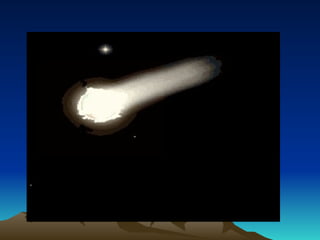
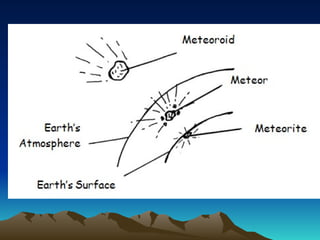
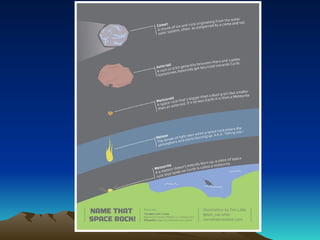
The document discusses the characteristics of comets, meteors, and asteroids in the solar system, posing the essential question of their differences. Comets are described as icy bodies that form tails when near the sun, meteors are meteoroids that burn up in the atmosphere, and asteroids are rocky objects found mainly in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Various activities are suggested for comparing these celestial objects and reinforcing the lesson's concepts.