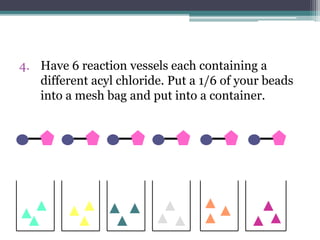
Combinatorial chemistry allows chemists to synthesize large numbers of similar compounds in a short period of time. The compounds generated are analogues of existing biologically active compounds. The goal is to find new medicines that are more effective or have fewer side effects than existing drugs. The process involves attaching different alcohols or acyl chlorides to polymer beads via linkers, generating multiple variations in parallel that can then be efficiently tested for biological activity. This approach dramatically accelerates drug discovery by enabling many compounds to be screened at once.