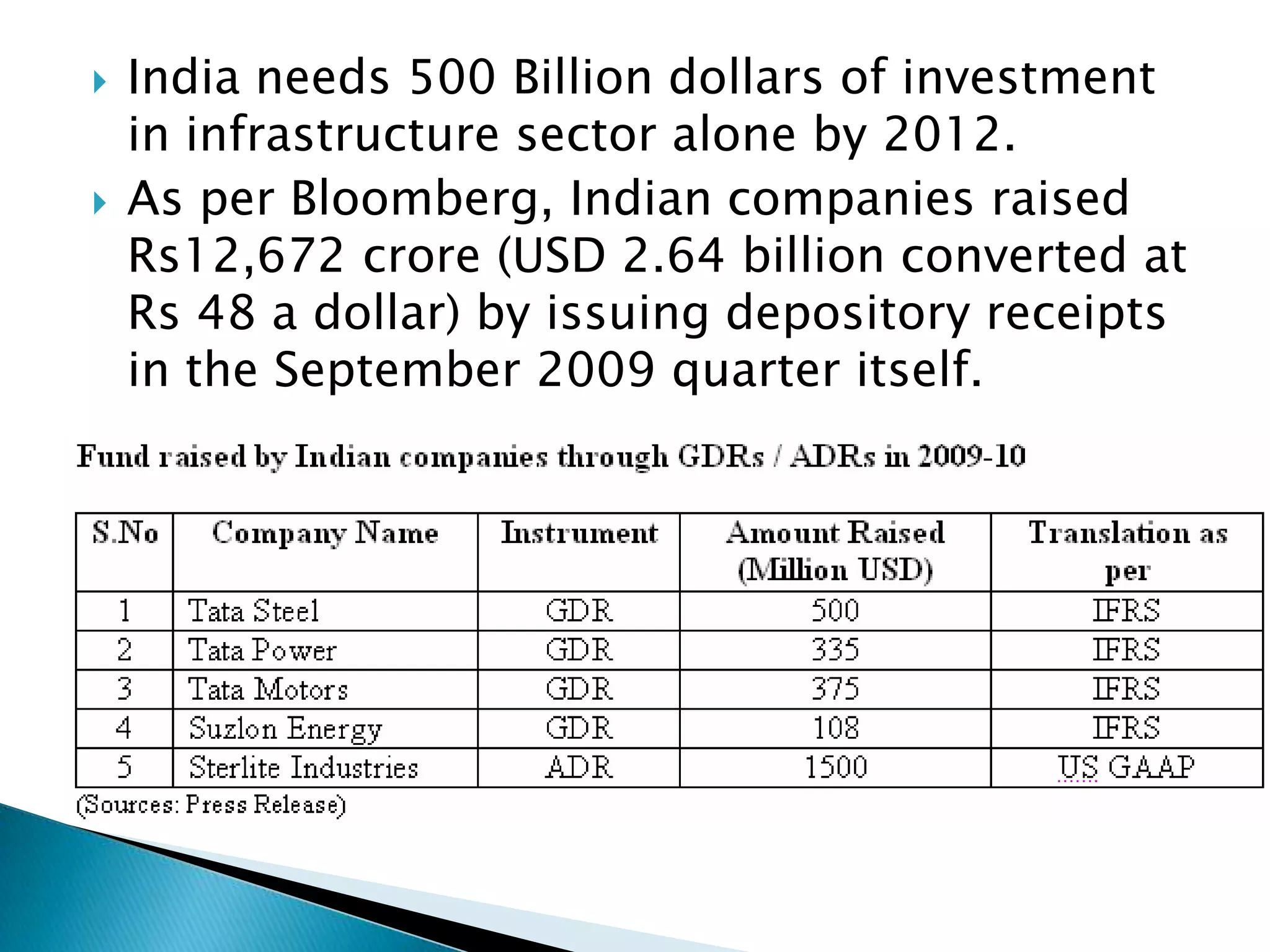
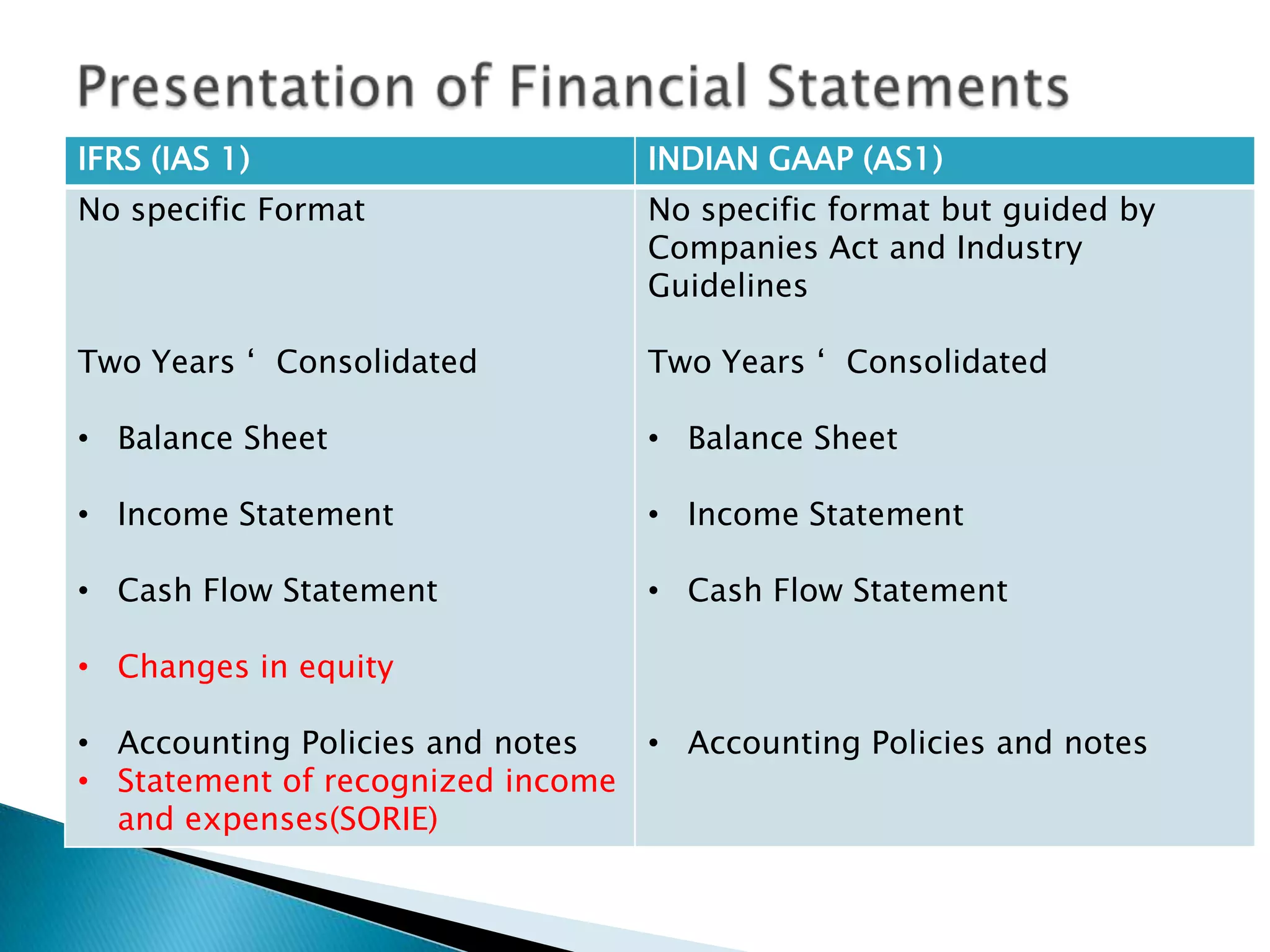
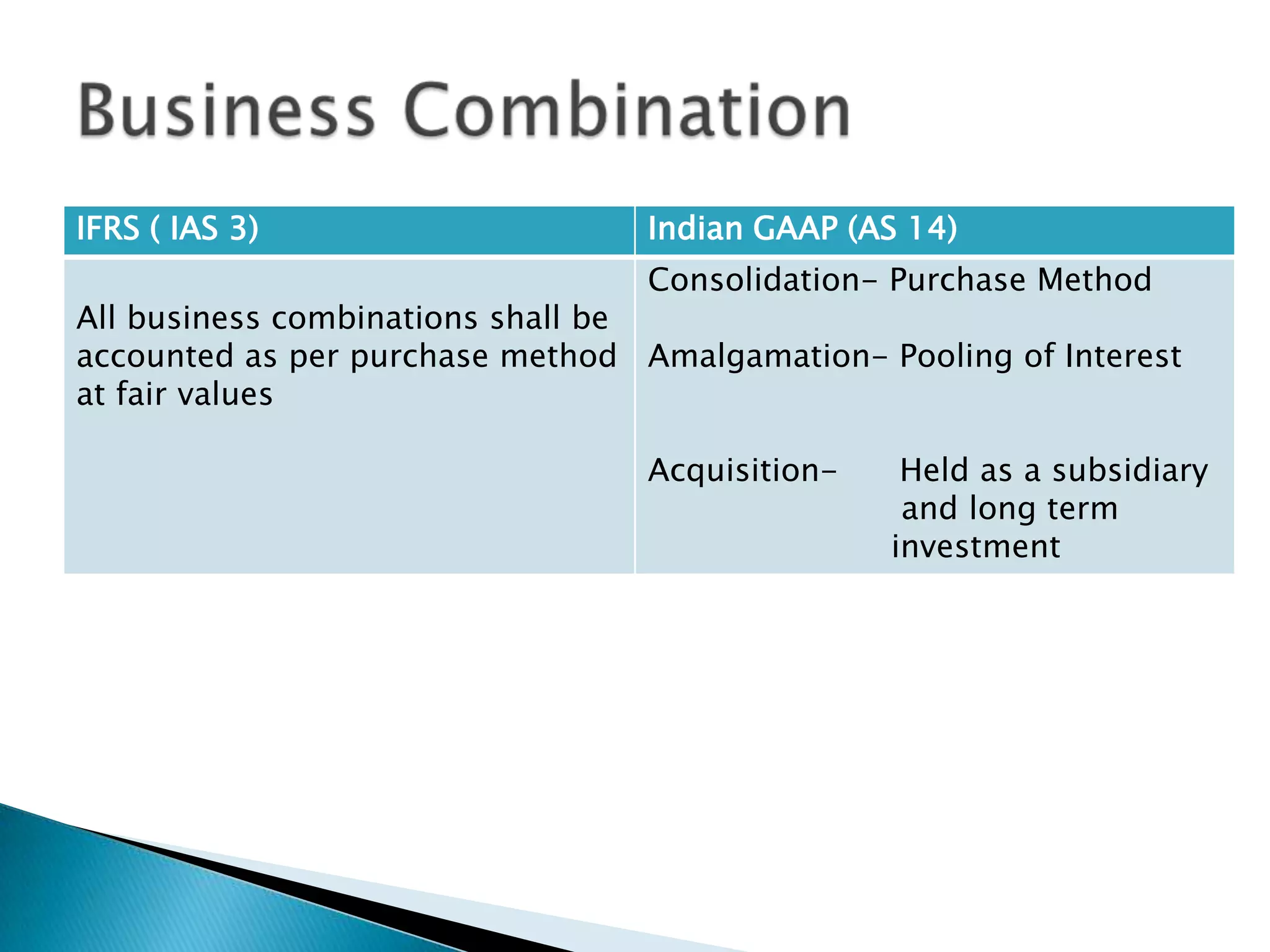
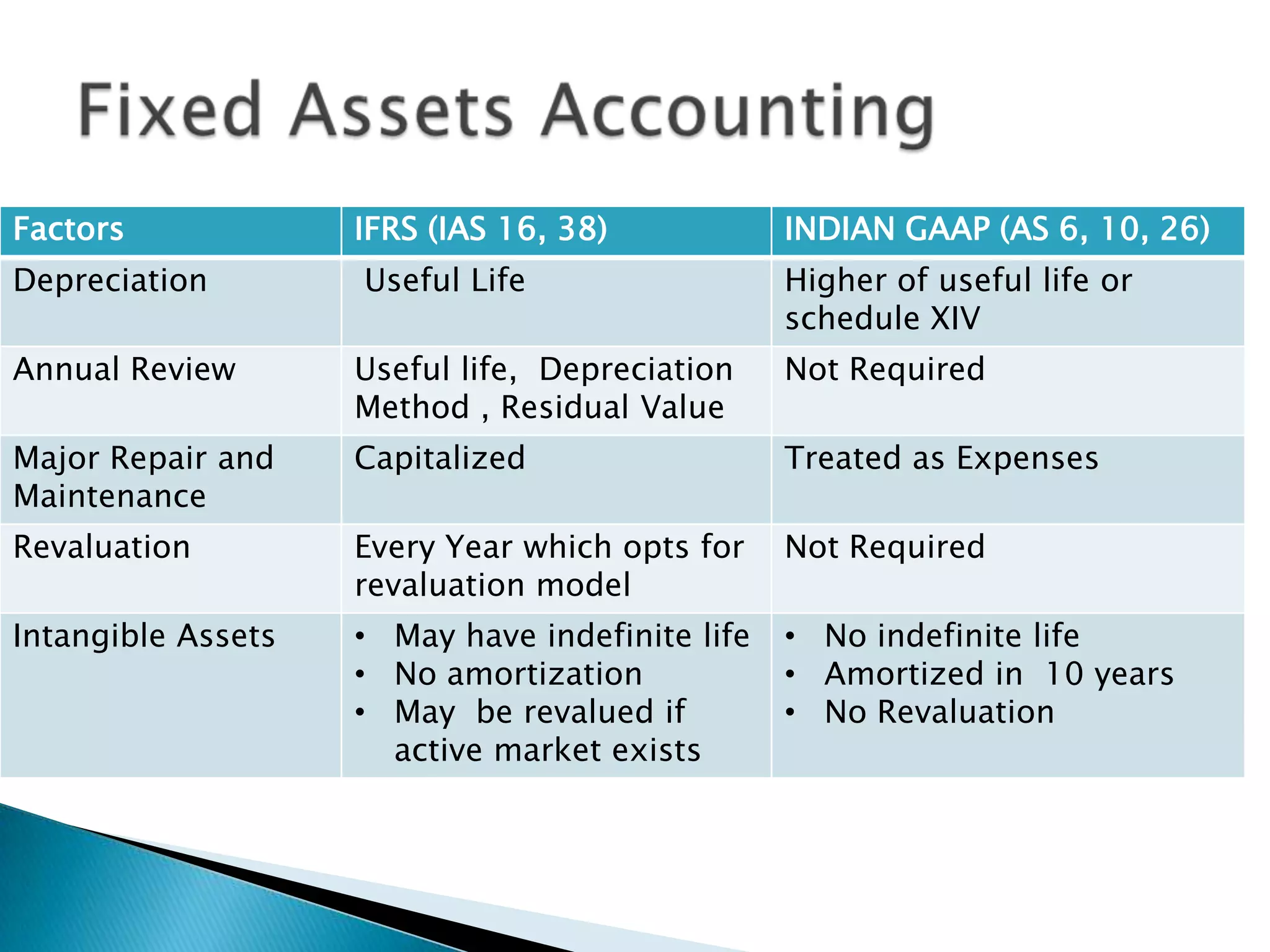
The document discusses the history and adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) globally and in India. Some key points include: IFRS were established in 1997 with the goal of uniform global accounting standards; over 110 countries including India have adopted IFRS; India's adoption of IFRS will improve financial statement comparability, transparency and credibility. The document also provides some comparisons between specific IFRS and Indian accounting standards.