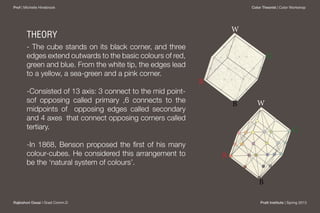
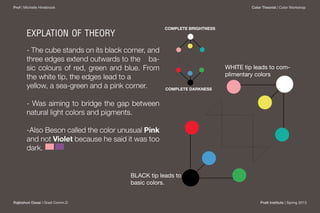
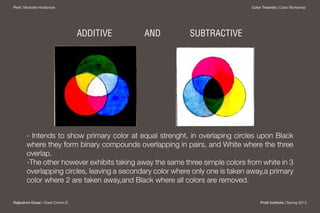
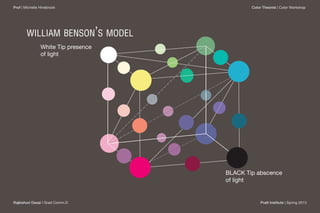
William Benson published the first color theory cube system in 1868 in London. The cube used red, blue, and green as the basic colors, with secondary colors like yellow and pink at the intersections of the edges meeting at the white tip. Benson proposed additive and subtractive color mixing and saw the cube as bridging the gap between natural light and pigment colors. However, the cube form did not fully represent brightness and could appear confusing to observers.