Embed presentation

















![Excel.Application excelApp = new Excel.Application();
Excel.Workbook excelBook = (Excel.Workbook)(oXls.Workbooks.Open(@"C:tmp
dummy.xls",...));
Excel.Worksheet excelSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)excelBook.Sheets[1];
Excel.Range excelRange = (Excel.Range)excelSheet.Cells[1,1];
String name = excelRange.Text.ToString();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7blog-090720194204-phpapp01/85/COM-18-320.jpg)





![try {
excelCells = excelSheet.Cells;
try {
excelRange = (Excel.Range)excelCells[1,1];
msg = excelRange.Text.ToString();
} finally {
Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excelRange);
}
} finally {
Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excelCells);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7blog-090720194204-phpapp01/85/COM-26-320.jpg)














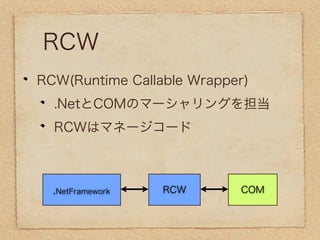
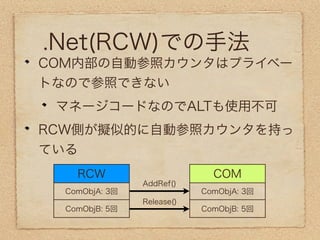
The document discusses Component Object Model (COM) and how it allows software components to communicate between different languages like Visual Basic and C++. It describes how .NET Framework builds upon COM to provide interoperability between .NET and COM components. It also provides a code example of how to automate Microsoft Excel using .NET and COM interoperability to open a workbook, get a worksheet, retrieve a cell range, and get the text from that cell.

















![Excel.Application excelApp = new Excel.Application();
Excel.Workbook excelBook = (Excel.Workbook)(oXls.Workbooks.Open(@"C:tmp
dummy.xls",...));
Excel.Worksheet excelSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)excelBook.Sheets[1];
Excel.Range excelRange = (Excel.Range)excelSheet.Cells[1,1];
String name = excelRange.Text.ToString();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7blog-090720194204-phpapp01/85/COM-18-320.jpg)







![try {
excelCells = excelSheet.Cells;
try {
excelRange = (Excel.Range)excelCells[1,1];
msg = excelRange.Text.ToString();
} finally {
Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excelRange);
}
} finally {
Marshal.ReleaseComObject(excelCells);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/windows7blog-090720194204-phpapp01/85/COM-26-320.jpg)













