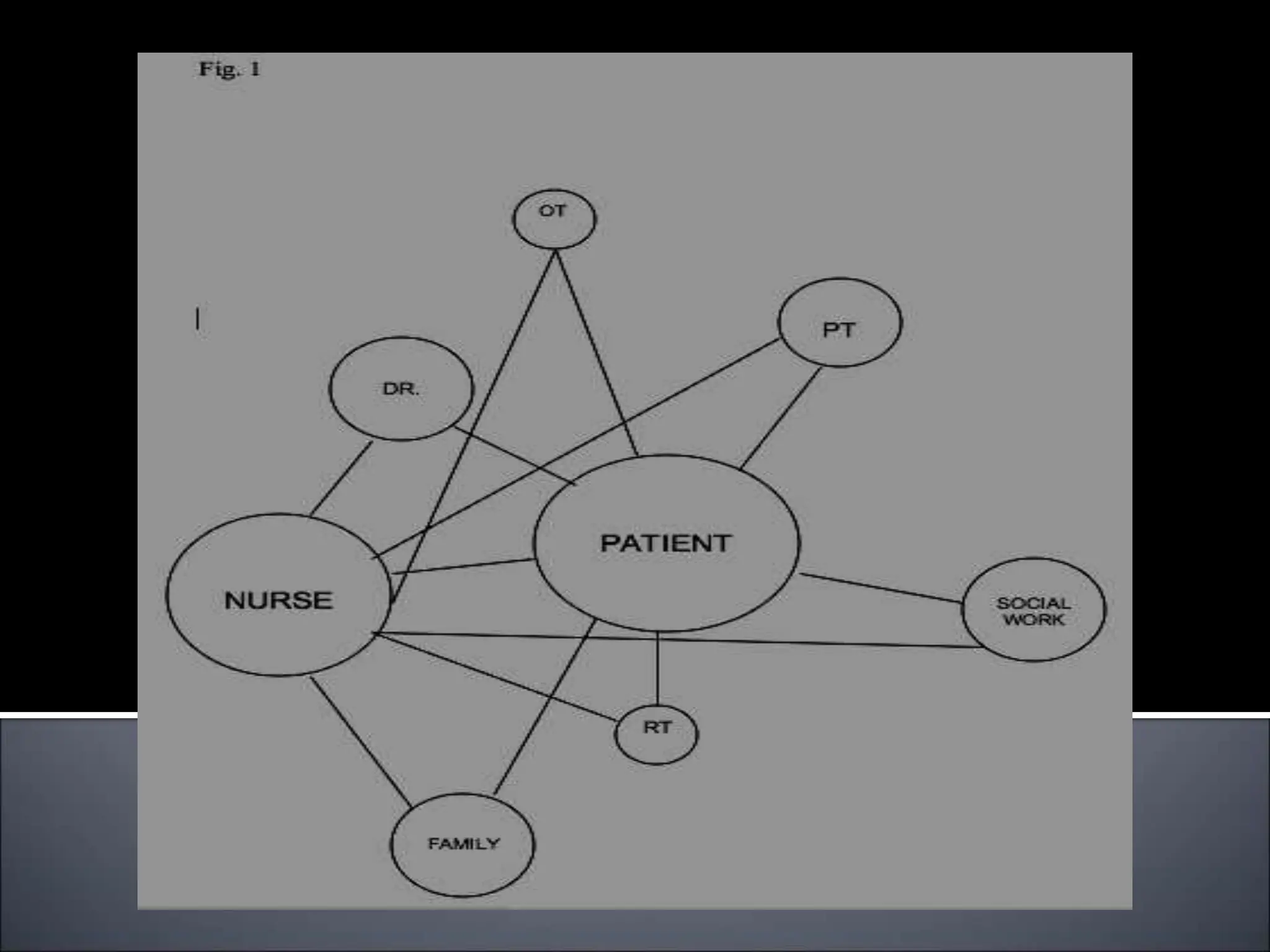
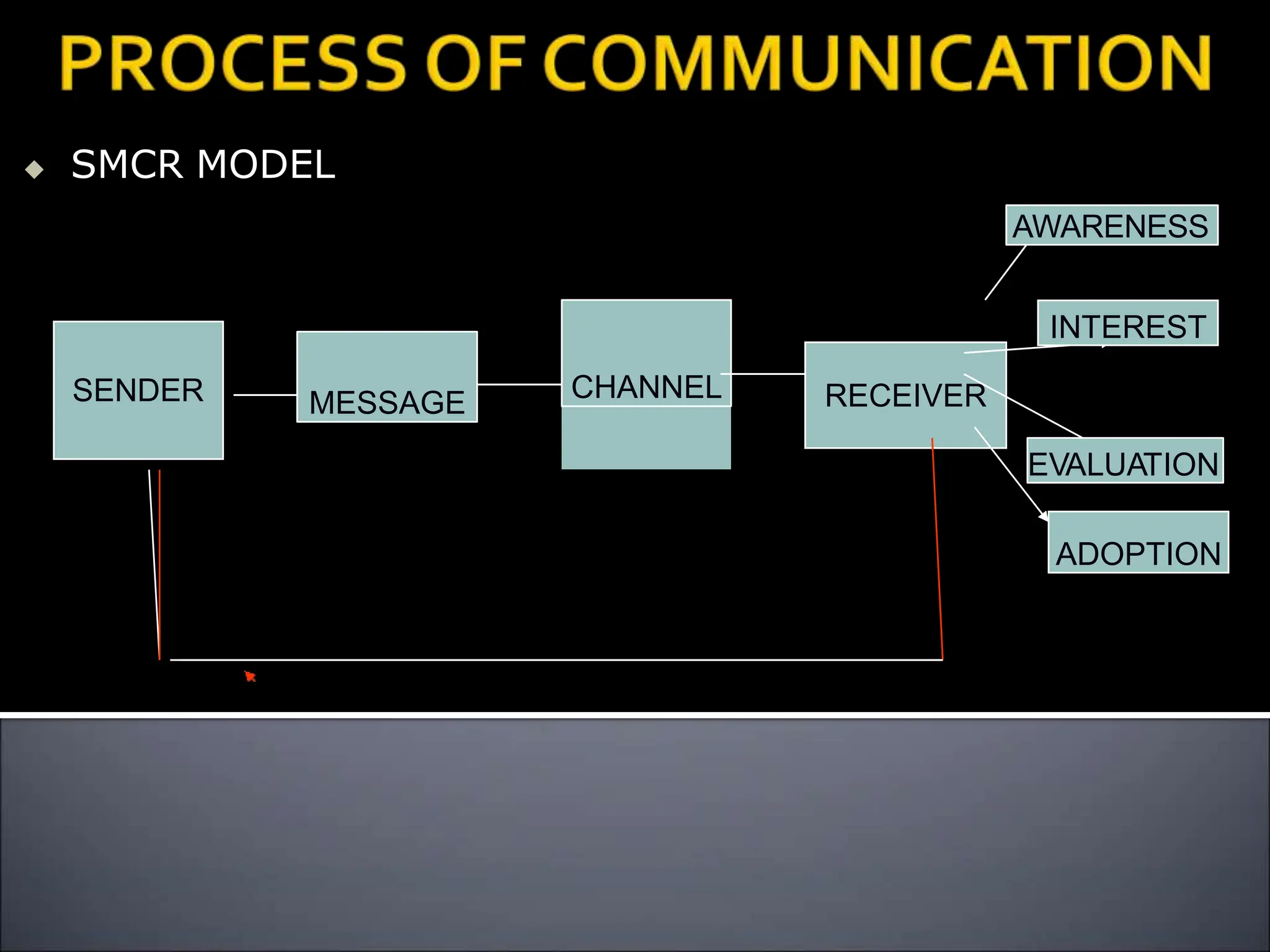
The document outlines the importance of communication in healthcare, emphasizing its role in nurse-patient interactions and organizational processes. It details different types of communication, including verbal and non-verbal methods, and highlights therapeutic techniques and common pitfalls to avoid. The text also mentions factors that influence communication and offers strategies for effective interpersonal interactions.