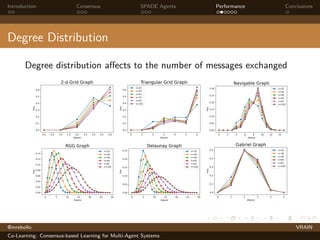
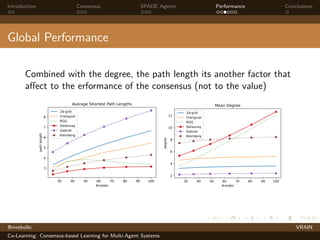
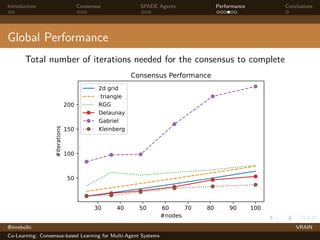
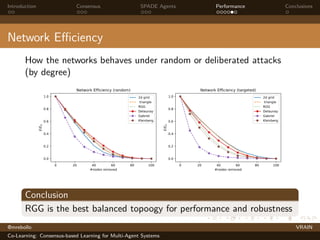
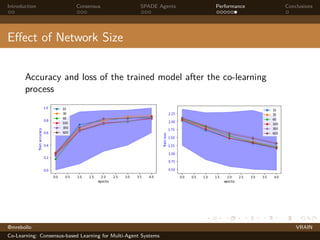
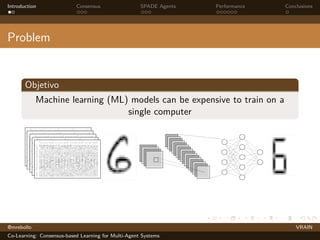
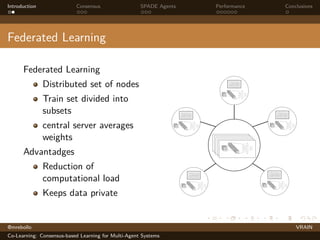
The document discusses a consensus-based learning approach for multi-agent systems, focusing on federated learning where distributed nodes train on subsets of data while keeping it private. It evaluates different network topologies, such as random geometric graphs, and their impact on performance and robustness in consensus processes. The findings conclude that random geometric graphs offer a favorable balance between efficiency and model accuracy during co-learning.

![Introduction Consensus SPADE Agents Performance Conclusions
Consensus Process in Networks
Process to share información on a
network, ruled by
xi (t+1) = xi (t)+ε
X
j∈Ni
[xj(t) − xi (t)]
Information from direct neighbors
only
0 20 40 60 80 100
EPOCH
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
VALUE
OLFATI CONSENSUS
@mrebollo VRAIN
Co-Learning: Consensus-based Learning for Multi-Agent Systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colearningmrebollopaams22slides-220713161806-523b69ae/85/Co-Learning-Consensus-based-Learning-for-Multi-Agent-Systems-4-320.jpg)
![Introduction Consensus SPADE Agents Performance Conclusions
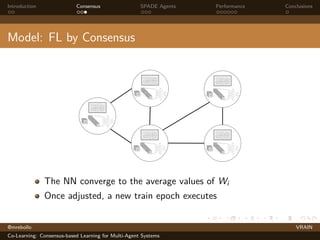
Model: FL by Consensus
Goal
To learn a global model (W , tr) of weights W for a training set tr.
n identical agents as nodes in a network. Each agent with a NN
model (Wi , tri ), being
Wi = (Wi,1, . . . , Wi,k) weight and bias matrices of node i for
component k
tri ⊆ tr fragment of the training set assigned to i.
Weights averaged in the neighborhood using consensus algorithm
(Olfati, 2007).
Wi (t + 1) = Wi (t) + ε
X
j∈Ni
[Wj(t) − Wi (t)]
@mrebollo VRAIN
Co-Learning: Consensus-based Learning for Multi-Agent Systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colearningmrebollopaams22slides-220713161806-523b69ae/85/Co-Learning-Consensus-based-Learning-for-Multi-Agent-Systems-5-320.jpg)
![Introduction Consensus SPADE Agents Performance Conclusions
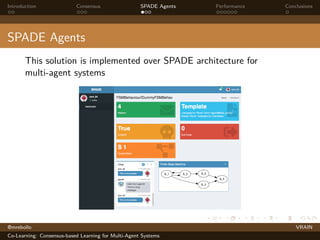
Co-Learning Algorithm
1: while !doomsday do
2: for f ← 1, e do
3: W ← Train(f )
4: end for
5: for j ← 1, k do
6: Xi (0) ← Wj
7: for t ← 1, c do
8: Receive Xj(t) from ai neighbors
9: Xi (t + 1) ← Xi (t) + ε
P
j∈Ni
[Xj(t) − Xi (t)]
10: Send Xi (t + 1) to ai neighbors
11: end for
12: end for
13: end while
@mrebollo VRAIN
Co-Learning: Consensus-based Learning for Multi-Agent Systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/colearningmrebollopaams22slides-220713161806-523b69ae/85/Co-Learning-Consensus-based-Learning-for-Multi-Agent-Systems-8-320.jpg)