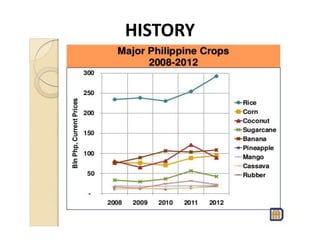
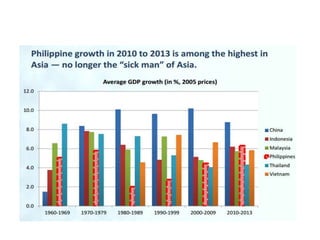
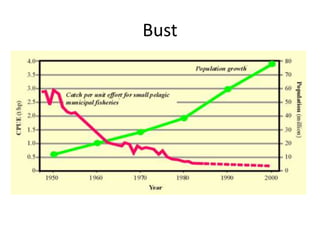
The document discusses several agricultural and natural resource development programs in the Philippines, including:
1. The Agricultural Modernization program, which aims to transform agriculture into a more advanced and competitive sector focused on human development.
2. The Agrarian Reform program which reforms land tenure systems and supports rural institutions.
3. The Cooperative Development program which promotes cooperatives for equity, social justice, and economic development.
4. The Fisheries Development program which supports fisheries production and post-harvest facilities through programs like fish ports and refrigeration infrastructure.
5. The Forest Development program which governs forest exploration, utilization, and conservation and implements programs like the National Greening Program.