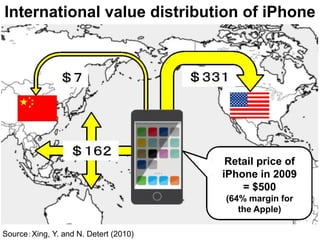
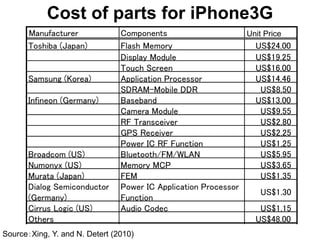
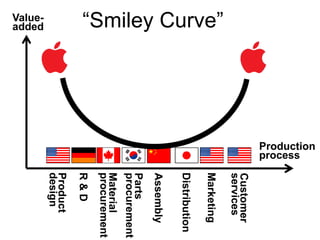
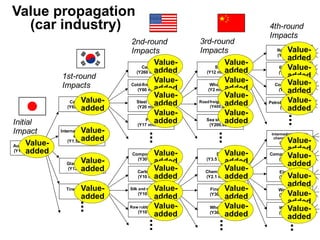
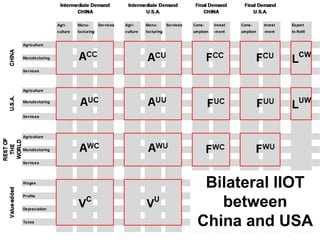
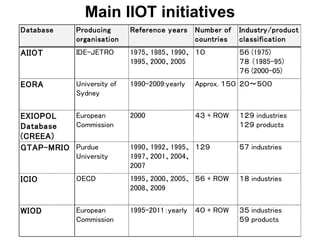
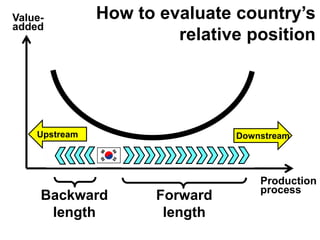
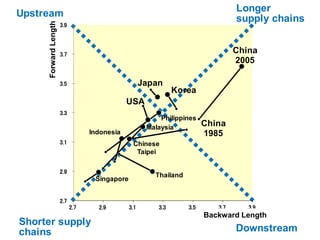
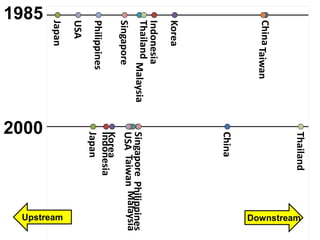
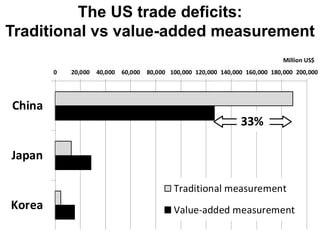
This document discusses international input-output analysis and its use in measuring global trade and value chains. It provides examples of how input-output tables can be used to analyze the domestic and international propagation of value-added through production linkages. International input-output tables allow measurement of countries' positions in global value chains in terms of upstreamness and downstreamness. They also provide a more accurate picture of bilateral trade balances by considering value-added rather than gross trade flows.