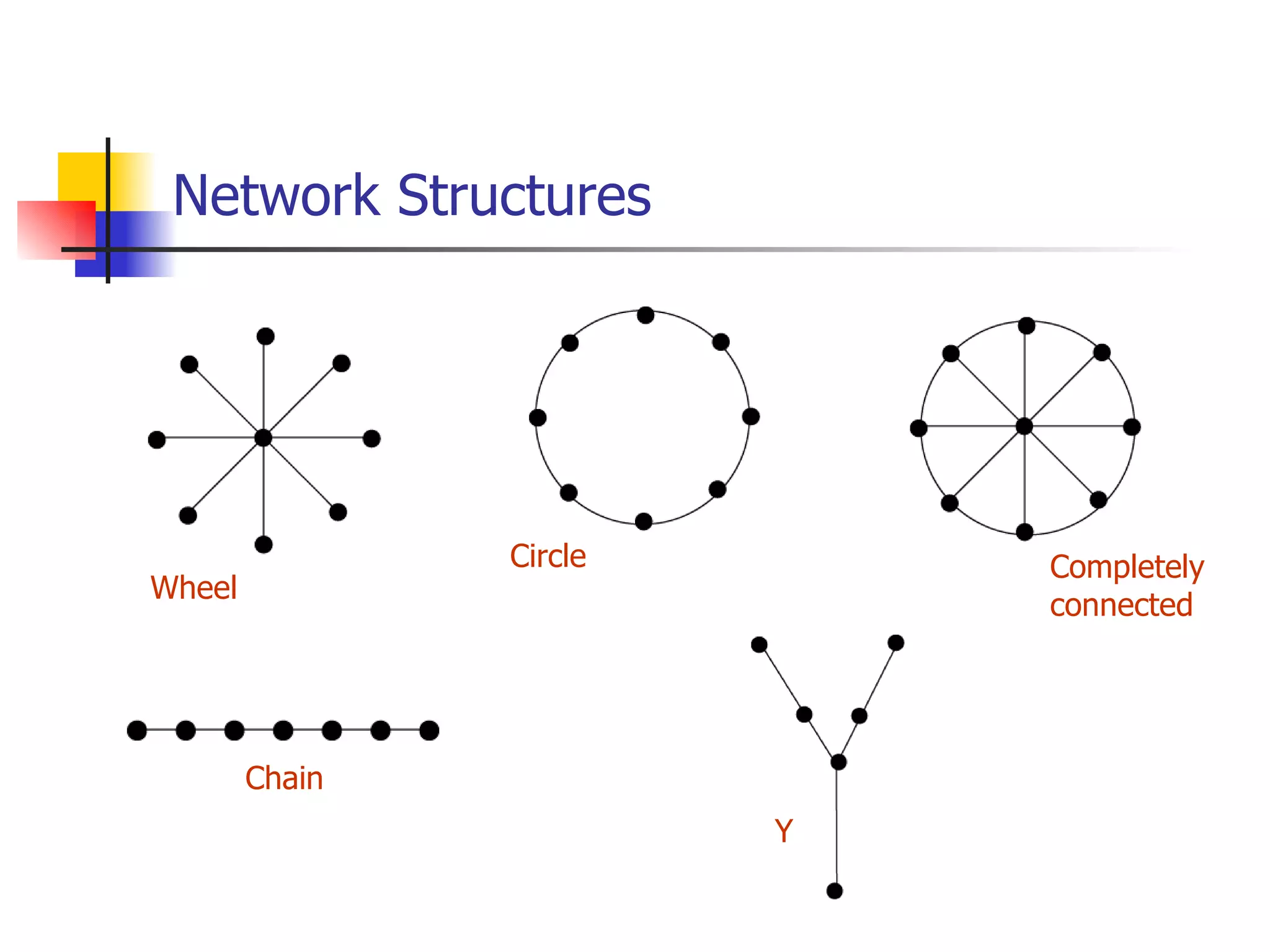
The document discusses different communication structures that can exist within groups:
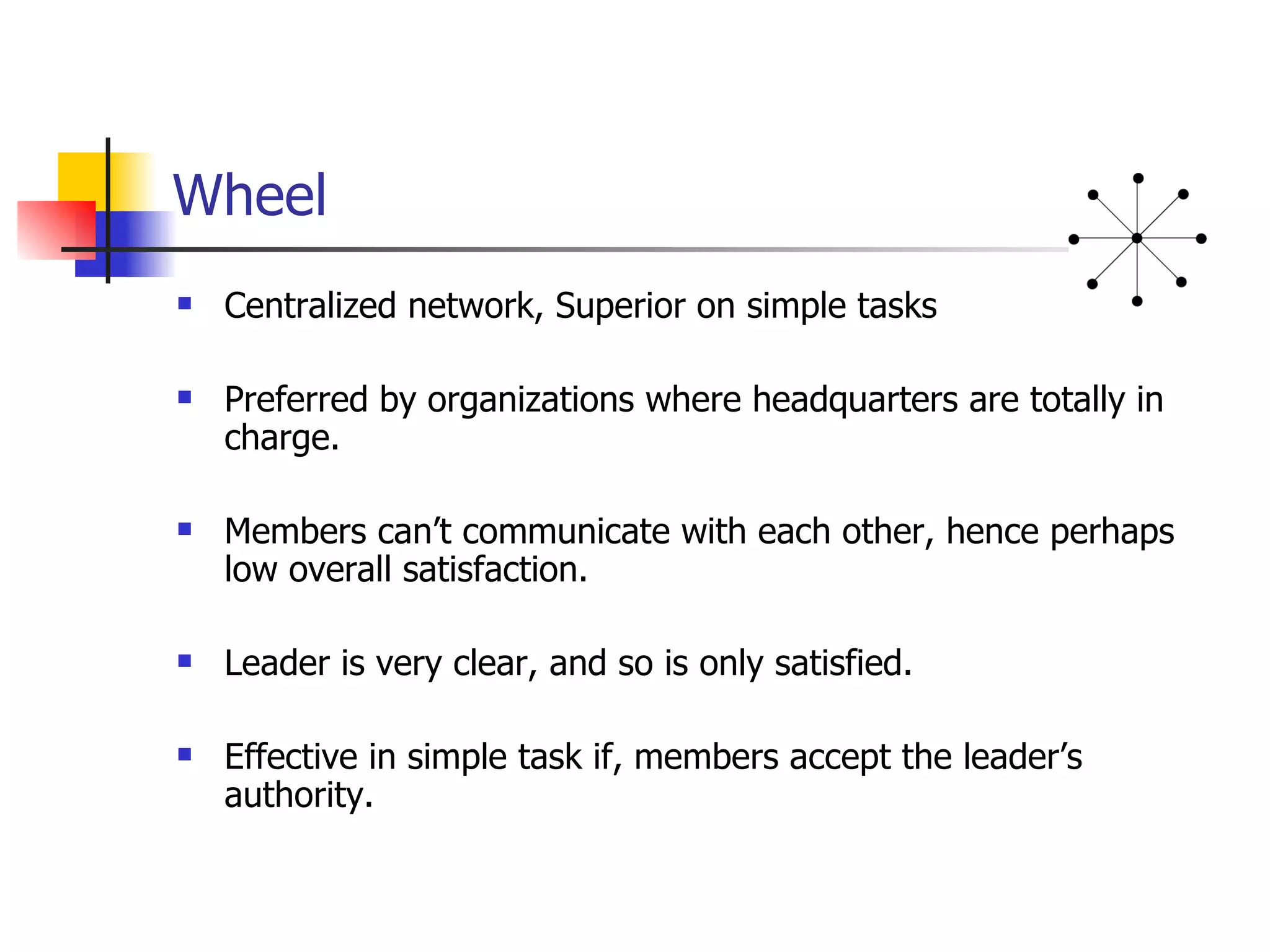
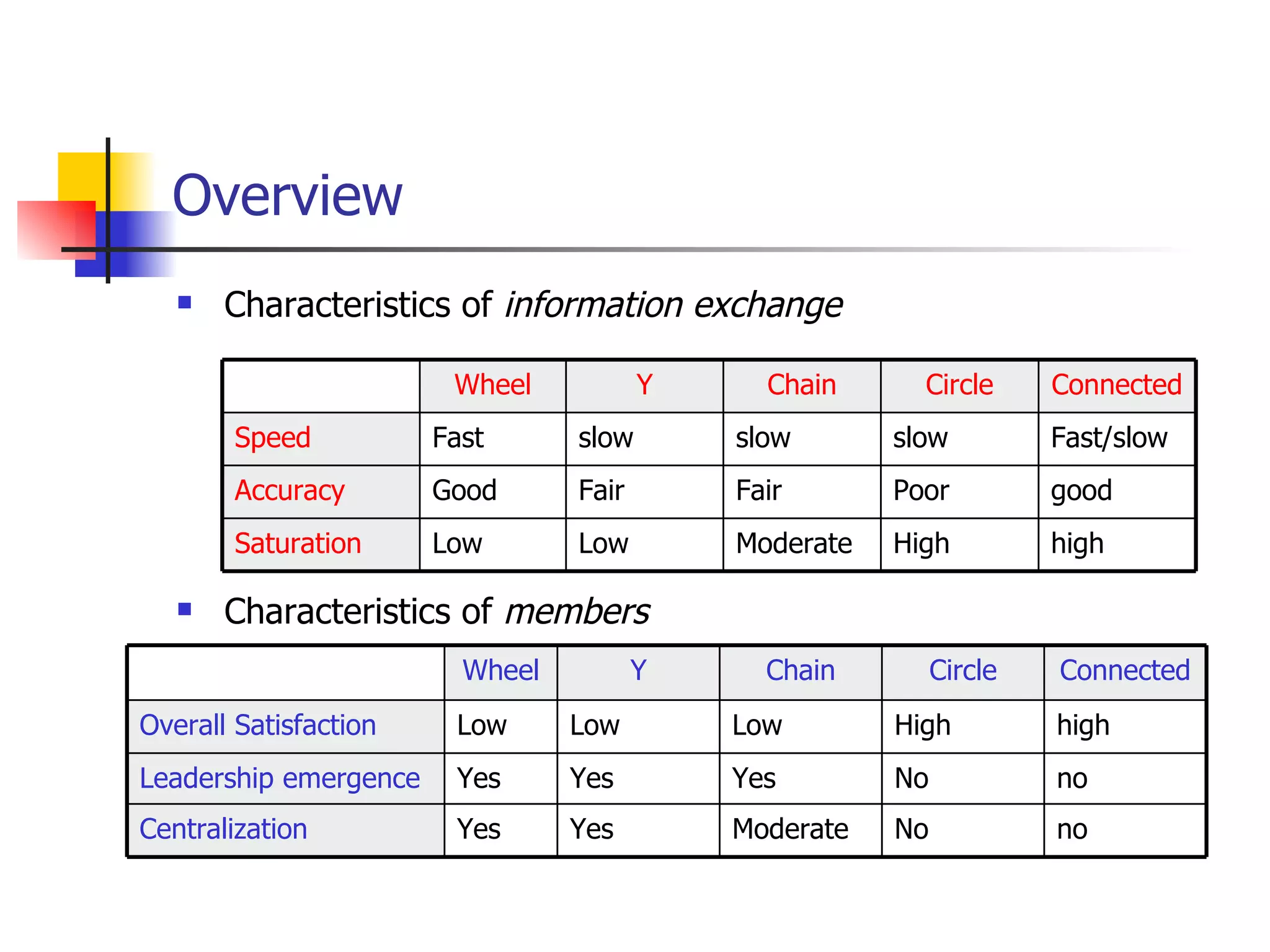
- Wheel structures have a centralized network with one central leader who communicates with all members but members cannot communicate with each other directly. They are effective for simple tasks but members and leaders may have low satisfaction.
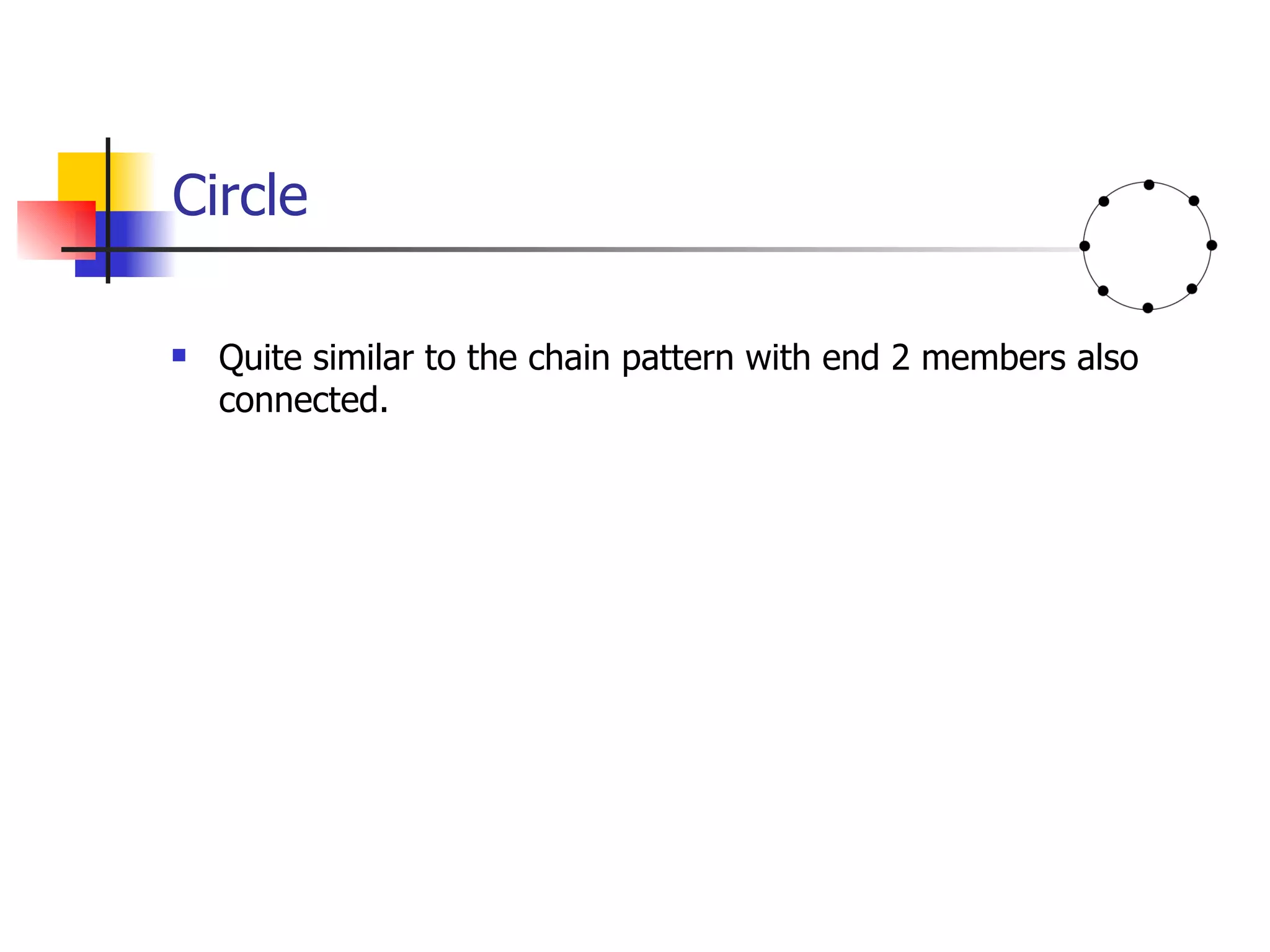
- Circle structures are similar to chain structures but with the end members also connected, allowing more connections.
- Line structures restrict communication only between certain members but all are ultimately connected. Leadership may not be clear. They can work moderately well for both simple and complex tasks but may lack coordination.
- Completely connected structures are decentralized with all members able to interact. They are superior for complex tasks but can be slow. Leadership is unclear as it is