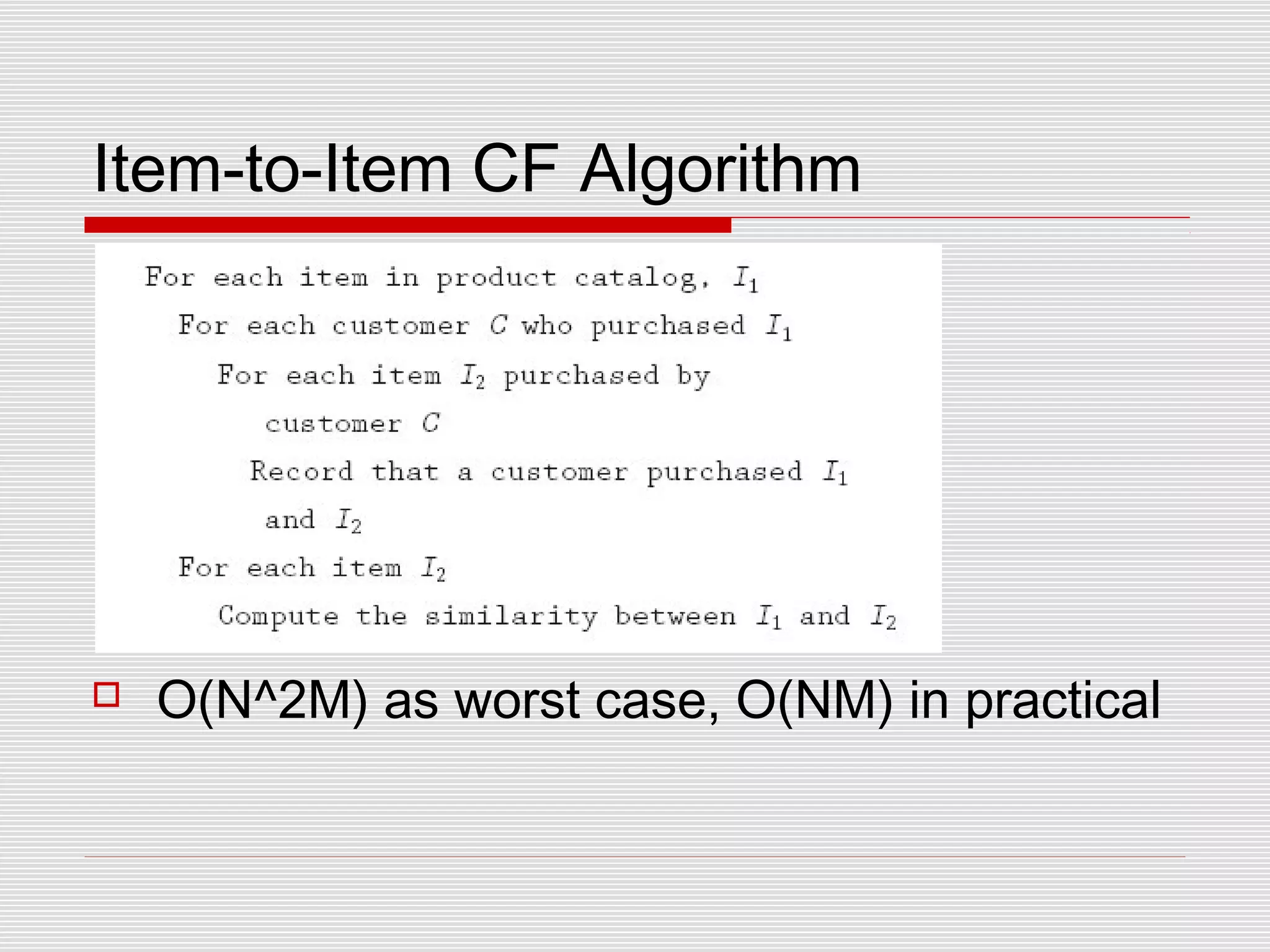
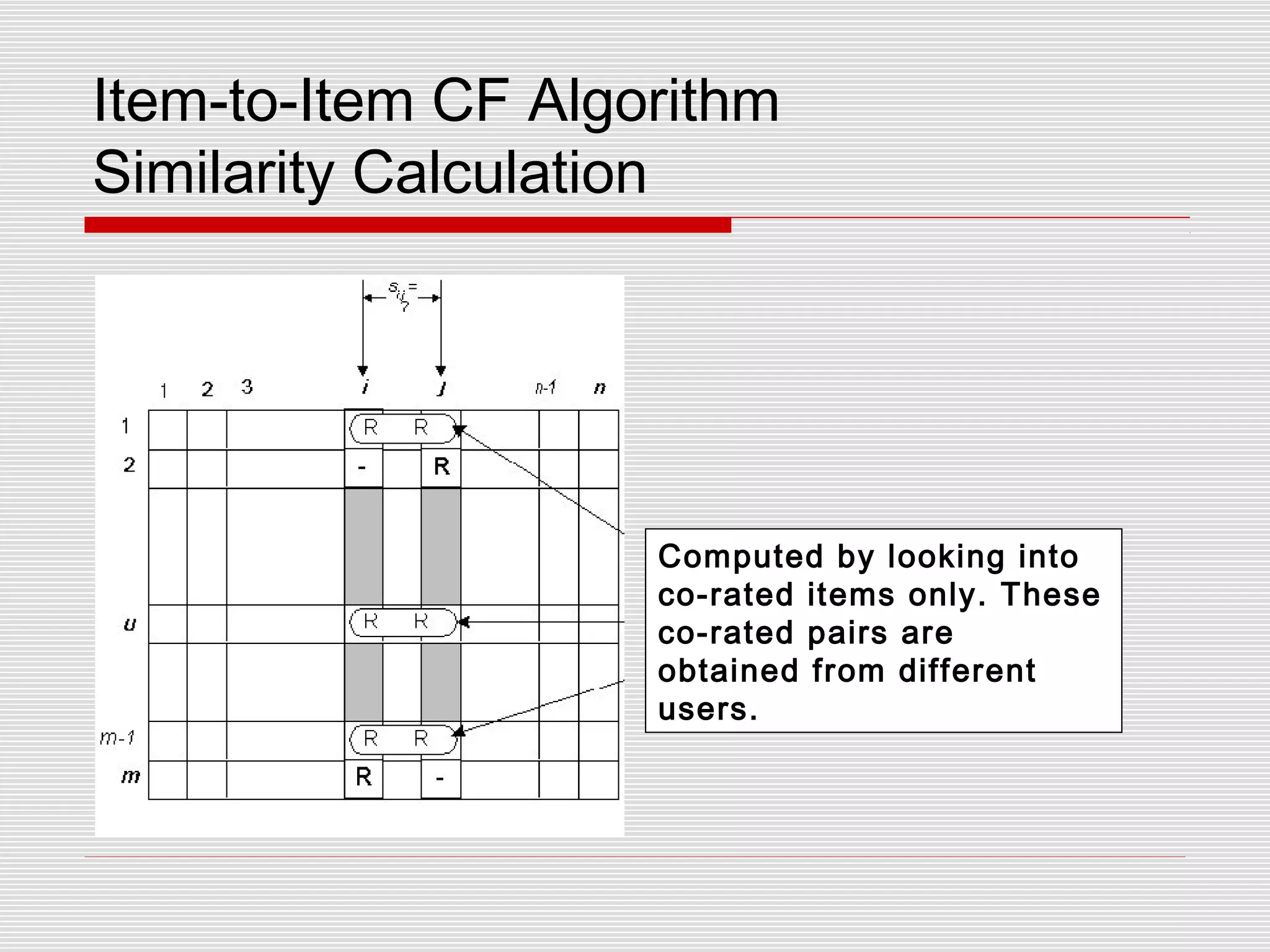
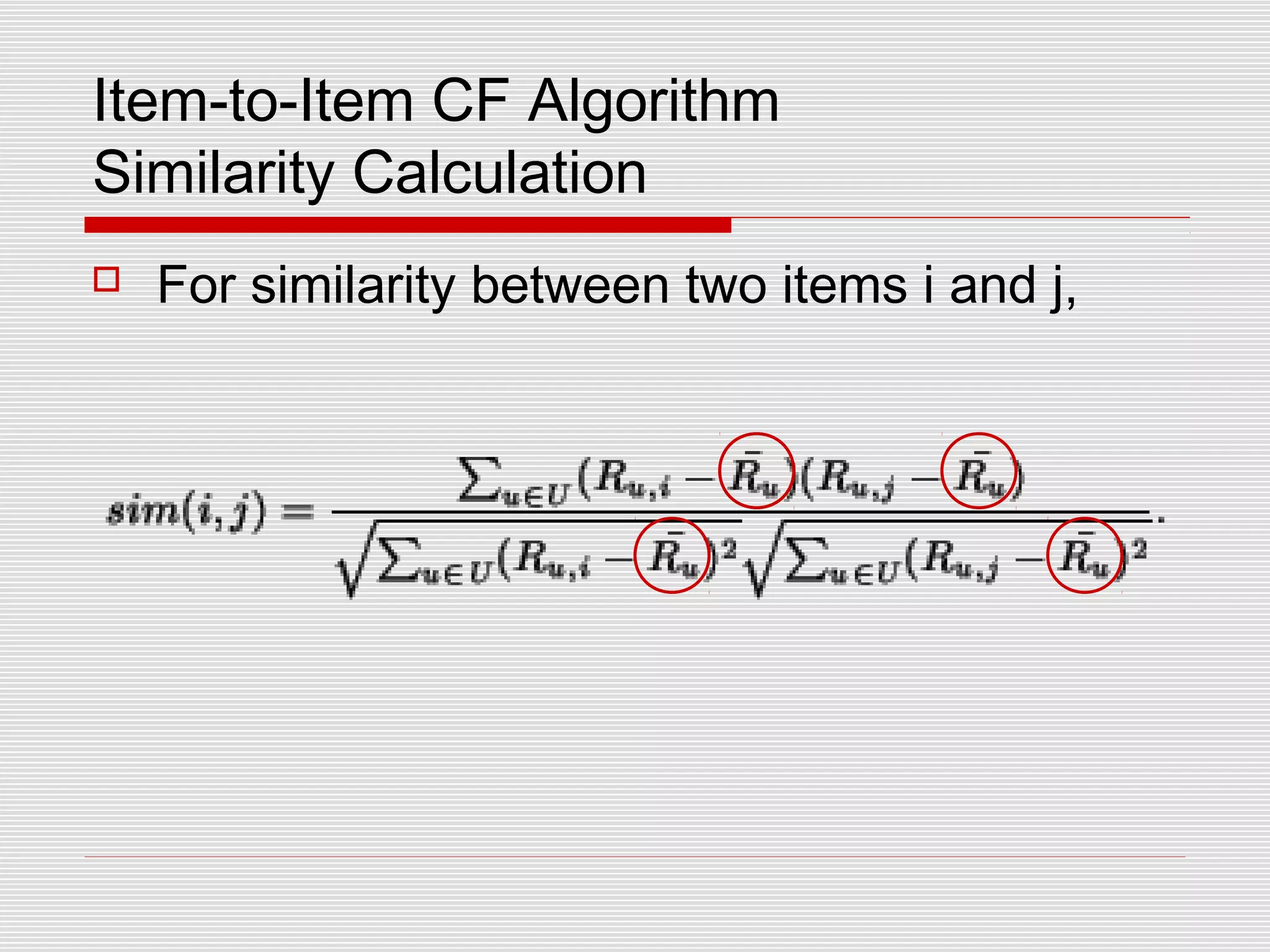
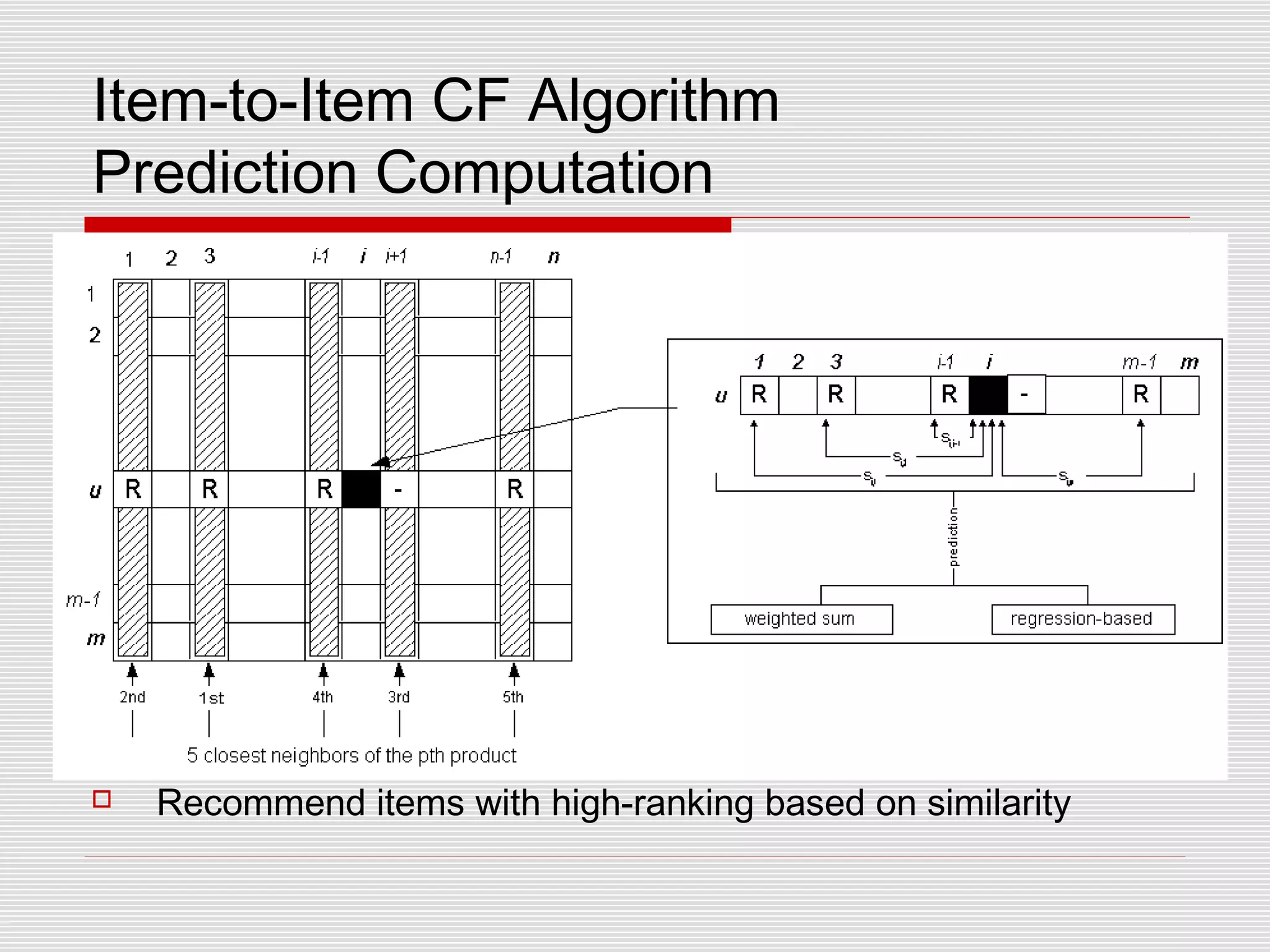
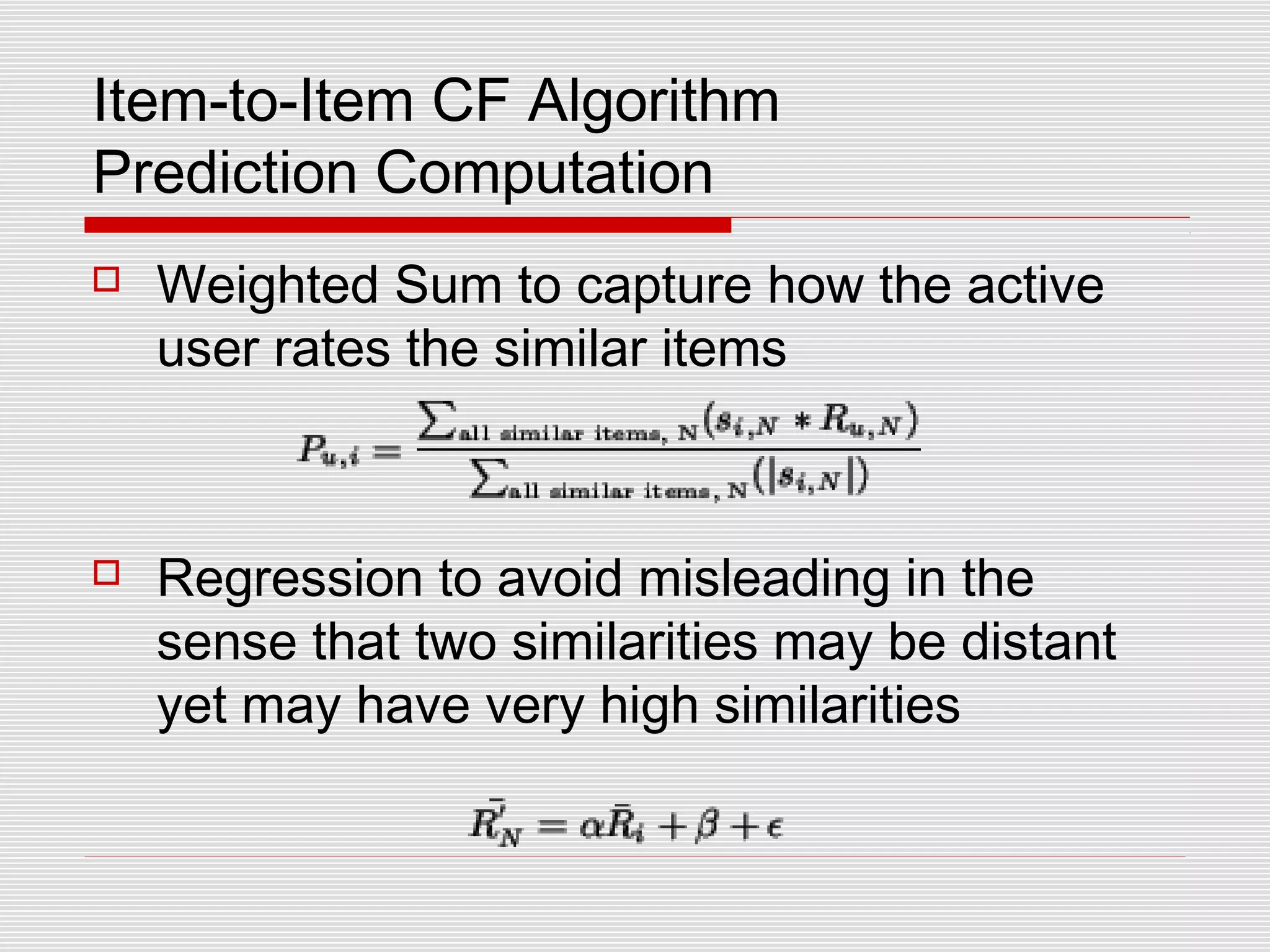
Collaborative filtering is a technique used by recommender systems to predict items a user may like based on their preferences and the preferences of similar users. It involves identifying correlations between people with similar tastes or opinions. Traditional collaborative filtering uses nearest neighbor algorithms and cosine distance to find similar users and make recommendations, but this has scaling issues. Item-based collaborative filtering improves scaling by identifying similar items and making predictions based on a user's ratings of similar items.