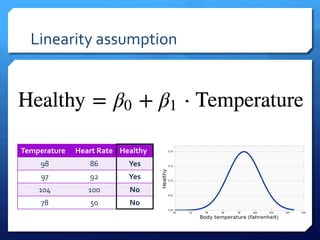
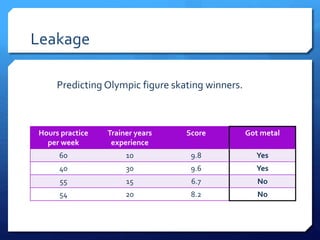
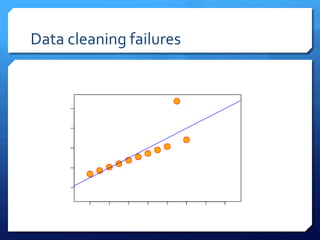
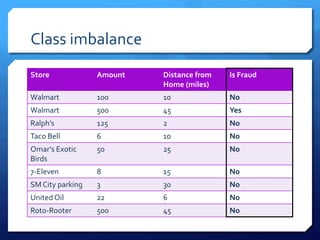
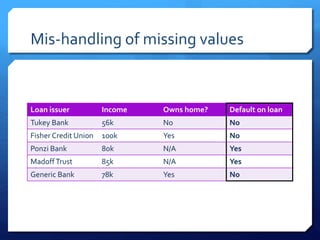
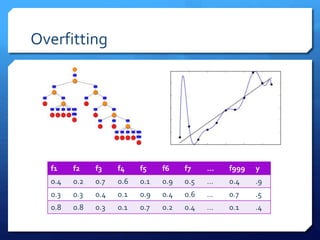
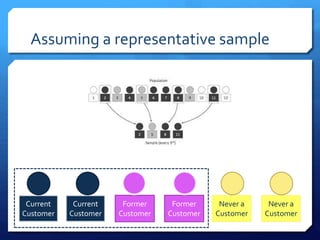
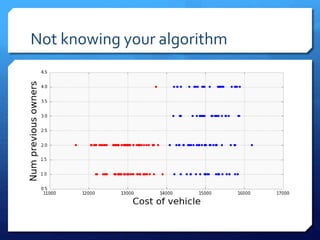
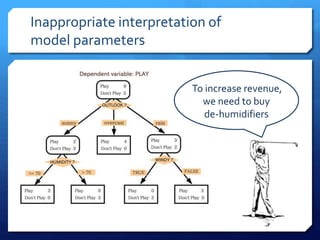
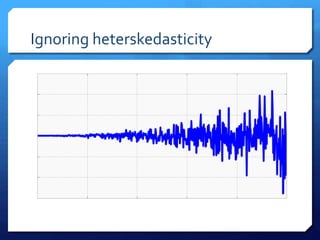
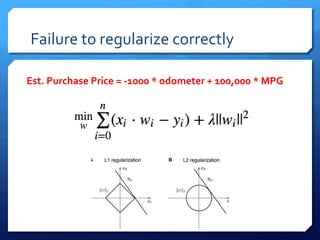
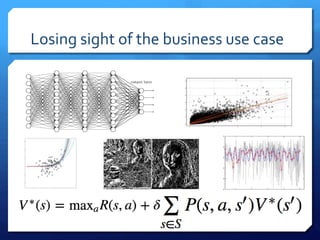
The document discusses common errors in machine learning, categorized into basics, intermediate, and advanced topics, including issues such as linearity assumption, data cleaning failures, and overfitting. It emphasizes the importance of proper experimental design and understanding the implications of model parameters and business use cases. Additionally, it provides general advice for continuous learning and effectiveness in the field.