The document presents a comparison between XAML and HTML technologies, addressing ten specific topics including layout, styles, drawing, local data, services, data binding, audio/video playback, controls, and unit testing. It outlines the strengths and weaknesses of each technology while providing a framework for understanding their differences in usability and capabilities in web and application development. The presentation is aimed at helping developers decide which technology to use based on their specific project requirements.















































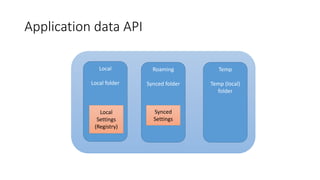
![IsolatedStorageSettings
• Simple usage to create Application Settings
• Use IsolatedStorageSettings to set/get settings
• ApplicationSettings are per .xap
• SiteSettings are per domain
IsolatedStorageSettings.ApplicationSettings["foo"] = "bar";
string appFoo = IsolatedStorageSettings.ApplicationSettings["foo"] as string;
IsolatedStorageSettings.SiteSettings["foo"] = "bar";
string siteFoo = IsolatedStorageSettings.SiteSettings["foo"] as string;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/comparingxamlandhtml-140501072547-phpapp01/85/Comparing-xaml-and-html-55-320.jpg)