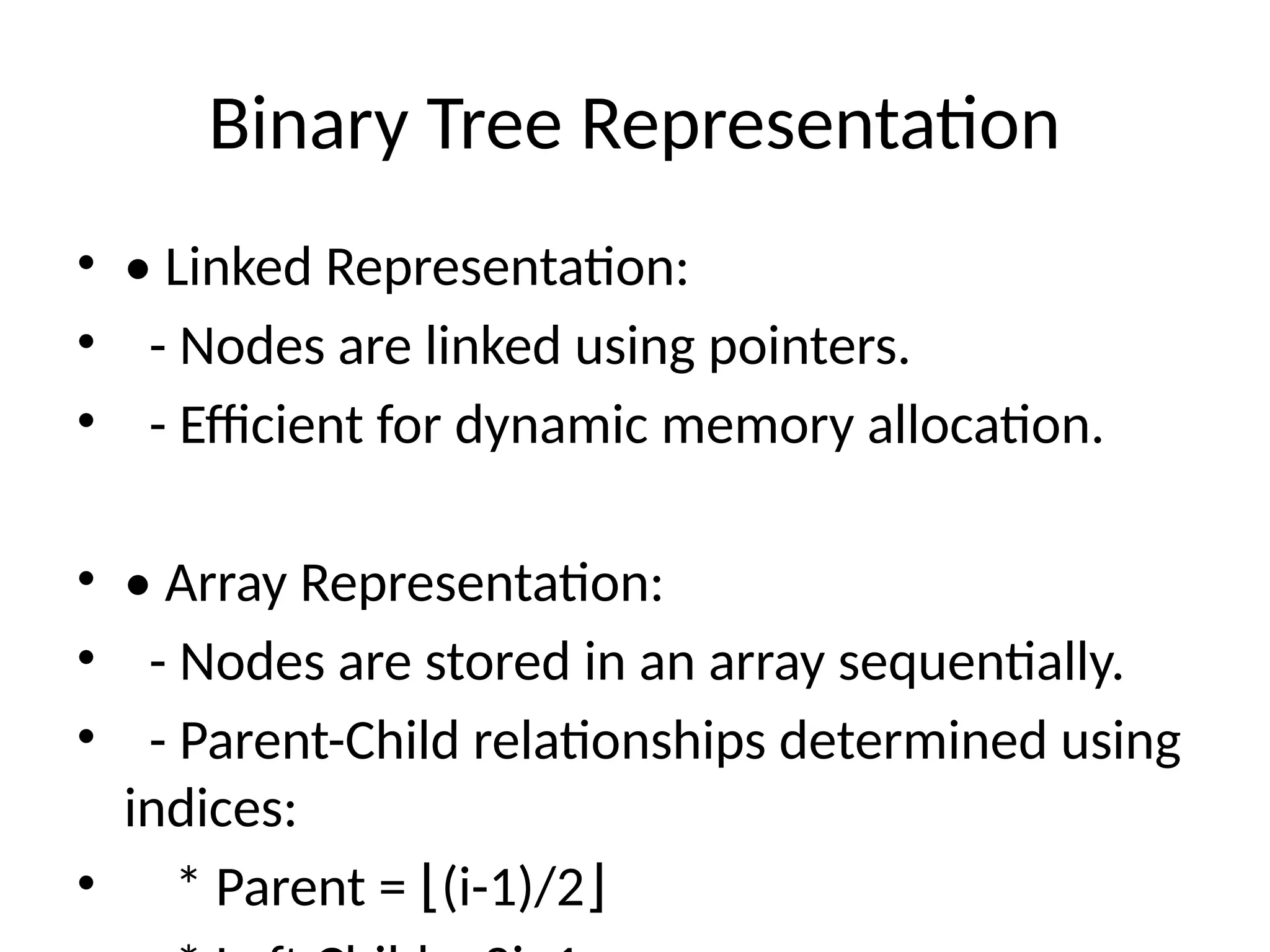
The document provides an introduction to trees in data structures, emphasizing their hierarchical nature and key terms associated with them. It details binary trees, including their properties, types, and implementations in Python, as well as various tree traversal methods. The explanation includes both linked and array representations of binary trees and offers Python code snippets for traversal techniques.