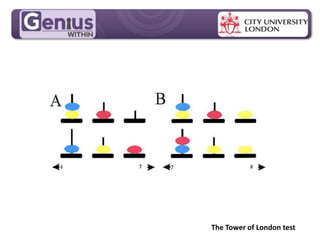
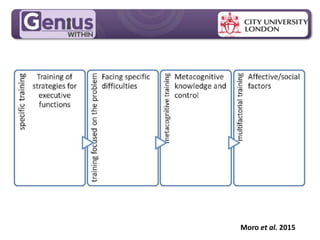
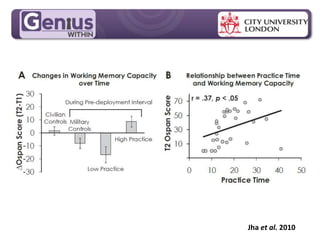
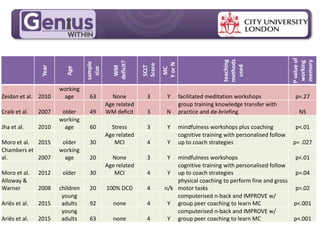
This document discusses cognitive skills and coping strategies. It provides information on improving cognitive skills through training and coaching. Some key points include:
- Studies have found improvements in memory and executive function tests from cognitive training programs lasting 6 months that include family members and follow up coaching.
- Mindfulness meditation training programs ranging from 10 days to 8 weeks have found improvements in working memory, attention switching, mood and anxiety. The effects depend on amount of practice.
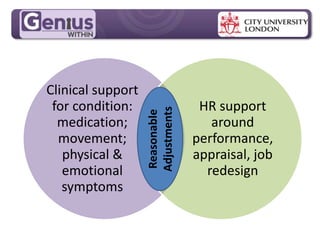
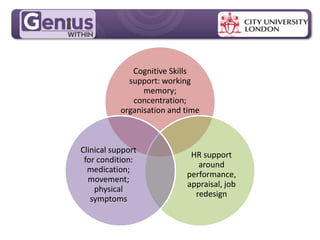
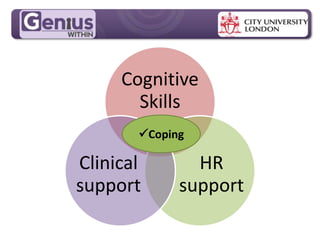
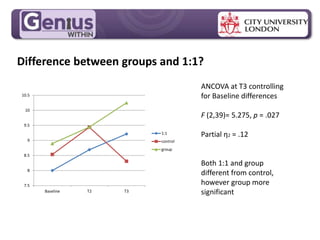
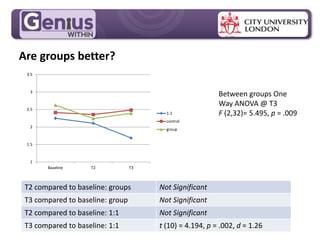
- Group cognitive training programs may be more effective than individual training, though individual training showed significant effects after 6 months in one study. Group support and stimulus could help bring such training into workplace reasonable adjustments.